Zynq-7000 AP SoC and 7 Series FPGAs MIS v4.1 311
UG586 November 30, 2016
www.xilinx.com
Chapter 2: QDR II+ Memory Interface Solution
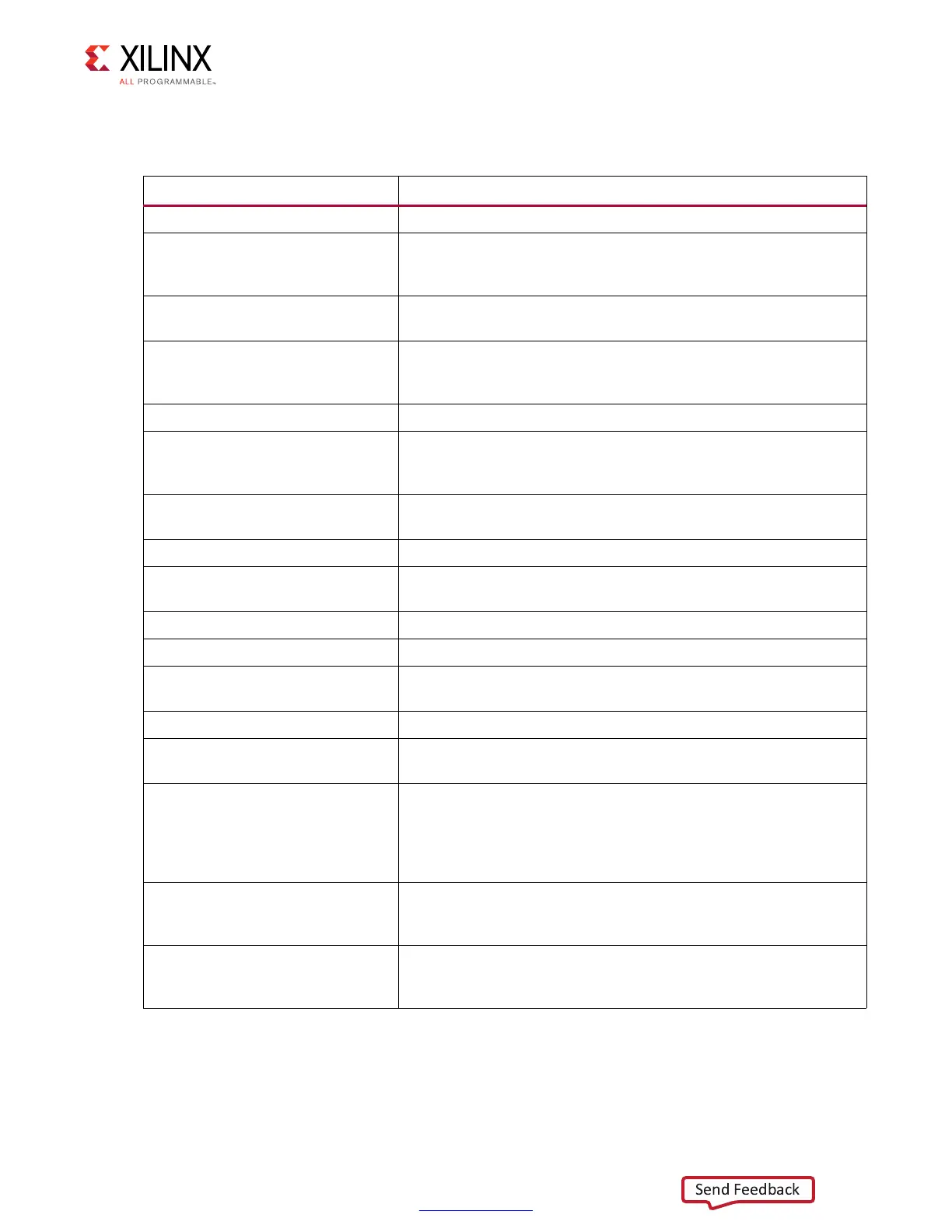
Table 2-2 lists the files in the example_design/rtl/traffic_gen directory.
Table 2-2: Files in example_design/rtl/traffic_gen Directory
Name
(1)
Description
memc_traffic_gen.v This is the top-level module of the traffic generator.
cmd_gen.v
This is the command generator. This module provides independent
control of generating the types of commands, addresses, and
burst lengths.
cmd_prbs_gen.v
This pseudo-random binary sequence (PRBS) generator generates
PRBS commands, addresses, and burst lengths.
memc_flow_vcontrol.v
This module generates flow control logic between the Memory
Controller core and the cmd_gen, read_data_path, and
write_data_path modules.
read_data_path.v This is the top-level for the read datapath.
read_posted_fifo.v
This module stores the read command that is sent to the Memory
Controller. Its FIFO output is used to generate expect data for read
data comparisons.
rd_data_gen.v
This module generates timing control for reads and ready signals
to memc_flow_vcontrol.v.
write_data_path.v This is the top-level for the write datapath.
wr_data_gen.v
This module generates timing control for writes and ready signals
to memc_flow_vcontrol.v.
s7ven_data_gen.v This module generates different data patterns.
a_fifo.v This is a synchronous FIFO using LUT RAMs.
data_prbs_gen.v
This 32-bit linear feedback shift register (LFSR) generates PRBS
data patterns.
init_mem_pattern_ctr.v This module generates flow control logic for the traffic generator.
traffic_gen_top.v
This module is the top-level of the traffic generator and comprises
the memc_traffic_gen and init_mem_pattern_ctr modules.
tg_prbs_gen.v
This PRBS uses one too many feedback mechanisms because it
always has a single level XOR (XNOR) for feedback. The TAP is
chosen from the table listed in XAPP052, Efficient Shift Registers,
LFSR Counters, and Long Pseudo-Random Sequence Generators.
The TAPS position can be defined in a parameter.
tg_status.v
This module compares the memory read data against compare
data generated from the data_gen module. The error signal is
asserted if the comparison is not equal.
vio_init_pattern_bram.v
This module takes external defined data inputs as its block RAM
init pattern. It allows users to change simple test data pattern
without recompilation.
Notes:
1. All file names are prefixed with the MIG version number. For example, for the MIG 4.1 release module name of
memc_traffic_gen in generated output is now mig_7series_v4_1_memc_traffic_gen.

 Loading...
Loading...











