Zynq-7000 AP SoC and 7 Series FPGAs MIS v4.1 557
UG586 November 30, 2016
www.xilinx.com
Chapter 4: LPDDR2 SDRAM Memory Interface Solution
Traffic Generator Operation
The traffic generator module contained within the synthesizable test bench can be
parameterized to create various stimulus patterns for the memory design. It can produce
repetitive test patterns for verifying design integrity as well as pseudo-random data
streams that model real-world traffic.
You can define the address range through the BEGIN_ADDRESS and END_ADDRESS
parameters. The Init Memory Pattern Control block directs the traffic generator to step
sequentially through all the addresses in the address space, writing the appropriate data
value to each location in the memory device as determined by the selected data pattern. By
default, the test bench uses the address as the data pattern, but the data pattern in this
example design can be modified using vio_data_mode signals that can be modified
within the Vivado logic analyzer feature.
When the memory has been initialized, the traffic generator begins stimulating the user
interface port to create traffic to and from the memory device. By default, the traffic
generator sends pseudo-random commands to the port, meaning that the instruction
sequences (R/W, R, W) and addresses are determined by PRBS generator logic in the traffic
generator module.
X-Ref Target - Figure 4-38
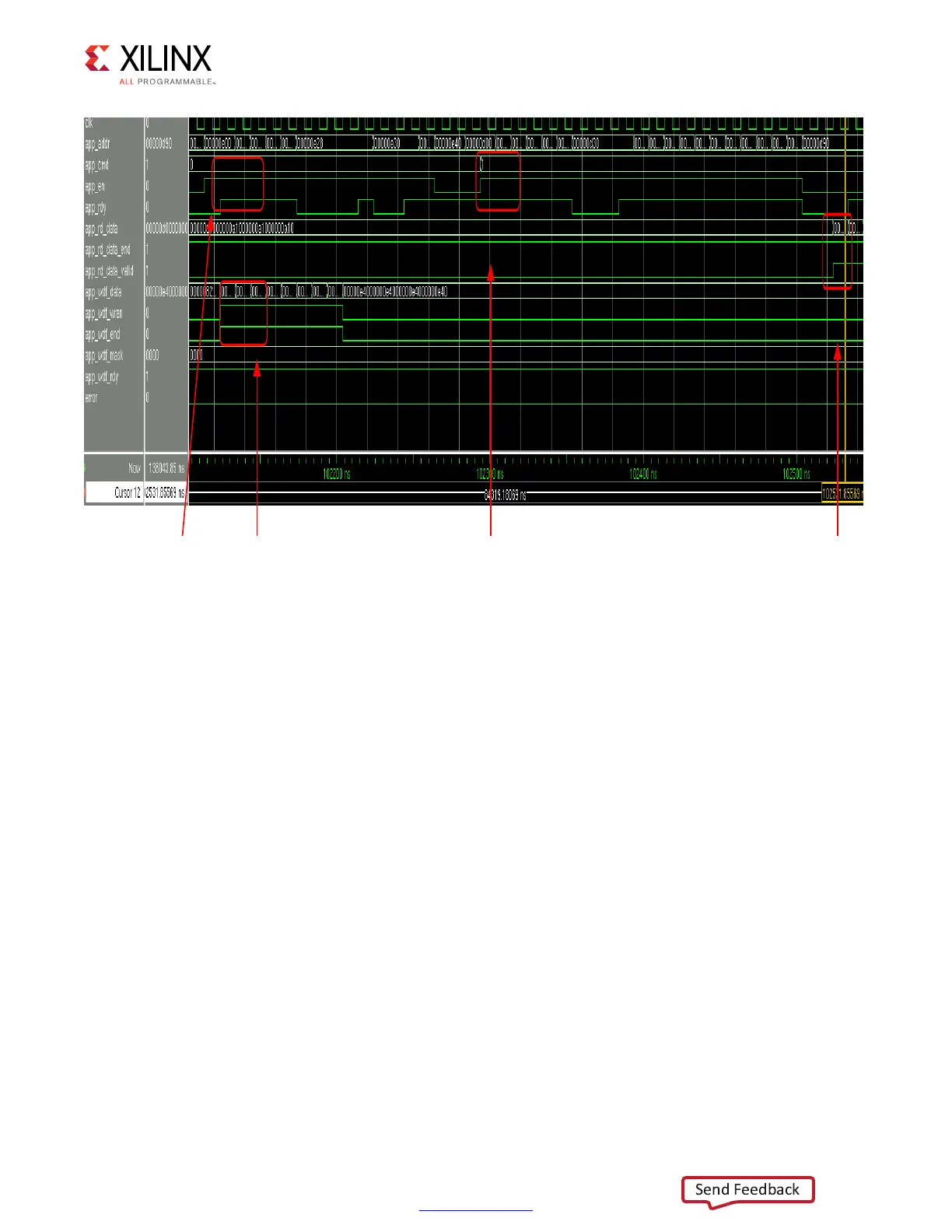
Figure 4-38: User Interface Read and Write Cycle

 Loading...
Loading...











