Operation Manual – MSTP
H3C S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 MSTP Configuration
1-52
Some other manufacturers' switches adopt proprietary spanning tree protocols that are
similar to RSTP in the way to implement rapid transition on designated ports. When a
switch of this kind operating as the upstream switch connects with a H3C series switch
running MSTP, the upstream designated port fails to change its state rapidly.
The rapid transition feature is developed to resolve this problem. When a H3C series
switch running MSTP is connected in the upstream direction to another manufacturer's
switch running proprietary spanning tree protocols, you can enable the rapid transition
feature on the ports of the H3C series switch operating as the downstream switch.
Among these ports, those operating as the root ports will then send agreement packets
to their upstream ports after they receive proposal packets from the upstream
designated ports, instead of waiting for agreement packets from the upstream switch.
This enables designated ports of the upstream switch to change their states rapidly.
1.8.2 Configuring Rapid Transition
I. Configuration prerequisites
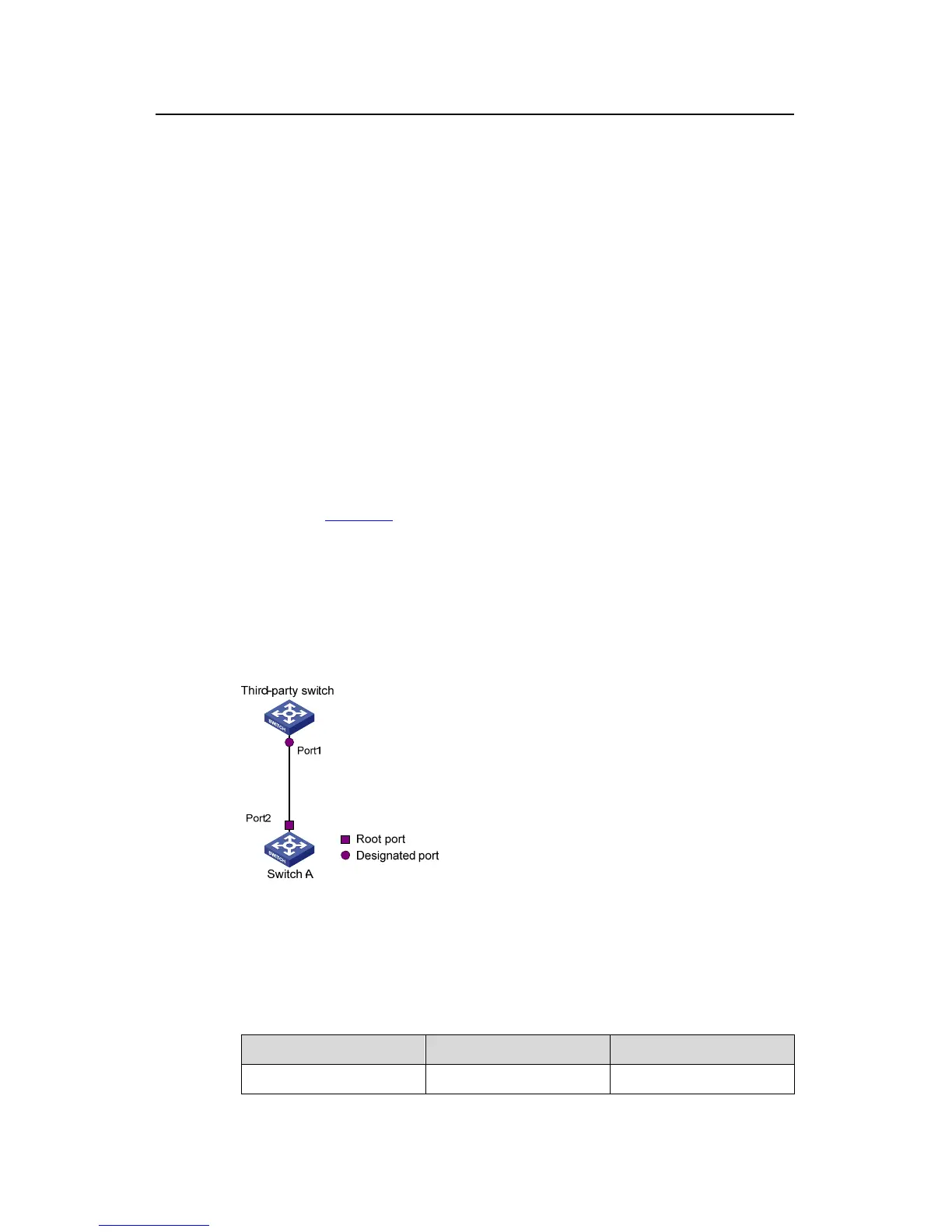
As shown in Figure 1-8, a H3C series switch is connected to another manufacturer's
switch. The former operates as the downstream switch, and the latter operates as the
upstream switch. The network operates normally.
The upstream switch is running a proprietary spanning tree protocol that is similar to
RSTP in the way to implement rapid transition on designated ports. Port 1 is the
designated port.
The downstream switch is running MSTP. Port 2 is the root port.
Figure 1-8 Network diagram for rapid transition configuration
II. Configuration procedure
1) Configure the rapid transition feature in system view
Table 1-43 Configure the rapid transition feature in system view
Operation Command Description
Enter system view
system-view
—

 Loading...
Loading...