Operation Manual - DNS
H3C S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 DNS Configuration
1-5
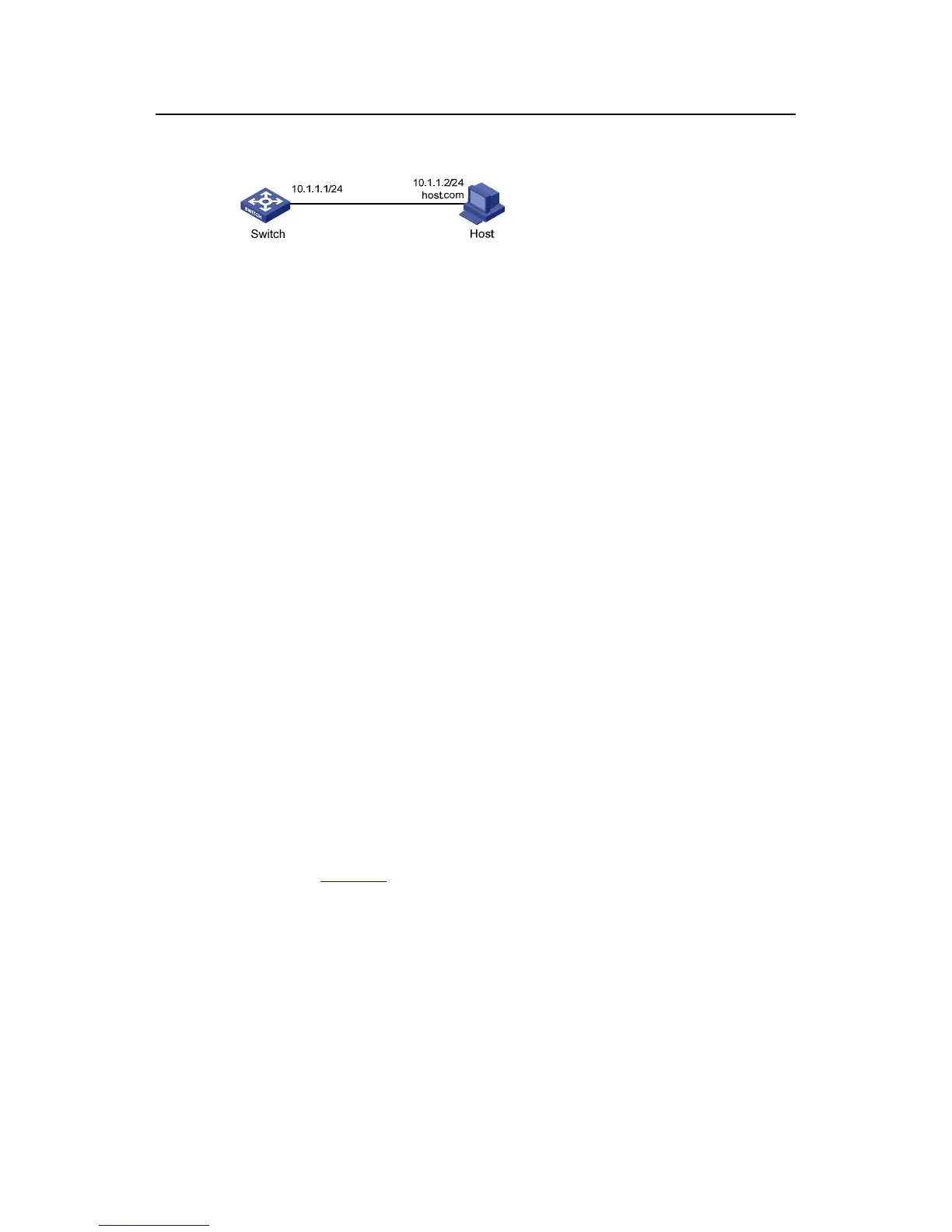
II. Network diagram
Figure 1-2 Network diagram for static DNS configuration
III. Configuration procedure
# Configure a mapping between host name host.com and IP address 10.1.1.2.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip host host.com 10.1.1.2
# Execute the ping host.com command to verify that the device can use static domain
name resolution to get the IP address 10.1.1.2 corresponding to host.com.
[Sysname] ping host.com
PING host.com (10.1.1.2): 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Reply from 10.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=127 time=3 ms
Reply from 10.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=127 time=3 ms
Reply from 10.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=127 time=2 ms
Reply from 10.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=127 time=5 ms
Reply from 10.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=127 time=3 ms
--- host.com ping statistics ---
5 packet(s) transmitted
5 packet(s) received
0.00% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 2/3/5 ms
1.4.2 Dynamic Domain Name Resolution Configuration Example
I. Network requirements
As shown in Figure 1-3, the switch serving as a DNS client uses dynamic domain name
resolution to access the host at 3.1.1.1/16 through its domain name host. The DNS
server has the IP address 2.1.1.2/16. The DNS suffix is com.

 Loading...
Loading...