Operation Manual – 802.1x-System Guard
H3C S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 802.1x Configuration
1-7
z PEAP creates and uses TLS security channels to ensure data integrity and then
performs new EAP negotiations to verify supplicant systems.
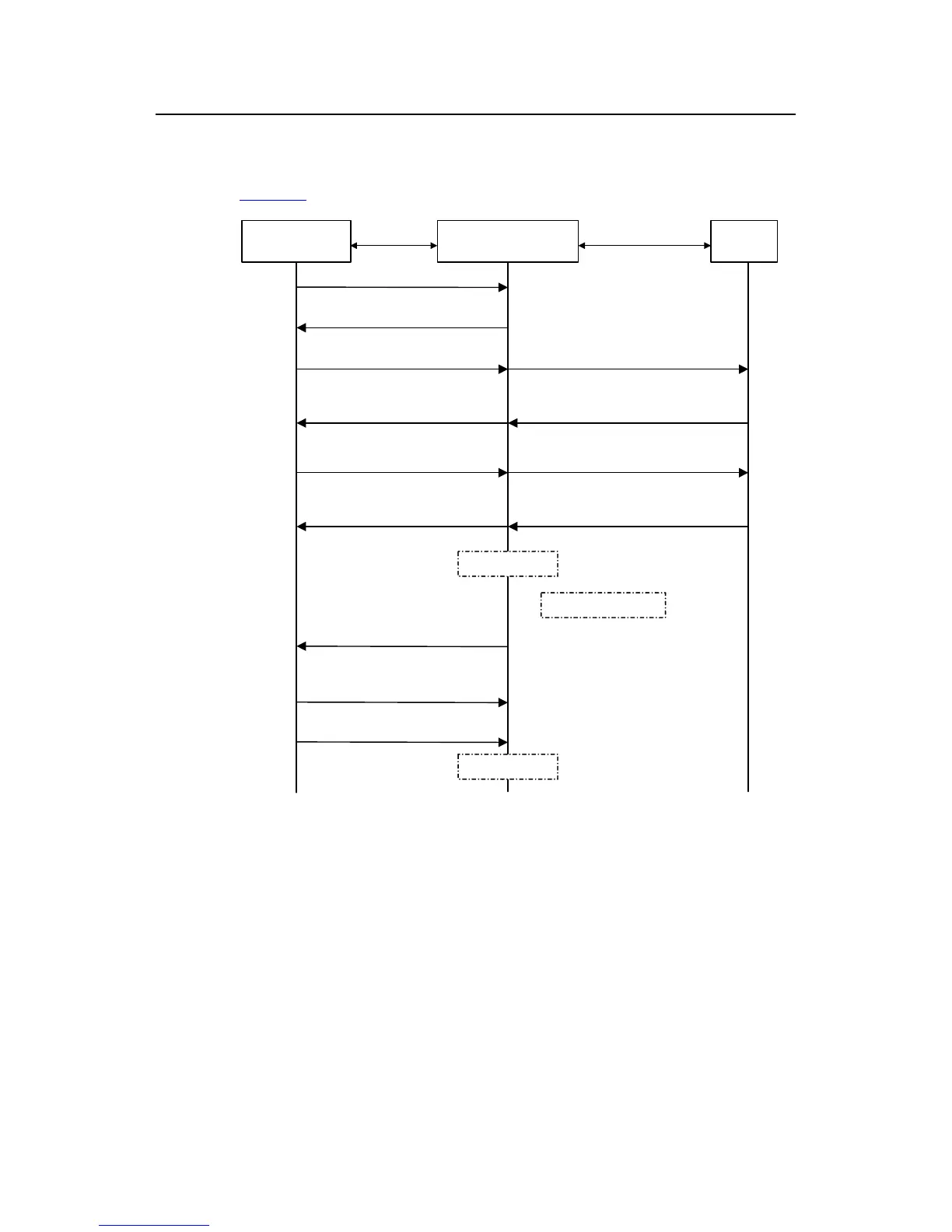
Figure 1-8 describes the basic EAP-MD5 authentication procedure.
Supplicant System
PAE
RADUIS
server
EAPOL
EAPOR
EAPOL-Start
EAP-Request / Identity
EAP-Response / Identity
EAP-Request / MD5 challenge
EAP-Success
EAP-Response / MD5 challenge
RADIUS Access-Request
(EAP-Response / Identity)
RADIUS Access-Challenge
(EAP-Request / MD5 challenge)
RADIUS Access-Accept
(EAP-Success)
RADIUS Access-Request
(EAP-Response / MD5 challenge)
Port authorized
Handshake timer
Handshake request
[ EAP-Request / Identity ]
Handshake response
[ EAP-Response / Identity ]
EAPOL-Logoff
......
Port unauthorized
Authenticator System
PAE
Figure 1-8 802.1x authentication procedure (in EAP relay mode)
The detailed procedure is as follows:
z A supplicant system launches an 802.1x client to initiate an access request by
sending an EAPoL-start packet to the switch, with its user name and password
provided. The 802.1x client program then forwards the packet to the switch to start
the authentication process.
z Upon receiving the authentication request packet, the switch sends an
EAP-request/identity packet to ask the 802.1x client for the user name.
z The 802.1x client responds by sending an EAP-response/identity packet to the
switch with the user name contained in it. The switch then encapsulates the packet
in a RADIUS Access-Request packet and forwards it to the RADIUS server.

 Loading...
Loading...