8-62
Configuring Demand Routing for Primary ISDN Modules
Viewing Information about Demand Routing
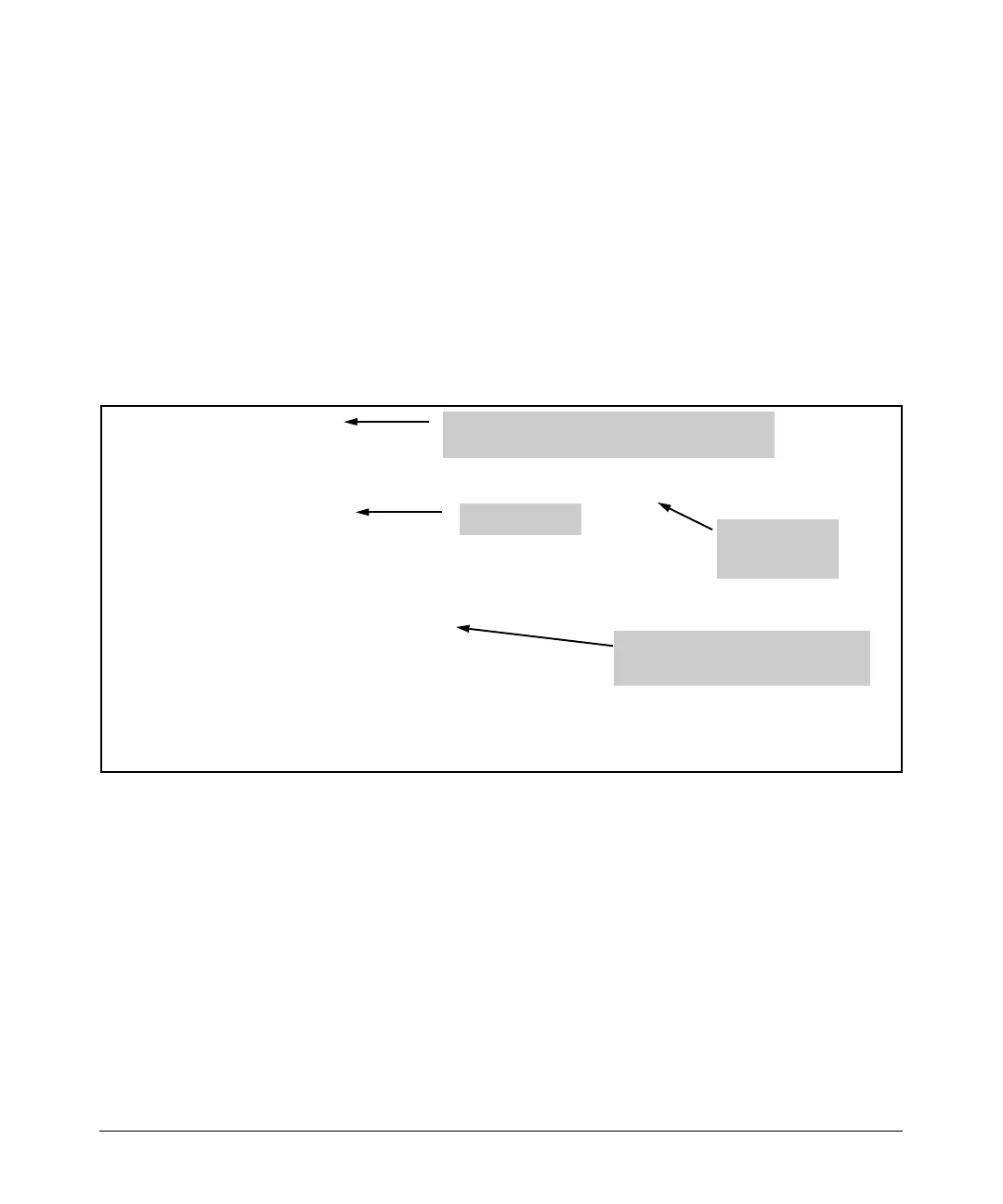
Figure 8-16 shows the results of this command if demand interface 1 is
spoofing its up status and a dial-up connection has not been established. In
addition to showing the status of the interface, this command displays settings
for the following commands:
■ connect-mode
■ resource pool
■ connect-sequence
■ idle-timeout
■ fast-idle
■ ip address
Figure 8-16. Viewing the Status of the Demand Interface When a Dial-Up
Connection Has Not Been Established
If a connection has been established through the demand interface, the show
interfaces demand 1 command shows:
■ the number of seconds until the ISDN connection is terminated
■ the number of frames in and out
■ the traffic that triggered the connection (the interesting traffic)
■ the amount of time the connection has been up
■ the BRI interface and channel through which the connection was
established
Demand 1 is UP (Spoofing)
Configuration:
Keep-alive is set (10 sec.)
Admin MTU = 1500
Mode: Either, 1 dial entries, idleTime = 120, fastIdle = 20
Resource pool Pool
No authentication configured
IP address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252
Recovery enabled, interval = 60, max-retries = 5
Connect Sequence: Successes = 1, Failures = 0
Seq DialString Technology Successes Busys NoAnswers NoAuths InUse
1 9634444 IsdnForced 1 0 0 0
Current values:
Local IP address 10.10.10.1, Peer IP address 0.0.0.0
Queueing method: weighted fair
Output queue: 0/1/428/64/0 (size/highest/max total/threshold/drops)
Conversations 0/1/256 (active/max active/max total)
Available Bandwidth 48 kilobits/sec
Bandwidth=64 Kbps
Demand interface is spoofing its up status; a dial-up
connection is not actually established
Information configured in the connect
sequence: dial-string (the number the
interface will call) and technology
Resource pool
connect-mode,
idle time, and
fast idle

 Loading...
Loading...