13-16
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Configuring a DHCP Server
After you enable 802.1Q encapsulation (for VLAN tagging) on the Ethernet
interface, you can configure Ethernet subinterfaces. You assign the subinter-
faces a VLAN ID and an IP address. To configure the DHCP scope, you simply
specify that IP address as the default router of the DHCP pool configured for
the VLAN.
These are the only configurations that you must make on the ProCurve Secure
Router. You can add options for the server addresses and lease time in the
same way that you would for any pool. (You would also configure the connect-
ing switch to pass DHCP packets from hosts on a specific VLAN to the address
of the corresponding Ethernet subinterface on the router. This configuration
ensures that clients receive an address on the correct subnet.)
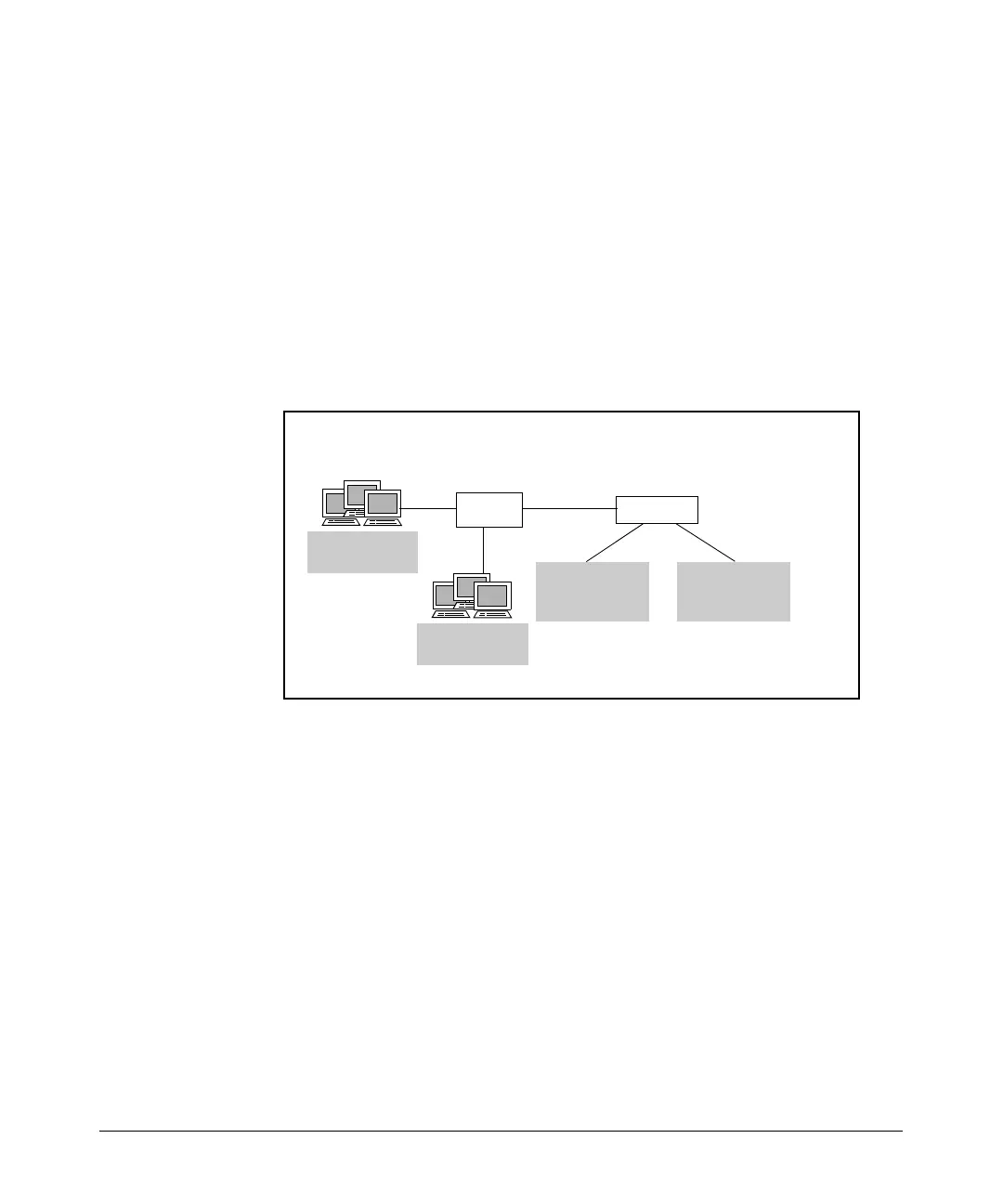
Figure 13-4. DHCP Scopes with VLANs
In Figure 13-4, Router A connects to Switch B on its Ethernet 0/1 interface.
Switch B connects to hosts in VLANs 101 and 102. You enable VLAN tagging
on the router so that traffic to both VLANs can be carried over the same cable.
You configure IP address 192.168.1.1 /24 on Ethernet subinterface 0/1.1 and IP
address 192.168.2.1 /24 on Ethernet subinterface 0/1.2.
You would configure the DHCP scopes as follows:
1. Enable VLAN tagging:
ProCurve(config)# interface eth 0/1
ProCurve(config-eth 0/1)# encapsulation 802.1q
ProCurve(config-eth 0/1)# no shutdown
10.2.1.0 /24
Gateway
10.2.1.1
10.3.1.0 /24
Gateway
10.3.1.1
Router A
VLAN 101
10.2.1.0/24
VLAN 102
10.3.1.0/24
Scope 2Scope 1
Switch B
Eth 0/1.1
10.2.1.1
Eth 0/1.2
10.3.1.1

 Loading...
Loading...