C
HAPTER
15
| Multicast Filtering
Layer 3 IGMP (Query used with Multicast Routing)
– 410 –
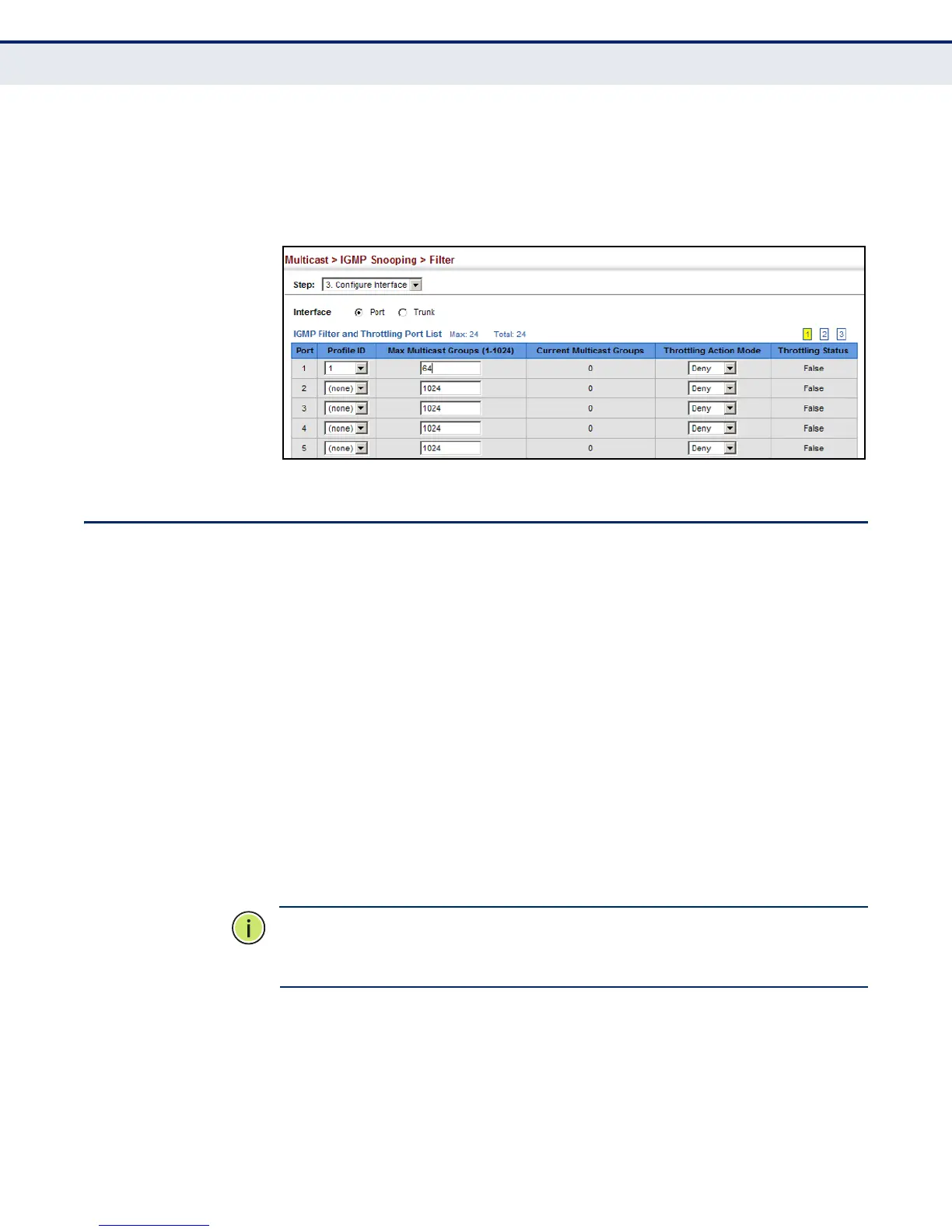
3. Select a profile to assign to an interface, then set the maximum
number of allowed multicast groups and the throttling response.
4. Click Apply.
Figure 242: Configuring IGMP Filtering and Throttling Interface Settings
LAYER 3 IGMP (QUERY USED WITH MULTICAST ROUTING)
IGMP Snooping – IGMP Snooping (page 391) is a key part of the overall set
of functions required to support multicast filtering. It is used to passively
monitor IGMP service requests from multicast clients, and dynamically
configure the switch ports which need to forward multicast traffic.
IGMP Query – Multicast query is used to poll each known multicast group
for active members, and dynamically configure the switch ports which need
to forward multicast traffic. Layer 3 IGMP Query, as described below, is
used in conjunction with both Layer 2 IGMP Snooping and multicast
routing.
IGMP – This protocol includes a form of multicast query specifically
designed to work with multicast routing. A router periodically asks its hosts
if they want to receive multicast traffic. It then propagates service requests
on to any upstream multicast router to ensure that it will continue to
receive the multicast service. IGMP can be enabled for individual VLAN
interfaces (page 413).
N
OTE
:
Multicast Routing Discovery (MRD) is used to discover which
interfaces are attached to multicast routers. (For a description of this
protocol, see “Multicast Router Discovery” on page 399.)
IGMP Proxy – A device can learn about the multicast service requirements
of hosts attached to its downstream interfaces, proxy this group
membership information to the upstream router, and forward multicast
packets based on that information.

 Loading...
Loading...











