HIGH DATA RATE RECEIVER
HDR-4G+ USER’S MANUAL
Ref. DTU 100782
Is.Rev 3.5
Date: June 1, 2021
© Safran Data Systems – IMP000074 e14r1
This document is the property of Safran Data Systems.
It cannot be duplicated or distributed without expressed written consent.
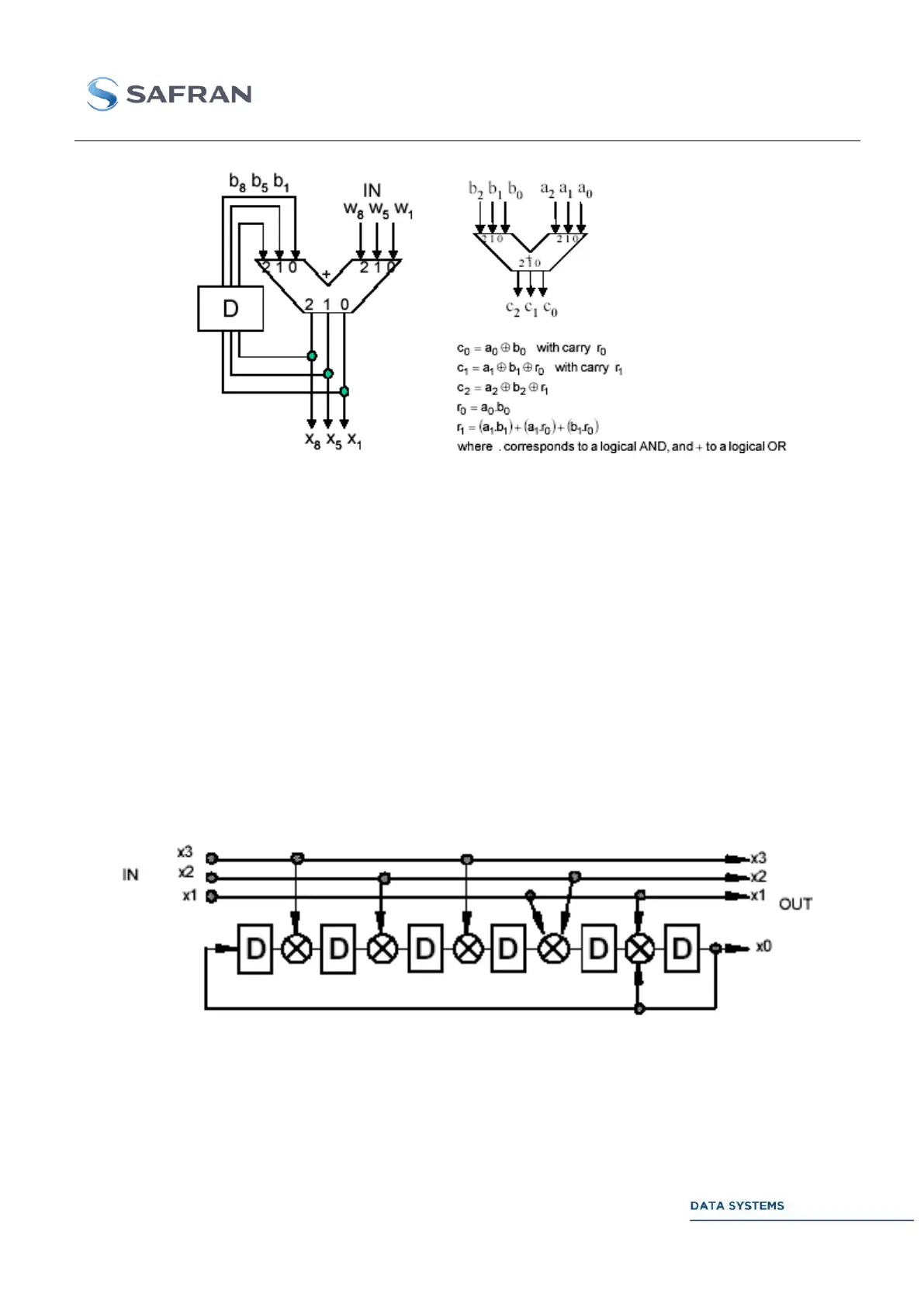
Figure 20: Differential Coder and Modulo-8 Adder Principle
For all the bits non concerned by the differential encoding, we have then:
Convolutional Coder 3.3.7.2.2
The convolutional coder used to implement the trellis is depicted in Figure 21. This code corresponds
to one of the “best” codes for phase transparency.
The systematic coder is implemented with the following characteristics:
number of states: 64 states,
constraint length: K = 7
The convolutional encoder is specified by the following polynomial in octal: h
3
= 050, h
2
= 024, h
1
= 006,
h
0
= 103. Figure 21 shows the recommended convolutional encoder. The shift registers of the encoder
are clocked at the rate of R
ChS
/4.
Figure 21: Convolutional Coder Recommended for High Data Rates
The number of coded bits is the same for the four modulation efficiencies (i.e., the same structure is
used for 2, 2.25, 2.5, and 2.75 bits/channel-symbol), only the number of uncoded bits is changed. The
advantage of this coder is its optimized performance and the reduced internal rate which is equal to
1/8, 1/9, 1/10, or 1/11 of the information rate.

 Loading...
Loading...