Zynq-7000 AP SoC and 7 Series FPGAs MIS v4.1 620
UG586 November 30, 2016
www.xilinx.com
Chapter 4: LPDDR2 SDRAM Memory Interface Solution
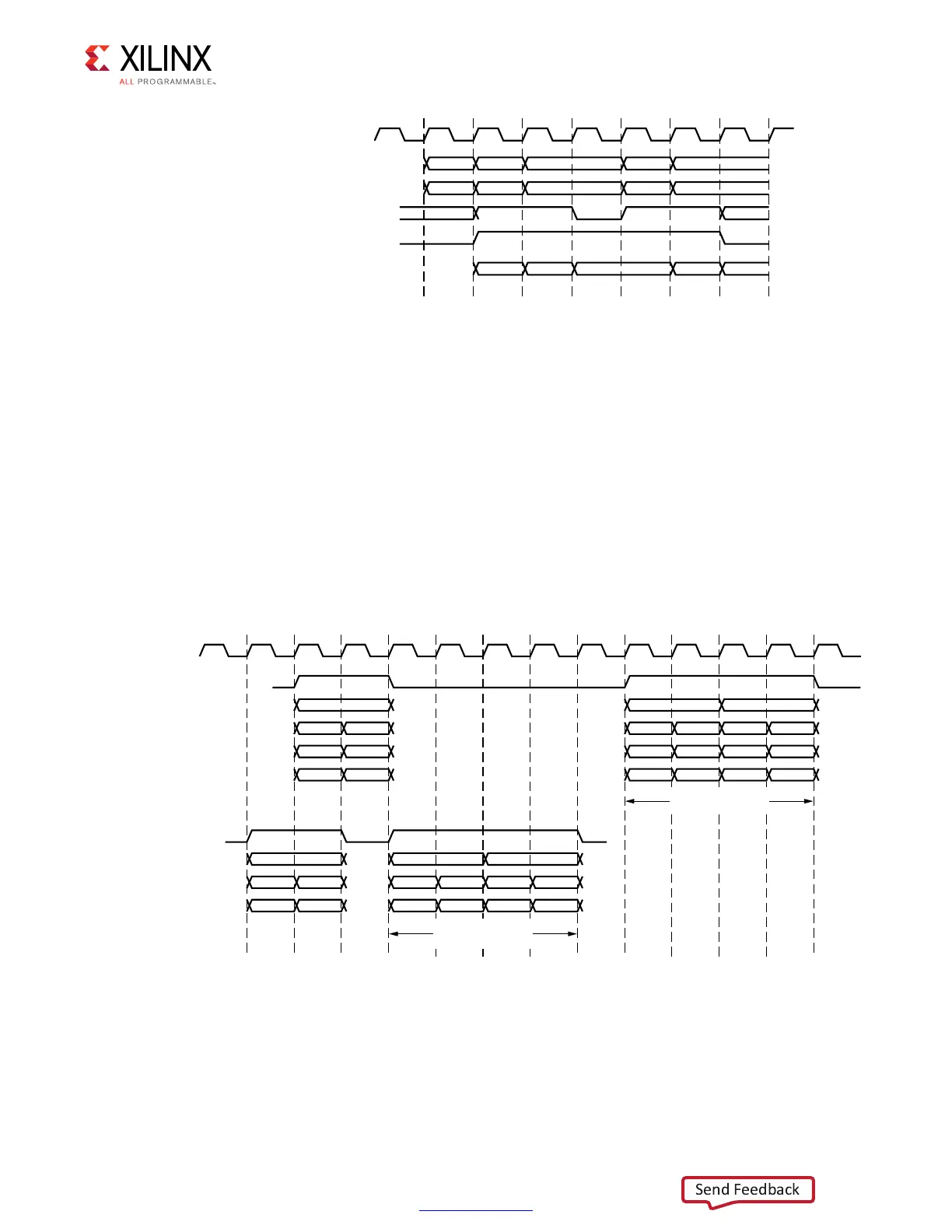
In Figure 4-68, requests 1 and 2 are accepted normally. The first time request 3 is presented,
accept is driven Low, and the request is not accepted. The user design retries request 3,
which is accepted on the next attempt. Request 4 is subsequently accepted on the first
attempt.
The data_buf_addr bus must be supplied with requests. This bus is an address pointer
into a buffer that exists in the user design. It tells the core where to locate data when
processing write commands and where to place data when processing read commands.
When the core processes a command, the core echoes data_buf_addr back to the user
design through wr_data_addr for write commands and rd_data_addr for read
commands. This behavior is shown in Figure 4-69. Write data must be supplied in the same
clock cycle that wr_data_en is asserted.
Transfers can be isolated with gaps of non-activity, or there can be long bursts with no gaps.
The user design can identify when a request is being processed and when it finishes by
monitoring the rd_data_en and wr_data_en signals. When the rd_data_en signal is
asserted, the Memory Controller has completed processing a read command request.
X-Ref Target - Figure 4-68
Figure 4-68: Native Interface Flow Control
CLK
ANKBANKROWCOLUMN
CMDHI?PRIORITY
ACCEPT
USE?ADDR
DATA?BUF?ADDR
5'?C??
X-Ref Target - Figure 4-69
Figure 4-69: Command Processing
CLK
WR?DATA?EN
WR?DATA?ADDR
WR?DATA?OFFSET
WR?DATA
WR?DATA?MASK
RD?DATA?EN
RD?DATA?ADDR
RD?DATA?ADDR
RD?DATA
$$
$$
$$
$$
$$
$$
$$
$$
$$
$$
4WO"ACKTO"ACK
$ATA"URSTS
$$
$$
5'?C??
4WO"ACKTO"ACK
$ATA"URSTS

 Loading...
Loading...











