Saturation of current transformers
There are basically two types of saturation phenomena that have to be detected:
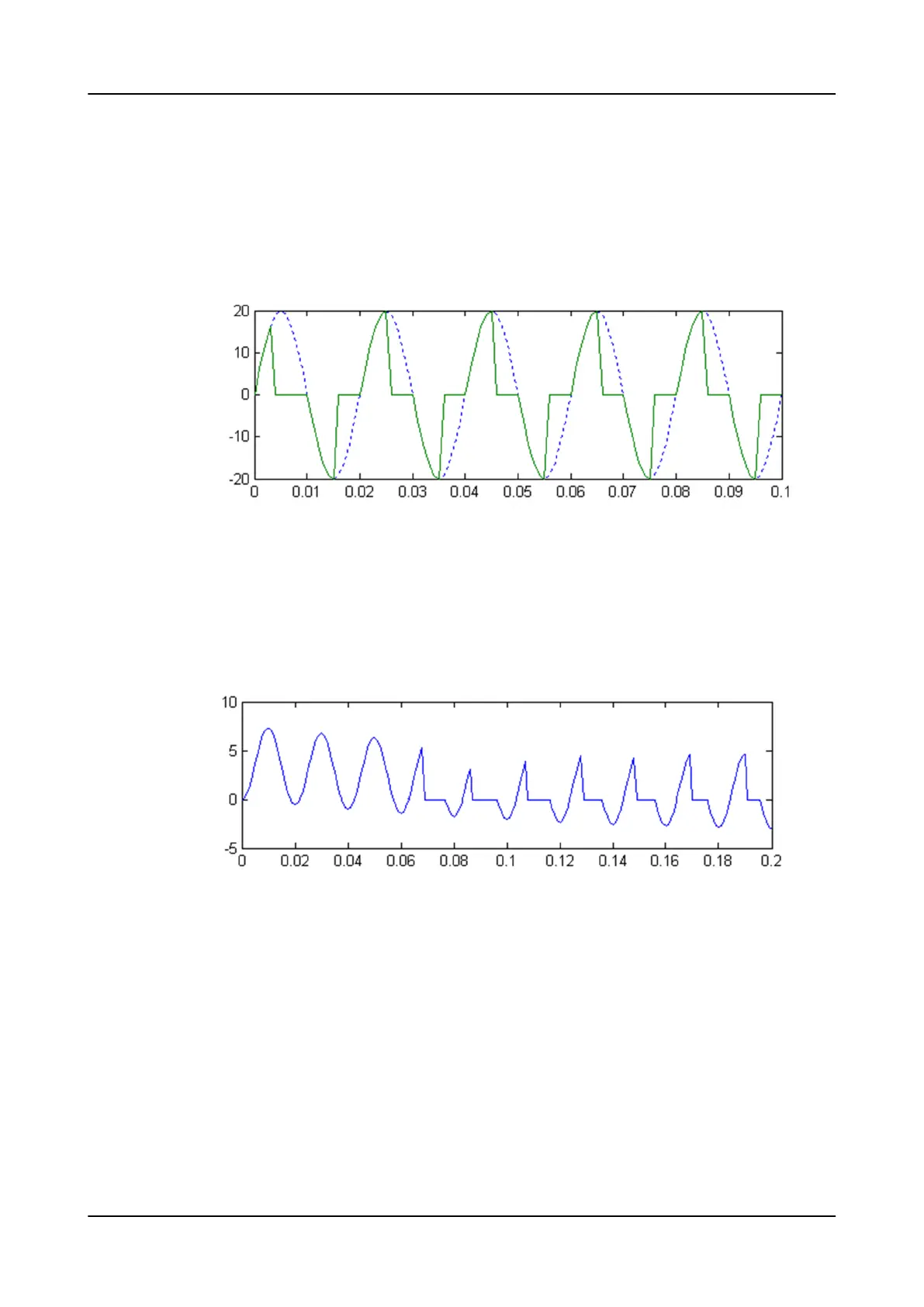
the AC saturation and the DC saturation. The AC saturation is caused by a high
fault current where the CT magnetic flux exceeds its maximum value. As a result,
the secondary current is distorted as shown in
Figure 456
. A DC component in the
current also causes the flux to increase until the CT saturates. This is known as DC
saturation.
Figure 456: AC saturation
When having a short circuit in a power line, the short circuit current contains a DC
component. The magnitude of the DC component depends on the phase angle when
the short circuit occurs.
Figure 457
shows the secondary current of the CT in the
fault situation. Because of the DC component, the flux reaches its maximum value
at 0.07 seconds, causing saturation. As the DC component decays, the CT recovers
gradually from the saturation.
Figure 457: DC saturation
4.3.7.7 Signals
1MRS759142 F
Protection functions
REX640
Technical Manual
801

 Loading...
Loading...
















