168
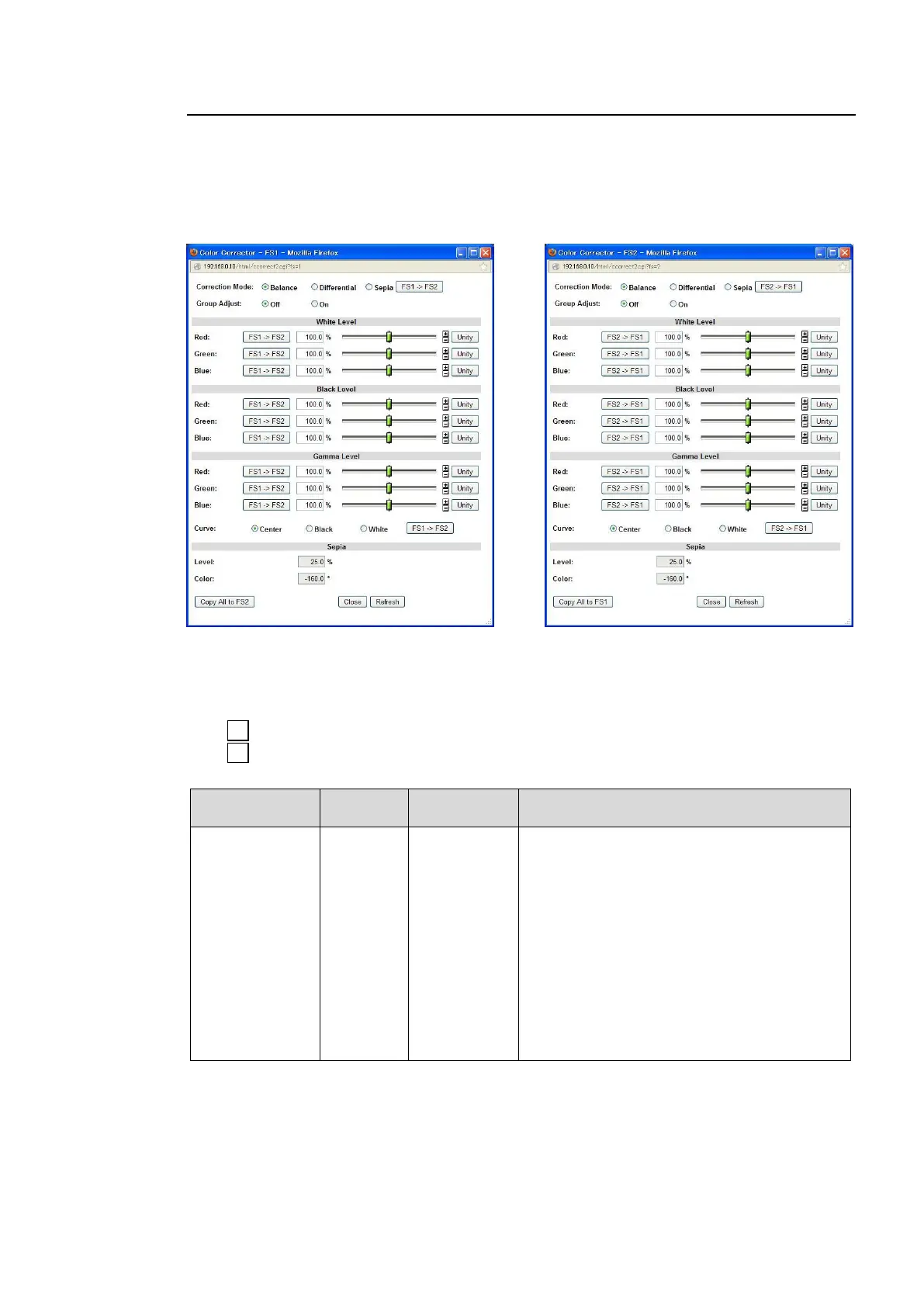
9-2-7. Color Corrector
Clicking block (7) on the video block diagram opens the Color Corrector dialog box for the
corresponding FS.
See section 5-2-4 “COLOR CORRECTOR (C.C.)” for details.
Auto Video Optimizer (AVO) and Color Corrector use the same circuit. The color corrector
settings are not fully changeable when AVO mode (9-2-2 “Auto Video Optimizer (AVO)”) is set
to Auto. See section 5-2-5 “Color Corrector and AVO Modes” for the available menu settings.
After completing the settings, click Close to close the dialog box.
Click Refresh to update the settings.
Click Unity to reset to the default settings.
Click to increase the value by the smallest steps.
Click to decrease the value by the smallest steps.
Correction Mode
Balance
Differential
Sepia
*1
Selects a correction mode from Balance
(RGB), Differential (YPbPr), or Sepia.
Balance: RGB signal correction mode
Allows you to adjust the white balance. Gray
scale can be changed by adjusting R, G and
B levels.
Differential: Color difference signal mode
Allows you to adjust contrast without
changing white balance. R, G and B levels
can be changed without affecting gray scale.
This adjustment is effective for images with
different color saturation levels.
Sepia: Sepia mode
Useful for creating black and white images.
*1 Sepia will not be displayed while changing FS1 and FS2 settings simultaneously. If
Correction Mode is set to Sepia, the White Level, Black Level, or Gamma Level R, B setting
cannot be changed. Also, it cannot be changed if AVO Control is set to Auto or Hold in the
Auto Video Optimizer (AVO) menu (9-2-2). Correction Mode cannot be set to Sepia, if LINK
setting mode is enabled in the FA-9520 or connected FA-95RU. To set to Sepia, disable LINK
setting mode. See section 4-2-8. “Switching Between 2-Channel Frame Synchronizers” for
details on LINK settings.
FS1 Color Corrector dialog box
FS2 Color Corrector dialog box
 Loading...
Loading...