6 Agilent X-Series Signal Generators SCPI Command Reference
SCPI Basics
SCPI Basics
Command Types
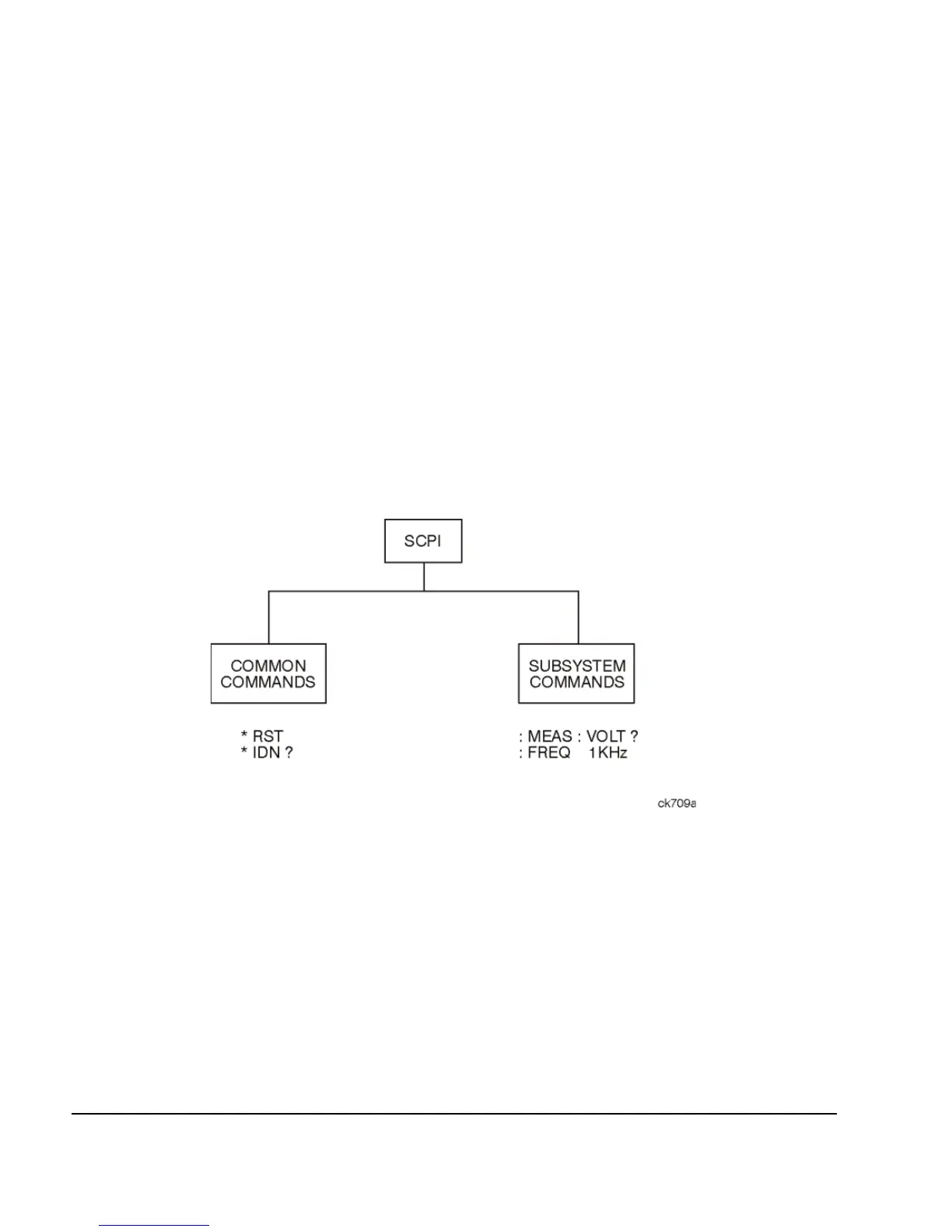
Commands can be separated into two groups: common commands and subsystem commands. Figure
1- 1, shows the separation of the two command groups.
Common commands are used to manage status registers, synchronization, and data storage and are
defined by IEEE 488.2. They are easy to recognize because they all begin with an asterisk. For
example *IDN?, *OPC, and *RST are common commands. Common commands are not part of any
subsystem and the signal generator interprets them in the same way, regardless of the current path
setting.
Subsystem commands are distinguished by the colon (:). The colon is used at the beginning of a
command statement and between keywords, as in :FREQuency[:CW?]. Each command subsystem is a
set of commands that roughly correspond to a functional block inside the signal generator. For
example, the power subsystem (:POWer) contains commands for power generation, while the status
subsystem (:STATus) contains commands for controlling status registers.
Figure 1-1 Command Types
Command Tree
Most programming tasks involve subsystem commands. SCPI uses a structure for subsystem
commands similar to the file systems on most computers. In SCPI, this command structure is called
a command tree and is shown in Figure 1- 2.

 Loading...
Loading...