January 2012 8.15 Command Set 1671
Word processing
with the ASSIGN
command
Syntax: = (STORE)
Operands: B, W, D
Action:
Assign the content of the word accumulator to the addressed operand. Unlike
bit processing, in word processing you can also use the = command within a
sequence of word-gating operations. This command can be used several
times in succession.
Example:
Gate a constant and byte B5 with AND, and assign the result to byte B8 and
byte B10.
Initial state:
Constant 54 = 36 (hex)
Byte B5 = 2A (hex)
Byte B8 = ?
Byte B10 = ?
8.15.9 ASSIGN BYTE (B=)
Syntax: B= (STORE BYTE)
Operands: M, I, O, T, C
Action:
Assign 8 bits from the word accumulator to markers, inputs, outputs, timers
or counters with ascending numbering. Every bit occupies an operand. The
control assigns the LSB in the accumulator to the operand address specified
in the command, the LSB +1 to the specified address +1, etc. The MSB is
assigned to the last (8th) operand.
Example:
See example command W=. Use command B= in the same way as W=.
However, the control processes 8 operands.
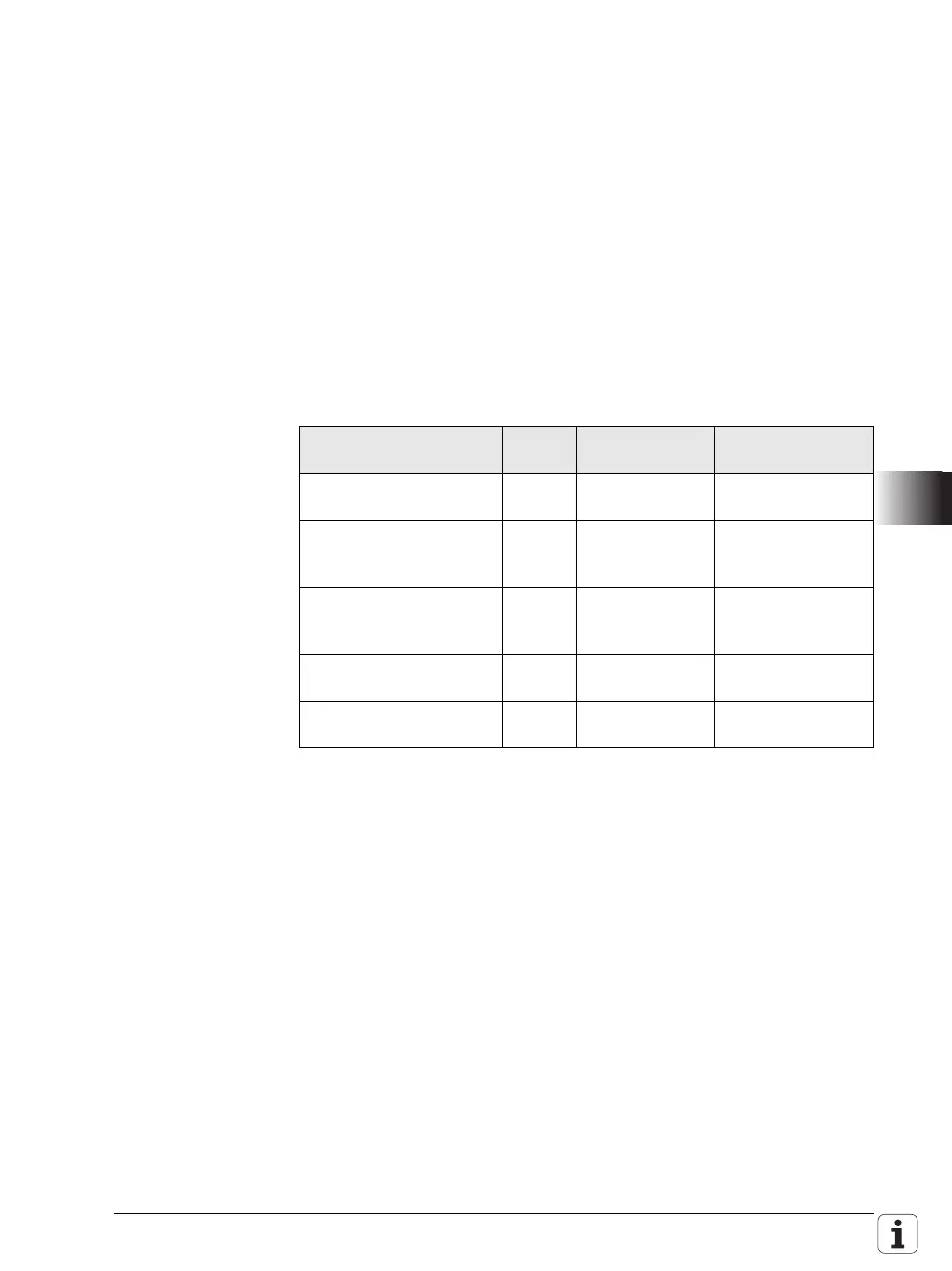
Function STL Accumulator
content
Operand content
Load the constant into the
word accumulator.
L K+54 36
Assign the contents of
the word accumulator to
byte B8.
= B8 36 36
Gate the contents of the
word accumulator and
byte B5 with AND.
A B5 22 2A
Assign the gating result to
byte B8.
= B8 22 22
Assign the gating result to
byte B10.
= B10 22 22

 Loading...
Loading...