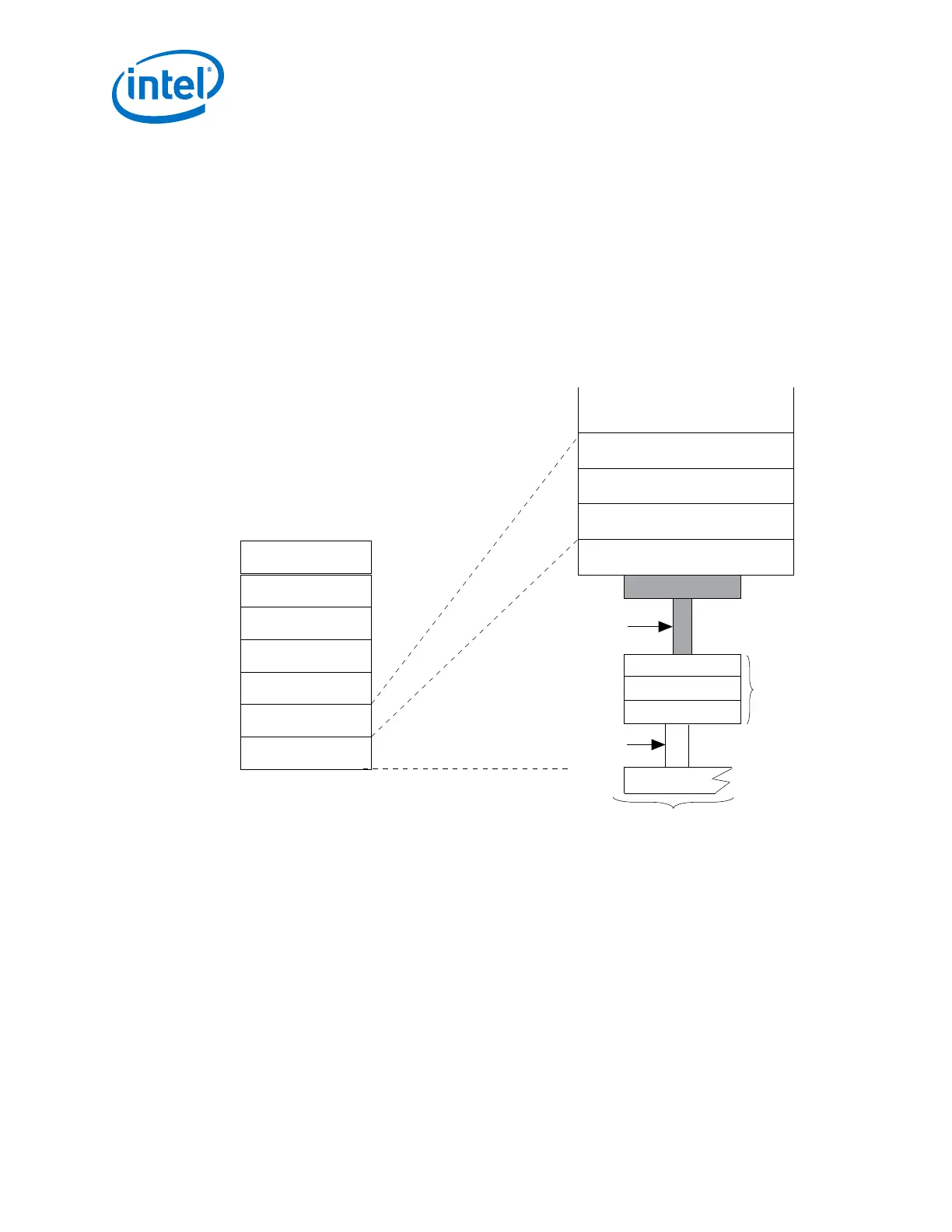
2.6.1. Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) and GbE with IEEE 1588v2
Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) is a high-speed local area network technology that provides
data transfer rates of about 1 Gbps. GbE builds on top of the ethernet protocol, but
increases speed tenfold over Fast Ethernet. IEEE 802.3 defines GbE as an intermediate
(or transition) layer that interfaces various physical media with the media access
control (MAC) in a Gigabit Ethernet system. Gigabit Ethernet PHY shields the MAC
layer from the specific nature of the underlying medium and is divided into three sub-
layers shown in the following figure.
Figure 42. GbE PHY Connection to IEEE 802.3 MAC and RS
Application
Presentation
Session
Transport
Network
Data Link
Physical
OSI
Reference
Model
Layers
Higher Layers
LAN
CSMA/CD
LAYERS
LLC (Logical Link Control)
or other MAC Client
MAC Control (Optional)
Media Access Control (MAC)
Reconciliation
PHY
Sublayers
GMII
MDI
PMA
PCS
RECONCILIATION
PMD
Medium
1 Gbps
2. Implementing Protocols in Arria 10 Transceivers
UG-01143 | 2018.06.15
Intel
®
Arria
®
10 Transceiver PHY User Guide
112
 Loading...
Loading...