Calculations and Judgments Using Inspection Item Data
FQ2-S/CH User’s Manual
329
4
Setting Up Inspections
Function List
The following functions can be used in calculations.
Function Description
SIN
Finds the sine. The result is a value between −1 and 1.
The angle in the expression is in degrees.
SIN(angle)
COS
Finds the cosine. The result is a value between −1 and 1.
The angle in the expression is in degrees.
COS(angle)
ATAN
Finds the arctangent of the value (Y component, X component). The result is a radian value between −π
and π.
ANGL(Y_component,X_component)
Example: Finding the angle between the straight line joining the centers of region 0 and region 1 and hori-
zontal.
ATAN(R1.Y-R0.Y,R1.X-R0.X)
If the two arguments are both 0, the result is 0 and the judgement is NG.
AND
Finds the logical AND.
If one of the arguments is 0, the calculation result is 0. Otherwise it is −1.
AND(argument_1,argument_2)
OR
Finds the logical OR.
If both of the arguments are 0, the calculation result is 0. Otherwise it is −1.
OR(argument_1,argument_2)
NOT
Applies a logical NOT operation.
If the argument is 0, the calculation result is −1. Otherwise it is 0.
NOT(argument)
ABS Finds the absolute value.
ABS(argument)
MAX Returns the larger of the two arguments.
MAX(argument_1, argument_2)
MIN Returns the smaller of the two arguments.
MAX(argument_1, argument_2)
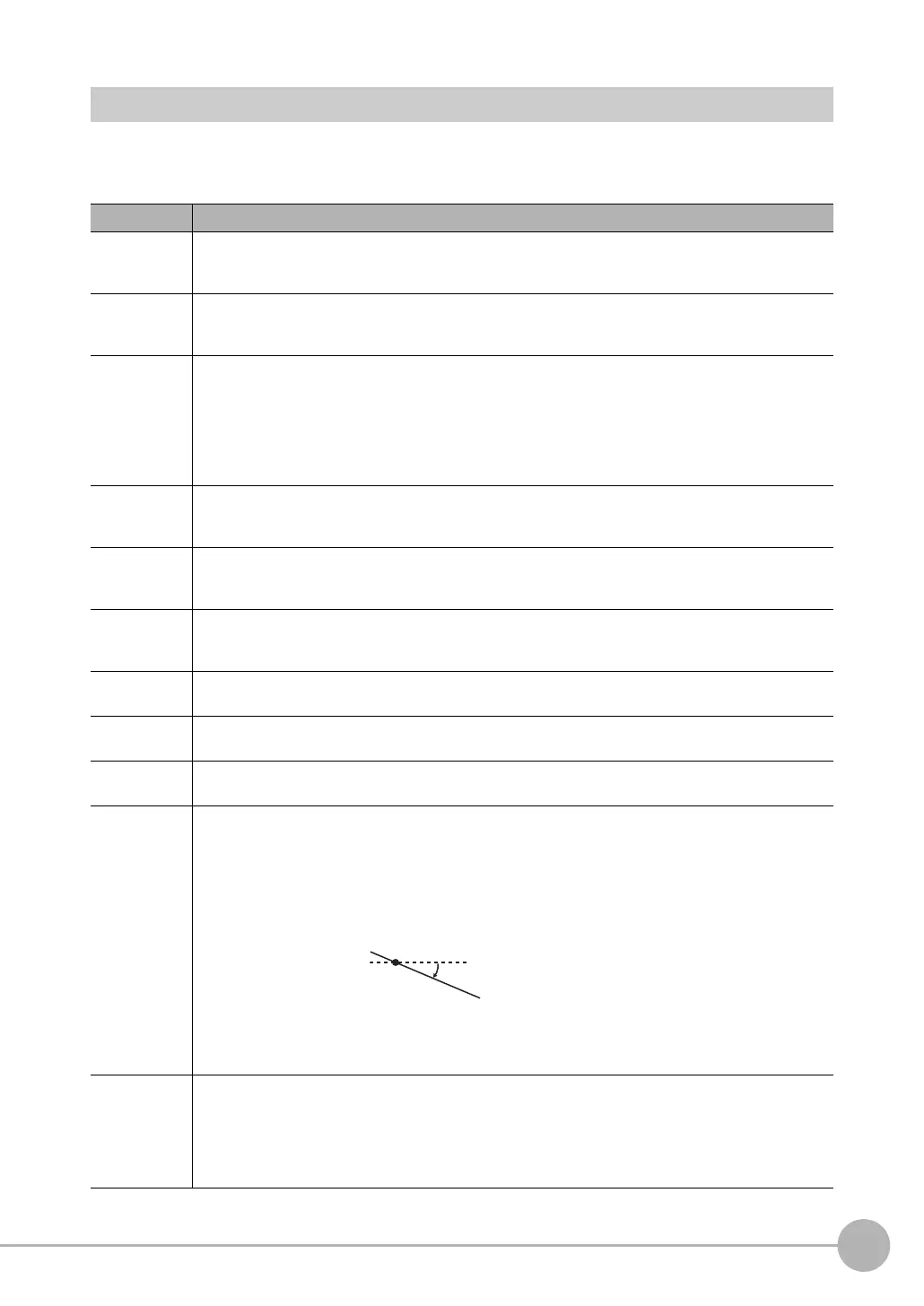
ANGL
Finds the angle of the straight line joining two points (the center of gravity and center of the model). The
angle against the horizontal is found. The result is a value between −180 and 180.
ANGL(Y_component,X_component)
Example: Finding the angle of the straight line joining the centers of region 0 and region 1
ANGL(R1.Y-R0.Y,R1.X-R0.X)
If the two arguments are both 0, the result is 0 and the judgement is NG.
MOD
Finds the remainder after dividing a non-ordinal number with an ordinal number.
MOD(non-ordinal, ordinal)
If any of the arguments are real numbers, the decimals are rounded off before calculating the remainder.
The remainder is the result of dividing integers.
Example: MOD(13,4) ... Result: 1 (remainder when 13 is divided by 4)
MOD(25.68,6.99) ... Result: 5 (remainder when 26 is divided by 7)
First point
(Horizontal)
Second point

 Loading...
Loading...











