The IEEE 802.3 specification requires GbE to transmit Idle ordered sets (/I/)
continuously and repetitively whenever the gigabit media-independent interface
(GMII) is Idle. This transmission ensures that the receiver maintains bit and word
synchronization whenever there is no active data to be transmitted.
For the GbE protocol, the transmitter replaces any /Dx.y/ following a /K28.5/ comma
with either a /D5.6/ (/I1/ ordered set) or a /D16.2/ (/I2/ ordered set), depending on
the current running disparity. The exception is when the data following the /K28.5/ is /
D21.5/ (/C1/ ordered set) or /D2.2/ (/C2/) ordered set. If the running disparity before
the /K28.5/ is positive, an /I1/ ordered set is generated. If the running disparity is
negative, a /I2/ ordered set is generated. The disparity at the end of a /I1/ is the
opposite of that at the beginning of the /I1/. The disparity at the end of a /I2/ is the
same as the beginning running disparity immediately preceding transmission of the
Idle code. This sequence ensures a negative running disparity at the end of an Idle
ordered set. A /Kx.y/ following a /K28.5/ does not get replaced.
Note: /D14.3/, /D24.0/, and /D15.8/ are replaced by /D5.6/ or /D16.2/ (for I1 and I2
ordered sets). D21.5 (/C1/) is not replaced.
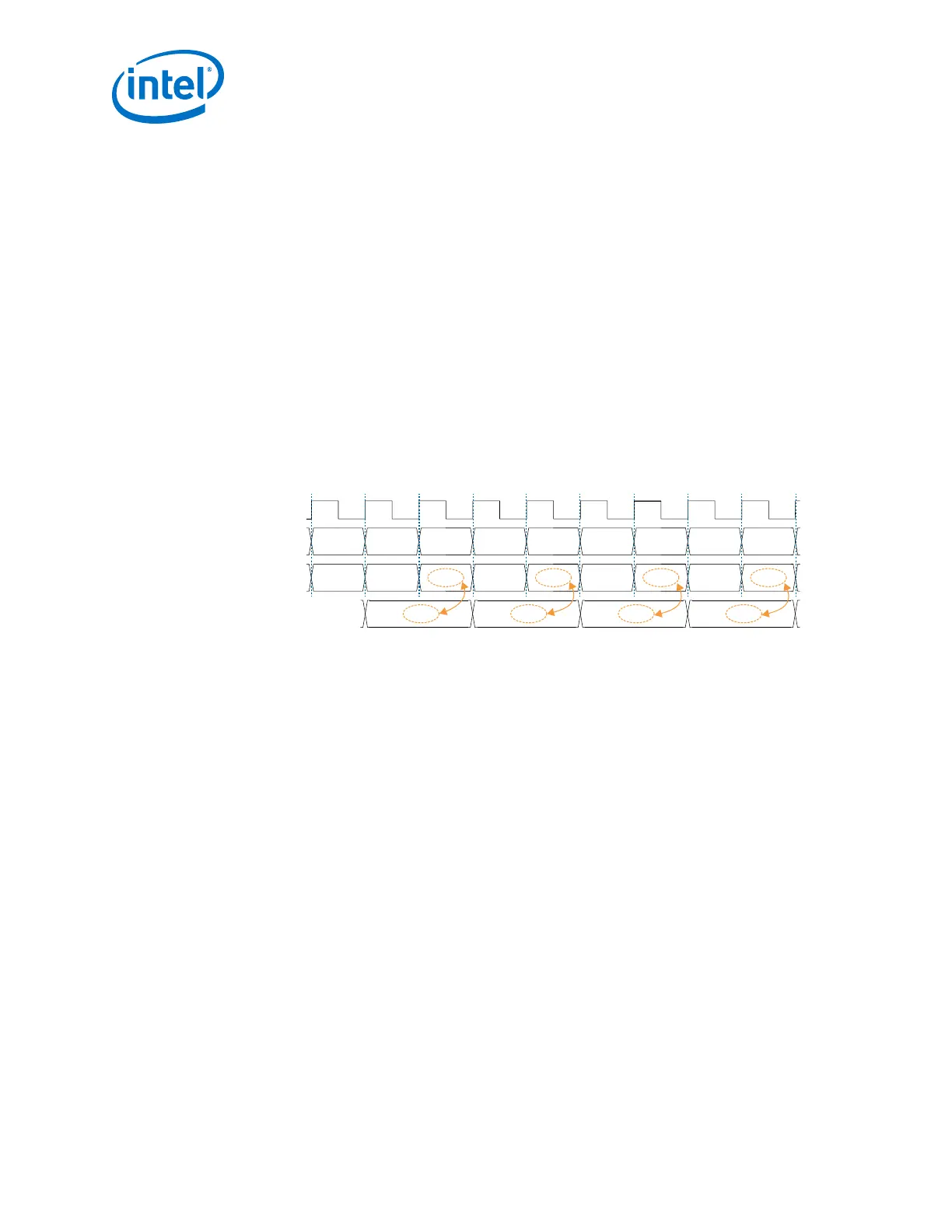
Figure 44. Idle Ordered-Set Generation Example
Clock (i)
tx_datain (i)
tx_dataout (o)
Ordered Set (o)
K28.5
D14.3
D24.0 D15.8 D21.5 Dx.yK28.5 K28.5 K28.5
Dx.y
K28.5 K28.5
K28.5
K28.5
D5.6 D16.2
D21.5
D16.2
/I1/ /I2/ /C1//I2/
Legend:
(i) = Input signal
(o) = Output signal
Related Information
8B/10B Encoder on page 482
2.6.1.1.1. Reset Condition for 8B/10B Encoder in GbE, GbE with IEEE 1588v2
After deassertion of tx_digitalreset, the transmitters automatically transmit at
least three /K28.5/ comma code groups before transmitting user data on the
tx_parallel_data port. This transmission could affect the synchronization state
machine behavior at the receiver.
Depending on when you start transmitting the synchronization sequence, there could
be an even or odd number of /Dx.y/ code groups transmitted between the last of the
three automatically sent /K28.5/ code groups and the first /K28.5/ code group of the
synchronization sequence. If there is an even number of /Dx.y/code groups received
between these two /K28.5/ code groups, the first /K28.5/ code group of the
synchronization sequence begins at an odd code group boundary. The synchronization
state machine treats this as an error condition and goes into the loss of
synchronization state.
2. Implementing Protocols in Arria 10 Transceivers
UG-01143 | 2018.06.15
Intel
®
Arria
®
10 Transceiver PHY User Guide
114
 Loading...
Loading...