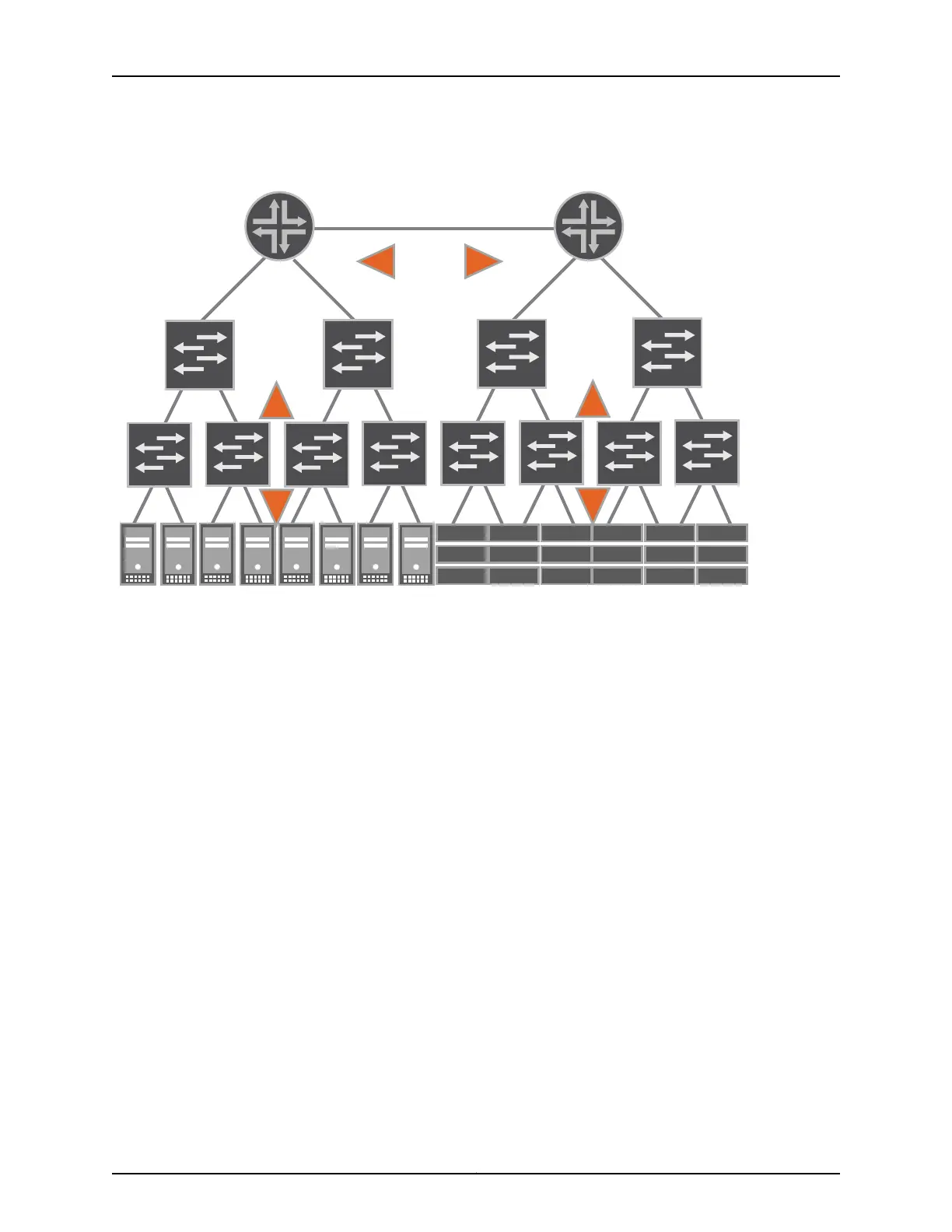
Figure 1: Legacy Data Center Architecture
The access layer connects servers and other devices to a Layer 2 switch and provides an
entry point into the data center. Several access switches are in turn connected to
intermediate Layer 2 switches at the aggregation layer (sometimes referred to as the
distribution layer) to consolidate traffic. A core layer interconnects the aggregation layer
switches. Finally, the core switches are connected to Layer 3 routers in the routing layer
to send the aggregated data center traffic to other data centers or a wide-area network
(WAN), receive external traffic destined for the data center, and interconnect different
Layer 2 broadcast domains within the data center.
The problems that exist with the multi-tier data center architecture include:
•
Limited scalability—The demands for electrical power, cooling, cabling, rack space,
and port density increase exponentially as the traditional data center expands, which
prohibits growth after minimal thresholds are met.
•
Inefficient resource usage—Up to 50 percent of switch ports in a legacy data center
are used to interconnect different tiers rather than support server and storage
connections. In addition, traffic that ideally should move horizontally between servers
within a data center often must also be sent vertically up through the tiers to reach a
router and down through the tiers to reach the required destination server.
•
Increased latency—By requiring the devices at each tier level to perform multiple
iterations of packet and frame processing, the data plane traffic takes significantly
longer to reach its destination than if the sending and receiving devices were directly
connected. This processing overhead results in potentially poor performance for
time-sensitive applications, such as voice, video, or financial transactions.
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks, Inc.4
QFX3000 Hardware Documentation
 Loading...
Loading...











