Protocol analysis
R&S
®
RTP
536User Manual 1337.9952.02 ─ 12
The Serial Peripheral Interface SPI is used for communication with slow peripheral
devices, in particular, for transmission of data streams.
Main characteristics of SPI are:
●
Master-slave communication
●
No device addressing; The slave is accessed by a chip select, or slave select line.
●
No acknowledgement mechanism to confirm receipt of data
●
Duplex capability
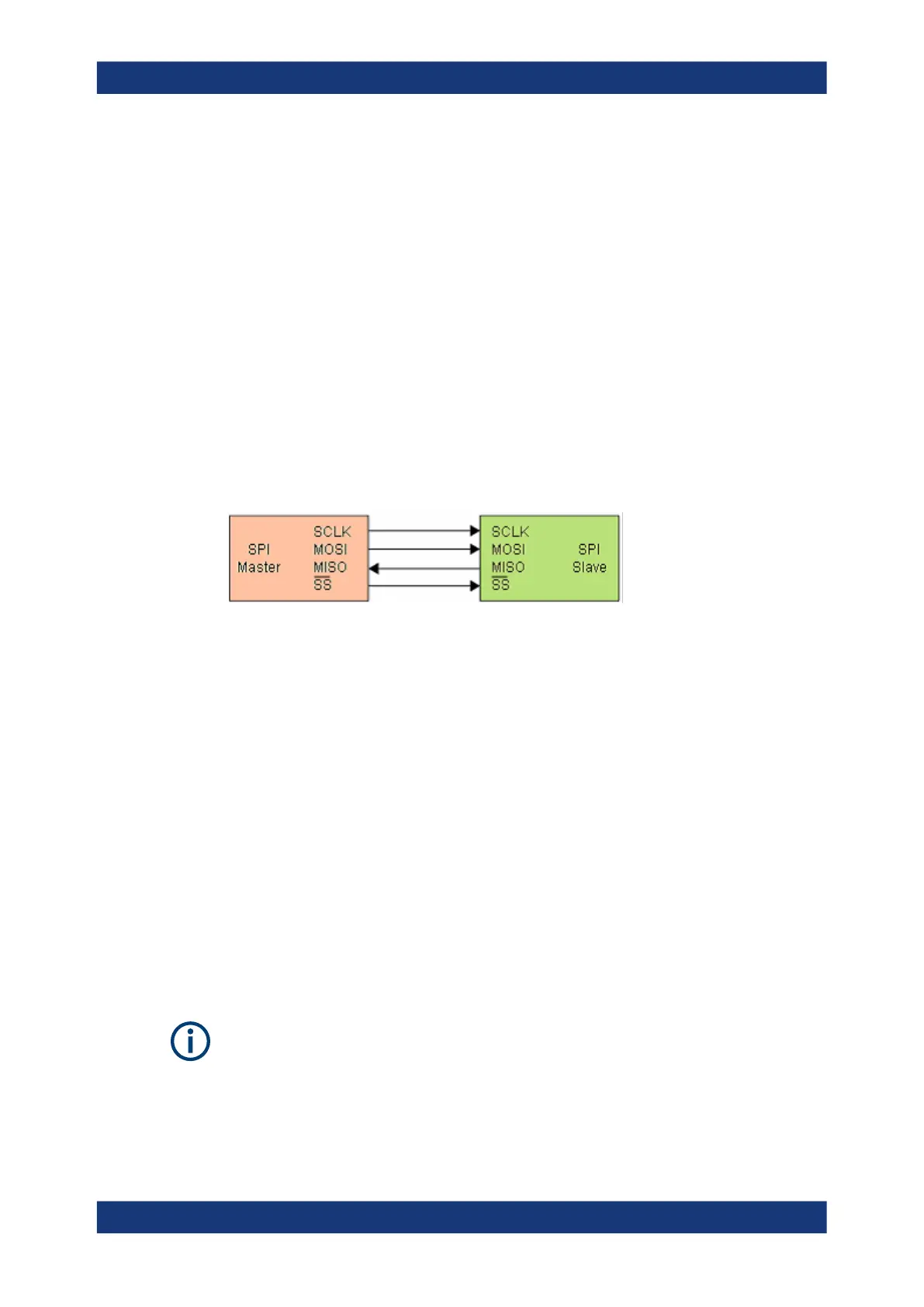
Most SPI buses have four lines, two data and two control lines:
●
Clock line to all slaves (SCLK)
●
Slave Select or Chip Select line (SS or CS)
●
Master data output, slave data input (MOSI or SDI)
●
Master data input, slave data output (MISO or SDO)
When the master generates a clock and selects a slave device, data may be transfer-
red in either or both directions simultaneously.
Figure 13-4: Simple configuration of SPI bus
The data bits of a message are grouped by following criteria:
●
A word contains a number of successive bits. The word length is defined in the pro-
tocol configuration.
●
A frame contains a number of successive words, at least one word.
For SPI buses, the R&S RTP provides the following trigger possibilities:
●
On frame start
●
On a serial pattern at a specified position
13.3.2 SPI configuration
13.3.2.1 SPI configuration settings
Access: [Protocol] > "Setup" tab > "Protocol" = SPI
Make sure that the tab of the correct serial bus is selected.
SPI bus (option R&S
RTP-K1)

 Loading...
Loading...











