DocID024597 Rev 5 1339/1830
RM0351 Universal synchronous asynchronous receiver transmitter (USART)
1411
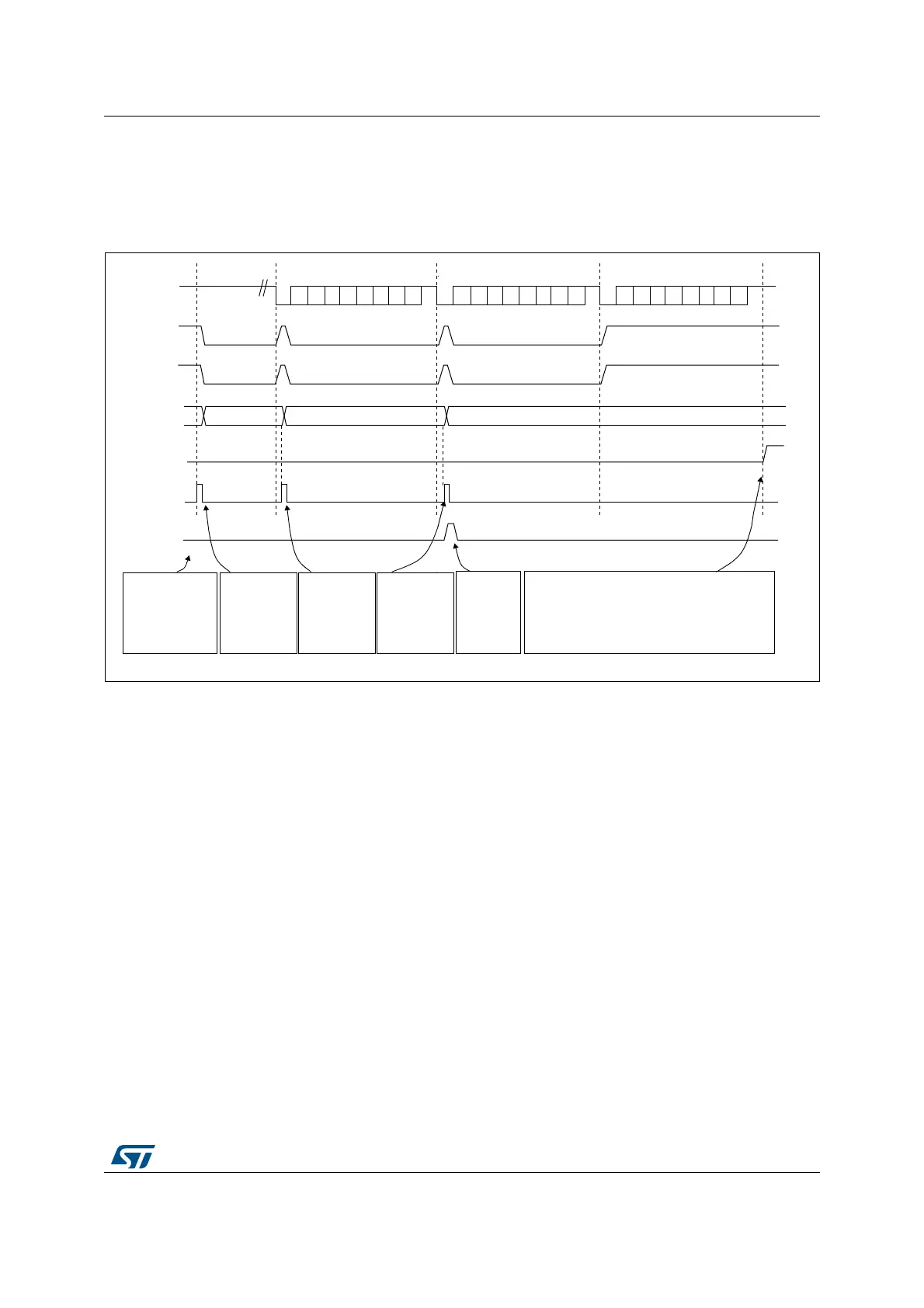
communication is complete. This is required to avoid corrupting the last transmission before
disabling the USART or entering Stop mode. Software must wait until TC=1. The TC flag
remains cleared during all data transfers and it is set by hardware at the end of transmission
of the last frame.
Figure 425. Transmission using DMA
Reception using DMA
DMA mode can be enabled for reception by setting the DMAR bit in USART_CR3 register.
Data is loaded from the USART_RDR register to a SRAM area configured using the DMA
peripheral (refer to Section 11: Direct memory access controller (DMA) on page 334)
whenever a data byte is received. To map a DMA channel for USART reception, use the
following procedure:
1. Write the USART_RDR register address in the DMA control register to configure it as
the source of the transfer. The data is moved from this address to the memory after
each RXNE event.
2. Write the memory address in the DMA control register to configure it as the destination
of the transfer. The data is loaded from USART_RDR to this memory area after each
RXNE event.
3. Configure the total number of bytes to be transferred to the DMA control register.
4. Configure the channel priority in the DMA control register
5. Configure interrupt generation after half/ full transfer as required by the application.
6. Activate the channel in the DMA control register.
When the number of data transfers programmed in the DMA Controller is reached, the DMA
controller generates an interrupt on the DMA channel interrupt vector.
) ))
AIB
6RIWZDUH
FRQILJXUHV'0$
WRVHQGGDWD
EORFNVDQG
HQDEOHV86$57
7KH'0$
WUDQVIHULV
FRPSOHWH
7&,) LQ
'0$B,65
'0$ZULWHV
)LQWR
86$57B7'5
'0$ZULWHV
)LQWR
86$57B7'5
'0$ZULWHV
)LQWR
86$57B7'5
6RIWZDUHZDLWVXQWLO7&
6HWE\KDUGZDUH
&OHDUHG
E\
VRIWZDUH
6HWE\
KDUGZDUH
7;OLQH
7;(IODJ
86$57B7'5
'0$UHTXHVW
'0$ZULWHV
86$57B7'5
'0$7&,)IODJ
WUDQVIHU
FRPSOHWH
7&IODJ
)UDPH
)UDPH
)UDPH
,GOHSUHDPEOH
6HWE\KDUGZDUH
FOHDUHGE\'0$UHDG
6HWE\KDUGZDUH
FOHDUHGE\'0$UHDG
6HWE\KDUGZDUH
,JQRUHGE\WKH'0$EHFDXVH
WKHWUDQVIHULVFRPSOHWH

 Loading...
Loading...