System window watchdog (WWDG) RM0351
1182/1830 DocID024597 Rev 5
The EWI interrupt is cleared by writing '0' to the EWIF bit in the WWDG_SR register.
Note: When the EWI interrupt cannot be served, e.g. due to a system lock in a higher priority task,
the WWDG reset will eventually be generated.
37.3.4 How to program the watchdog timeout
You can use the formula in Figure 373 to calculate the WWDG timeout.
Warning: When writing to the WWDG_CR register, always write 1 in the
T6 bit to avoid generating an immediate reset.
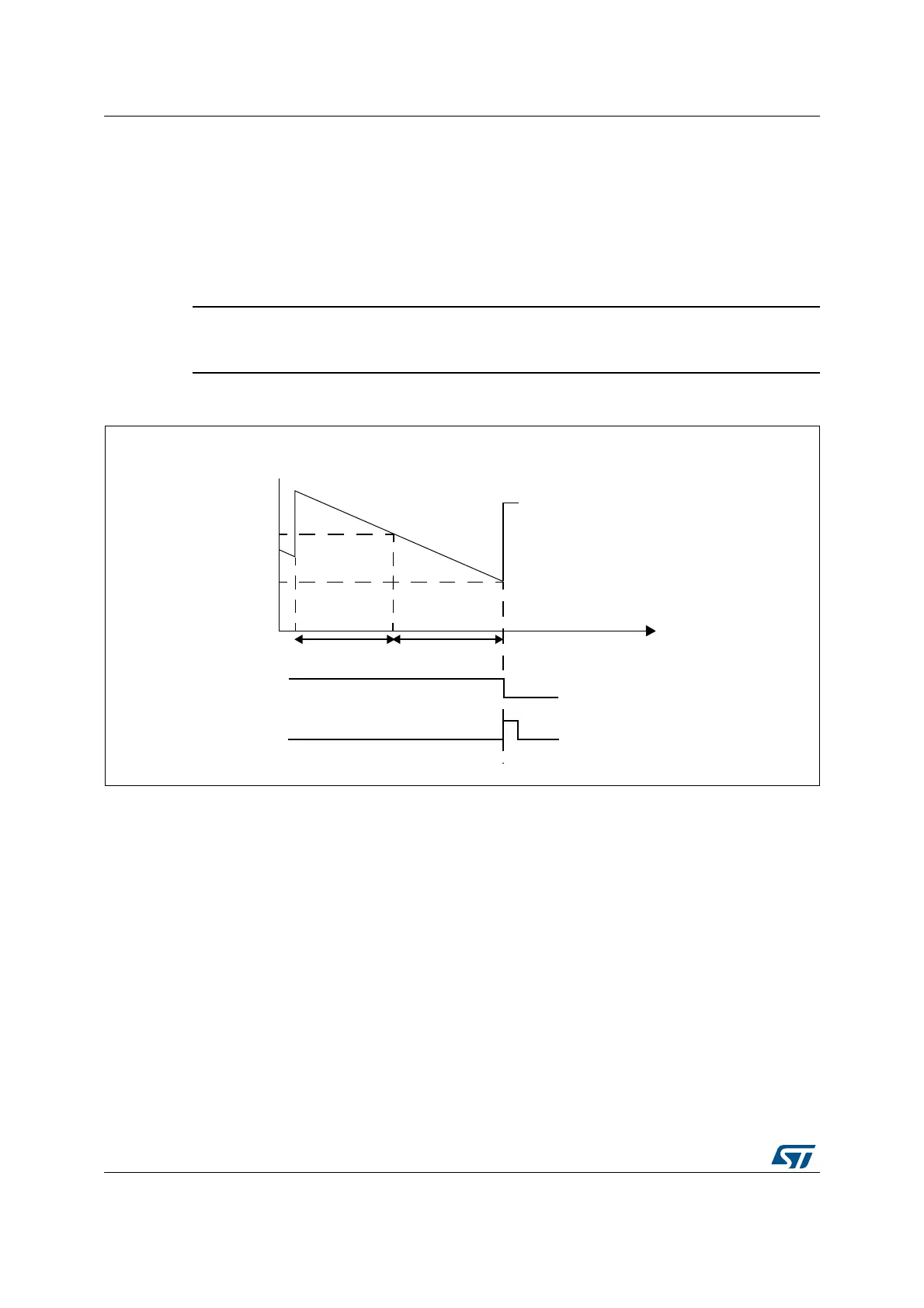
Figure 373. Window watchdog timing diagram
The formula to calculate the timeout value is given by:
where:
t
WWDG
: WWDG timeout
t
PCLK
: APB clock period measured in ms
4096: value corresponding to internal divider
As an example, lets assume APB frequency is equal to 48 MHz, WDGTB[1:0] is set to 3 and
T[5:0] is set to 63:
AIC
7;=
4;=#.4DOWNCOUNTER
2EFRESHNOTALLOWED
X&
2EFRESHALLOWED
4IME
4BIT
2%3%4
t
WWDG
t
PCLK
4096× 2
WDGTB[1:0]
× T5:0[]1+()×= ms()
t
WWDG
1 48000⁄ 4096× 2
3
× 63 1+()× 43.69 ms==

 Loading...
Loading...