Hash processor (HASH) RM0351
854/1830 DocID024597 Rev 5
SHA-1 (respectively SHA-256) algorithm
– 66 clock cycles for processing one 512-bit block of data using MD5 algorithm
• AHB slave peripheral, accessible through 32-bit word accesses only (else an AHB
error is generated)
• 8 × 32-bit words (H0 to H7) for output message digest
• Automatic data flow control with support of direct memory access (DMA) using one
channel. Fixed burst of 4 supported.
• Interruptible message digest computation, on a per-32-bit word basis
– Re-loadable digest registers
– Hashing computation suspend/resume mechanism, including using DMA
29.3 HASH functional description
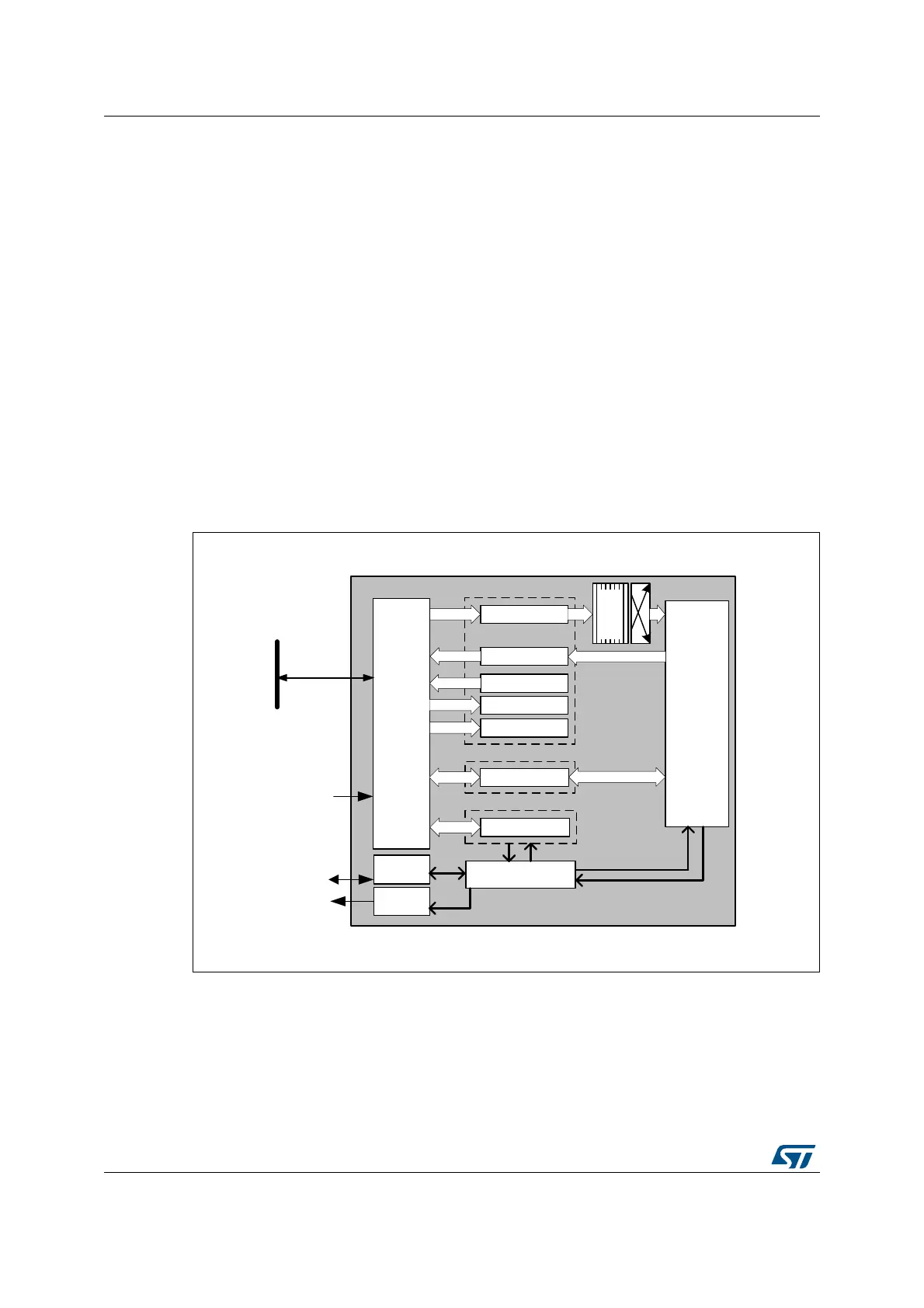
29.3.1 HASH block diagram
Figure 207 shows the block diagram of the hash processor.
Figure 207. HASH block diagram
29.3.2 HASH internal signals
Table 180 describes a list of useful to know internal signals available at HASH level, not at
product level (on pads).
06Y9
%DQNHG5HJLVWHUVPDLQ
+$6+B&5
+$6+
&RUH
6+$
6+$
6+$
0'
+0$&
ORJLF
+$6+B65
$+%
LQWHUIDFH
FRQWURO
VWDWXV
+$6+B',1
GDWDNH\
+$6+B+[
UHVXOW
&RQWURO/RJLF
VZDSSLQJ
%DQNHG5HJLVWHUV,54
&5<3B,05
[ELW
,1),)2
'0$
LQWHUIDFH
GLJHVW
+$6+B675
VWDUW
%DQNHG5HJLVWHUVFRQWH[WVZDSSLQJ
+$6+B&65[
&RQWH[WVZDS
KDVKBLW
KDVKBKFON
,54
LQWHUIDFH
ELW$+%EXV
KDVKBLQBGPD

 Loading...
Loading...