RM0008 Serial peripheral interface (SPI)
547/690
Figure 207. Single master/ single slave application
1. Here, the NSS pin is configured as an input.
The MOSI pins are connected together and the MISO pins are connected together. In this
way data is transferred serially between master and slave (most significant bit first).
The communication is always initiated by the master. When the master device transmits
data to a slave device via the MOSI pin, the slave device responds via the MISO pin. This
implies full-duplex communication with both data out and data in synchronized with the
same clock signal (which is provided by the master device via the SCK pin).
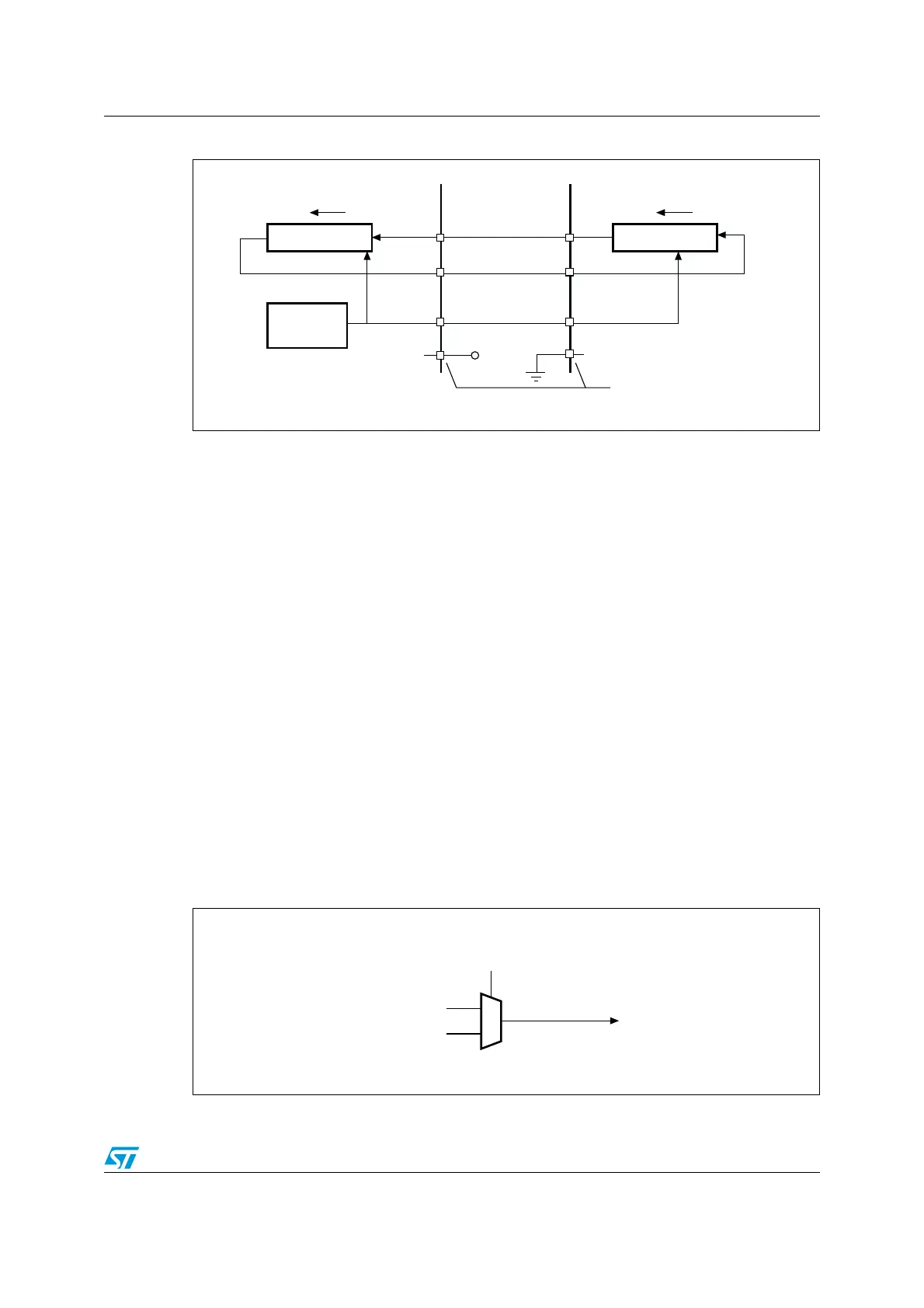
Slave select (NSS) pin management
There are two NSS modes:
● Software NSS mode: this mode is enabled by setting the SSM bit in the SPI_CR1
register (see Figure 208). In this mode, the external NSS pin is free for other
application uses and the internal NSS signal level is driven by writing to the SSI bit in
the SPI_CR1 register.
● Hardware NSS mode: there are two cases:
– NSS output is enabled: when the STM32F10xxx is operating as a Master and the
NSS output is enabled through the SSOE bit in the SPI_CR2 register, the NSS pin
is driven low and all the NSS pins of devices connected to the Master NSS pin see
a low level and become slaves when they are configured in NSS hardware mode.
In this case, the cell cannot work in a multimaster environment.
– NSS output is disabled: the multimaster capability is allowed.
Figure 208. Hardware/software slave select management
8-bit shift register
SPI clock
generator
8-bit shift register
MISO
MOSI MOSI
MISO
SCK SCK
SlaveMaster
NSS
(1)
NSS
(1)
V
DD
MSBit LSBit MSBit LSBit
Not used if NSS is managed
by software
ai14745
1
0
NSS Internal
SSM bit
SSI bit
NSS external pin
ai14746

 Loading...
Loading...