Execution Pipeline 2-9
18524C/0—Nov1996 AMD-K5 Processor Technical Reference Manual
dependencies are resolved using forwarding at all execution
units. Antidependencies (in which later instructions produce a
value that overwrites one used by an earlier instruction) are
removed automatically by buffering operands—or tags that
point to operands—at reservation stations. Output dependen-
cies (in which later instructions must be seen by software to
complete after earlier instructions in order to leave the correct
value in a register) are resolved by the reorder buffer.
Reservation stations are supplied with operands over eight 41-
bit operand buses. Execution results are sent to the reorder
buffer (ROB) over five 41-bit result buses. Tags forwarded to
the execution units represent results to watch for on one of the
result buses.
No special compiler optimizations are required for high-perfor-
mance execution on the AMD-K5 processor.
Integer/Shift Units Two ALUs perform integer, logic, and shift operations. Both
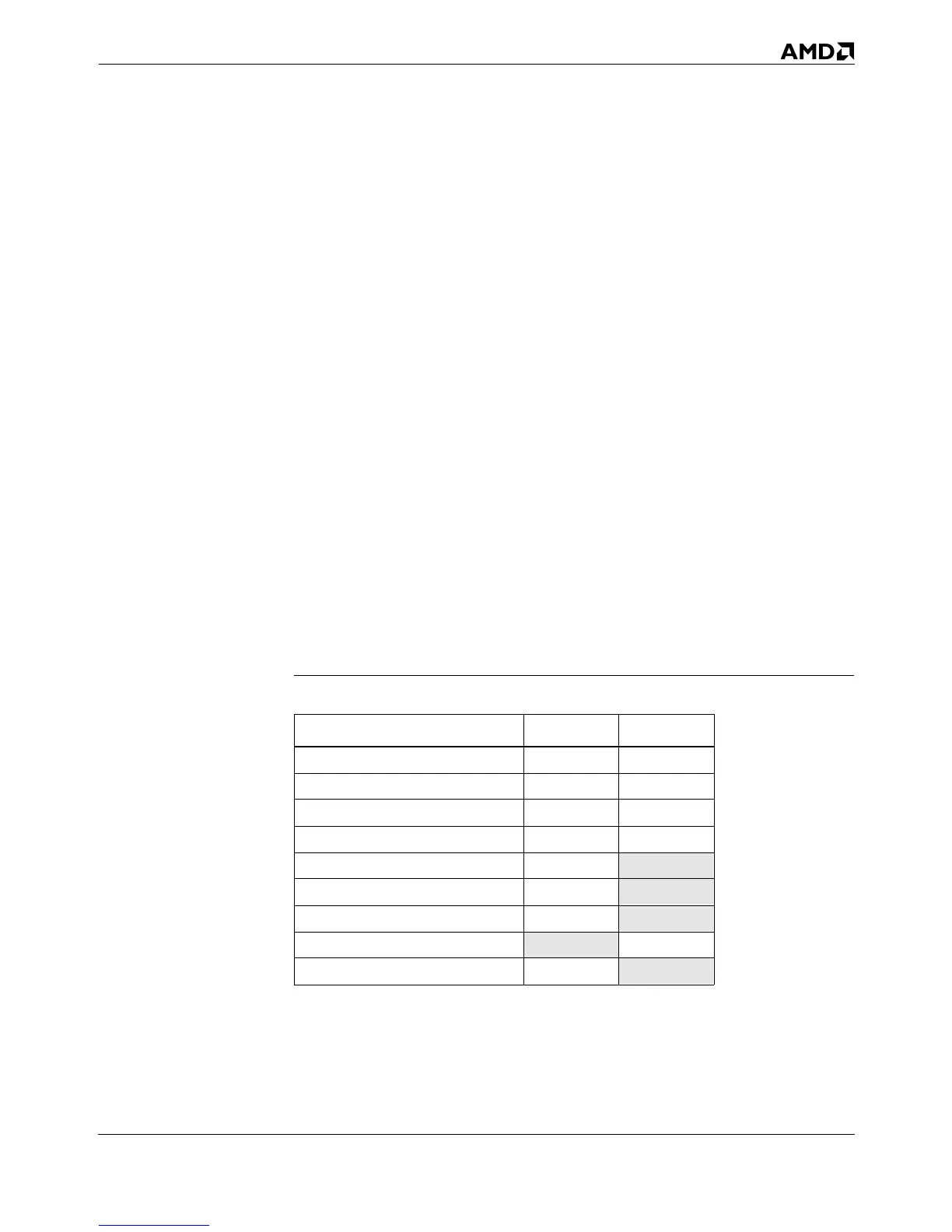
ALUs have two-entry reservation stations. Table 2-1 shows the
types of ROPs executed by each ALU. Unlike the Pentium pro-
cessor, the AMD-K5 processor has few restrictions on the pair-
ing of integer instructions needed to use both integer units in
parallel.
Table 2-1. ALU Instruction Classes
Instruction Class ALU0 ALU1
Addition Yes Yes
Subtraction Yes Yes
Logical Yes Yes
Compare Yes Yes
Packed BCD Yes
No
Unpacked BCD Yes
No
Special (ADDC, SUBB) Yes
No
Shift
No Yes
Divide Yes
No
 Loading...
Loading...