Signal Descriptions 5-51
18524C/0—Nov1996 AMD-K5 Processor Technical Reference Manual
CACHE is not asserted for the following types of memory reads
(M/IO =1):
■ Locked reads (that is, while LOCK is asserted)
■ TLB reads
■ Any read with PCD asserted (PCD is a factor in determining
the state of CACHE)
On the 486 processor, by comparison, the CACHE output does
not exist, but the BLAST output (in conjunction with KEN)
serves to determine cacheability. Although bursts are typically
four 32-bit transfers on the 486 processor, they can be longer
with narrower-width memories.
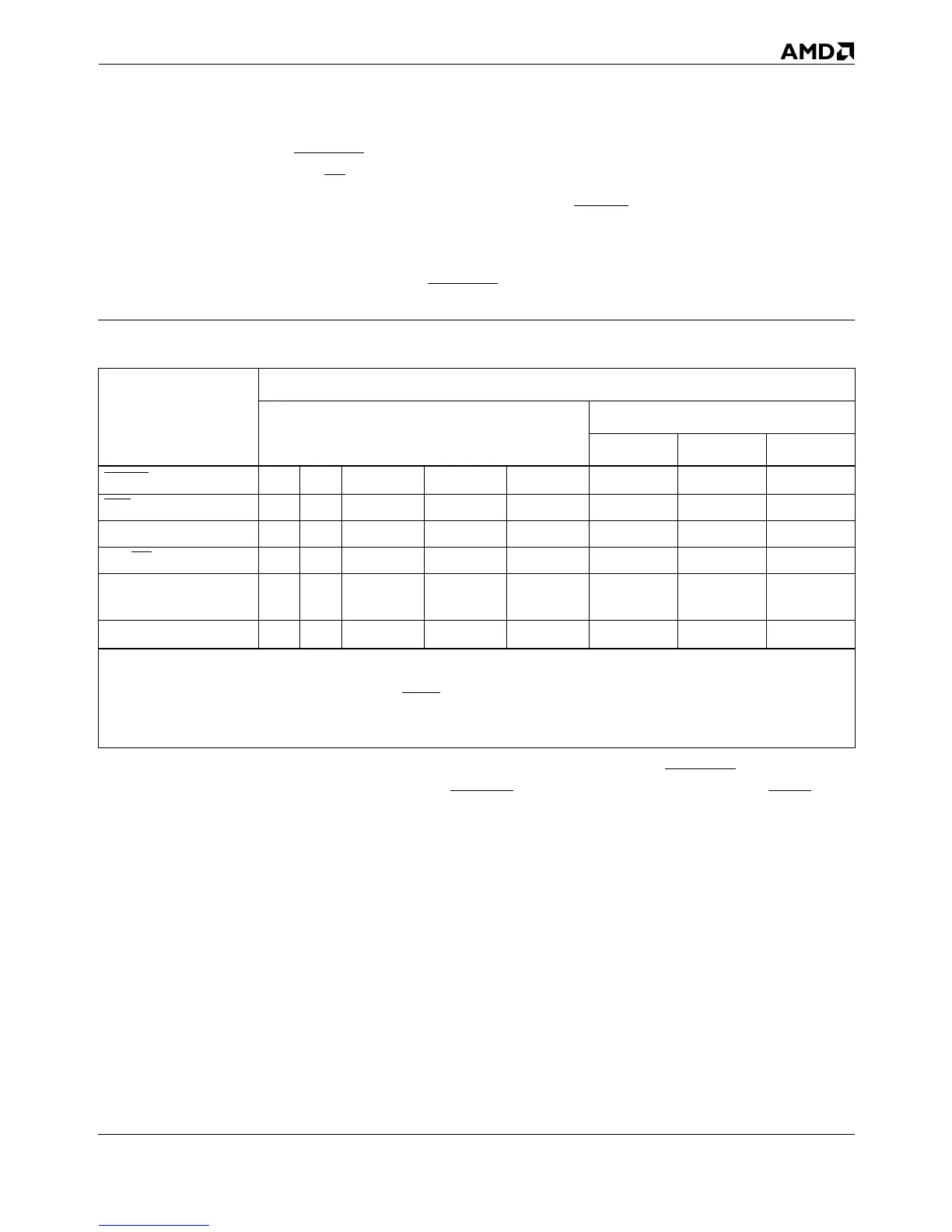
Table 5-9. MESI-State Transitions for Reads
Signal or Event
Result of Cache Lookup
Read Miss
Read Hit
shared exclusive modified
CACHE
, PCD
1
1 —000———
KEN
—1000———
PWT ——1—0———
WB/WT
———01———
Cache Line Fill
(32 bytes)
no no yes yes yes no no no
State After Read
2
—— shared shared exclusive shared exclusive modified
Notes:
— Don’t care or not applicable.
1. The PCD bit is one determinant of the state of CACHE
.
2. Transition occurs after any line fill. Lines in “shared” MESI state are said to be in “writethrough” state. Those in “exclusive” or “mod-
ified” MESI states are said to be in “writeback” state.
 Loading...
Loading...