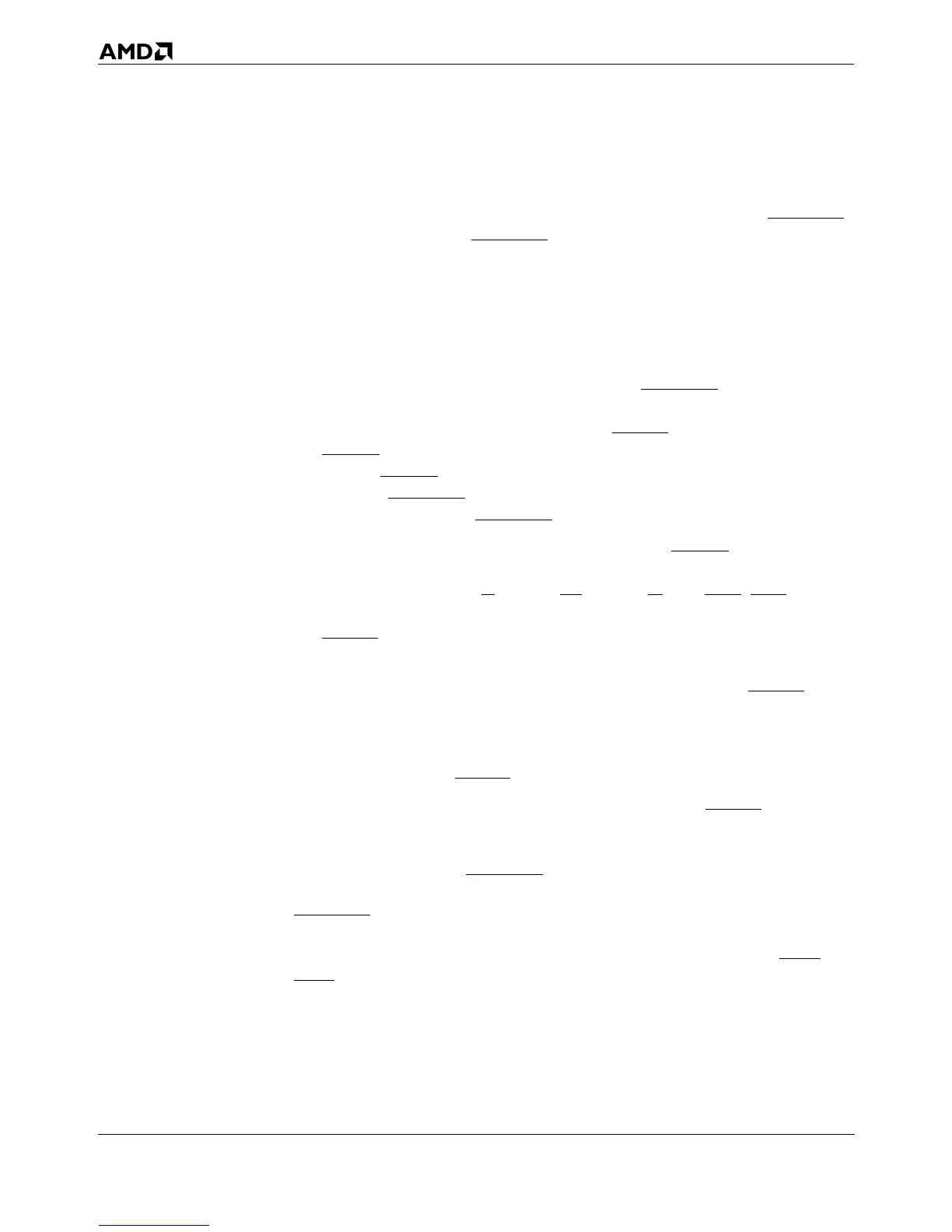5-192 Bus Interface
AMD-K5 Processor Technical Reference Manual 18524C/0—Nov1996
Stop-Grant and Stop-
Clock States
Figure 5-27A and Figure 5-27B show the processor’s transition
from normal execution to the Stop-Grant state, then to the
Stop-Clock state, and finally back to normal execution. The
series of transitions begins when system logic asserts STPCLK.
Upon recognizing a STPCLK interrupt at the next instruction-
retirement boundary, the processor performs the following
actions, in the order shown:
1. Flush Pipeline—The processor invalidates all instructions
remaining in the pipeline. This is not visible on the bus.
2. Complete In-Progress Cycle—If the processor had begun a
bus cycle or locked operation when STPCLK was asserted,
the processor completes the bus cycle and waits until the
system asserts the last expected BRDY and also asserts
EWBE. If no bus cycle is in progress, system logic must
assert EWBE at the same time as, or at sometime after, it
asserts STPCLK. In Figure 5-27A, a burst read is shown
completing after STPCLK is asserted.
3. Stop-Grant Cycle—After sampling both EWBE asserted, the
processor drives a Stop-Grant special bus cycle. This cycle
is identified by D/C = 0, M/IO = 0, W/R = 1, BE7–BE0 = FBh
and A31–A3 = 10h. System logic must respond by asserting
BRDY. This is visible on the bus, near the middle of Figure
5-27A.
4. Stop Internal Clock—When system logic returns BRDY for
the Stop-Grant special bus cycle, the processor stops its
internal clock and floats D63–D0 and DP7–DP0. This is on
the bus between Figure 5-27A and Figure 5-27B immedi-
ately after the BRDY of the Stop-Grant special bus cycle.
5. (Optional) Stop Bus Clock—After returning BRDY in
response to the Stop-Grant special bus cycle, power-man-
agement logic can transition to the Stop-Clock state by stop-
ping CLK while STPCLK is held asserted.
STPCLK must be held asserted throughout the Stop-Grant and
(if entered) Stop-Clock states.Figure 5-27B shows the processor
resuming normal execution after system logic negates STP-
CLK.
For details on clock control, see Section 6.4 on page 6-33.
 Loading...
Loading...