5-180 Bus Interface
AMD-K5 Processor Technical Reference Manual 18524C/0—Nov1996
5.4.6 Special Bus Cycles
The processor drives D/C =0, M/IO= 0, and W/R = 1 to define a
special bus cycle. The values of these cycle-definition signals
are the same for all special cycles. Only BE7–BE0 and A31–A3
differentiate among the special cycles, as shown in Table 5-23.
This function of BE7–BE0 bears no relationship to the D63–D0
data bus. It is particularly apparent in the case of the branch-
trace message special bus cycle, during which the value of
BE7–BE0 is DFh (1101_1111b) but, in contradiction to the byte-
enable bits, the four bytes on D31–D0 carry valid data during
both cycles of the operation. During the first cycle, D31–D0
carries the EIP value of the source (branch) instruction. Dur-
ing the second cycle, D31–D0 carries the EIP value of the
branch-target instruction.
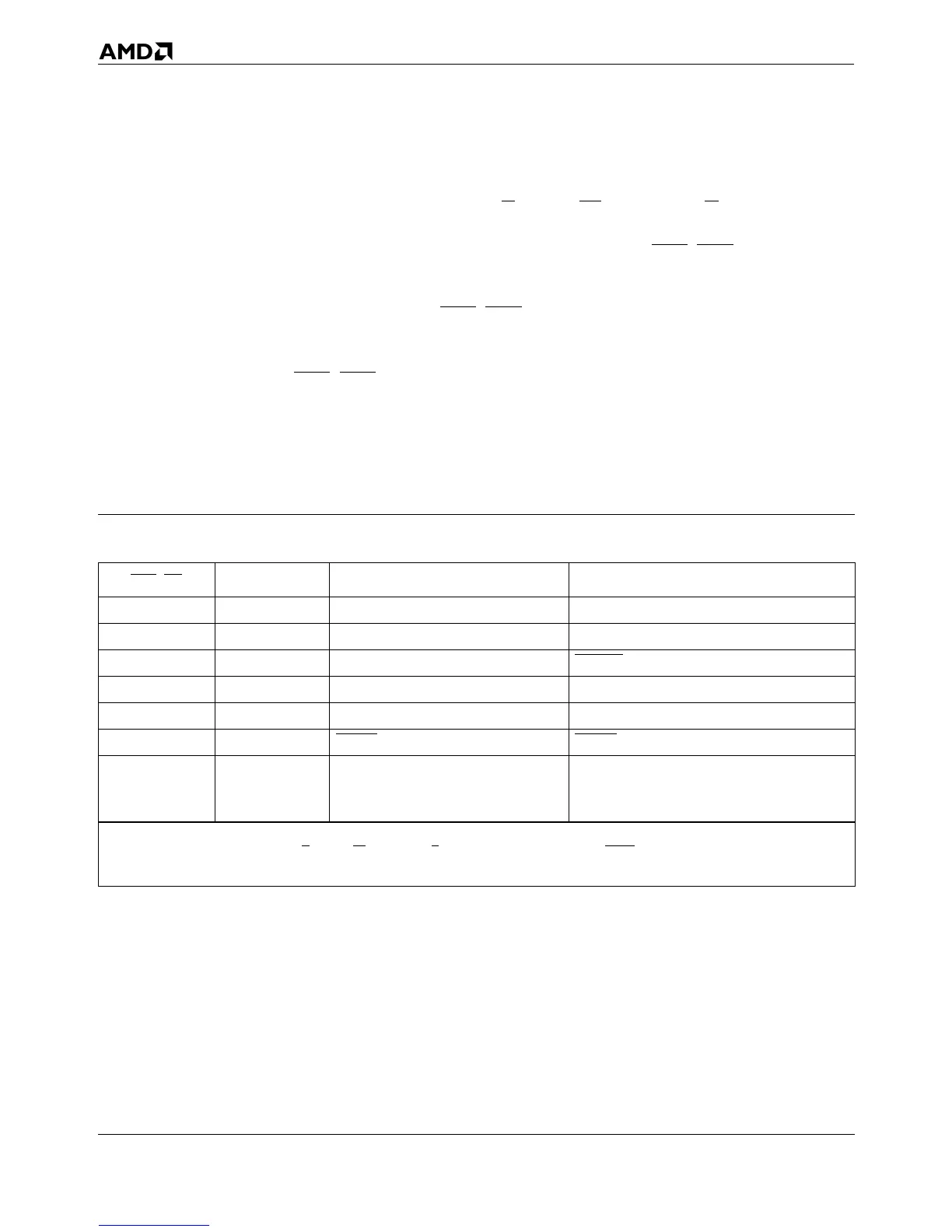
Table 5-23. Encodings For Special Bus Cycles
BE7–B0 A31–A3
Special Bus Cycle
1
Cause
FEh ...00h Shutdown Triple fault
FDh ...00h Cache Invalidation INVD instruction
FBh ...10h Stop Grant STPCLK
FBh ...00h Halt HLT instruction
F7h ...00h Cache Writeback and Invalidation WBINVD instruction
EFh ...00h FLUSH
Acknowledge FLUSH
DFh ...00h
Branch-Trace Message
2
Bit 5 = 1 and bits 3–1 = 001 in the hardware
configuration register (HWCR). See Section
7.1 on page 7-3 for details.
Notes:
1. For all special bus cycles, D/C = 0, M/IO = 0 and W/R = 1. System logic must return BRDY in response to this cycle.
2. The message in a branch-trace message special bus cycle is different in the AMD-K5 and Pentium processors.
 Loading...
Loading...