7-18 Test and Debug
AMD-K5 Processor Technical Reference Manual 18524C/0—Nov1996
7.7 Functional-Redundancy Checking
If FRCMC is asserted at RESET, the processor enters Func-
tional-Redundancy Checking mode as the checker, and reports
checking errors on the IERR output. If FRCMC is negated at
RESET, the processor operates normally, although it also
behaves as the master in a functional-redundancy checking
arrangement with a checker.
In the Functional-Redundancy Checking mode, two processors
have their signals tied together. One processor (the master)
operates normally. The other processor (the checker) has its
output and bidirectional signals (except for TDO and IERR)
floated to detect the state of the master’s signals. The master
controls instruction fetching and the checker mimics its behav-
ior by sampling the fetched instructions as they appear on the
bus. Both processors execute the instructions in lock step. The
checker compares the state of the master’s output and bidirec-
tional signals with the state that the checker itself would have
driven for the same instruction stream.
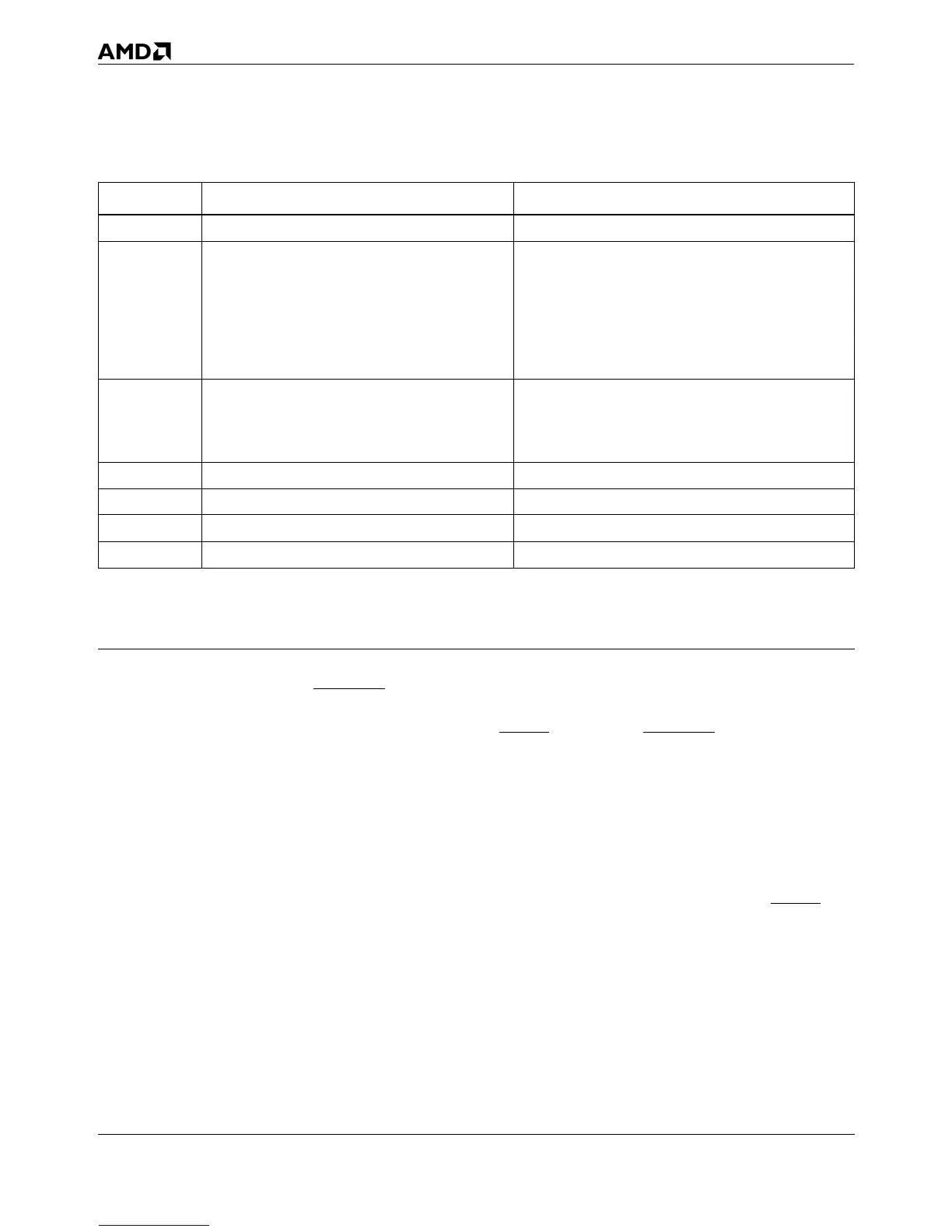
Table 7-4. Branch-Trace Message Special Bus Cycle Fields
Signals First Special Bus Cycle Second Special Bus Cycle
A31 0 = first special bus cycle (source) 1 = second special bus cycle (target)
A30–A29 not valid
Operating Mode of Target:
11 = Virtual-8086 Mode
10 = Protected Mode
01 = not valid
00 = Real Mode
A28 not valid
Default Operand Size of Target Segment:
1 = 32-bit
0 = 16-bit
A27–A20 0 0
A19–A4 Code Segment (CS) selector of Branch Source. Code Segment (CS) selector of Branch Target.
A3 0 0
D31–D0 EIP of Branch Source. EIP of Branch Target.

 Loading...
Loading...