142
20. Sequence Function
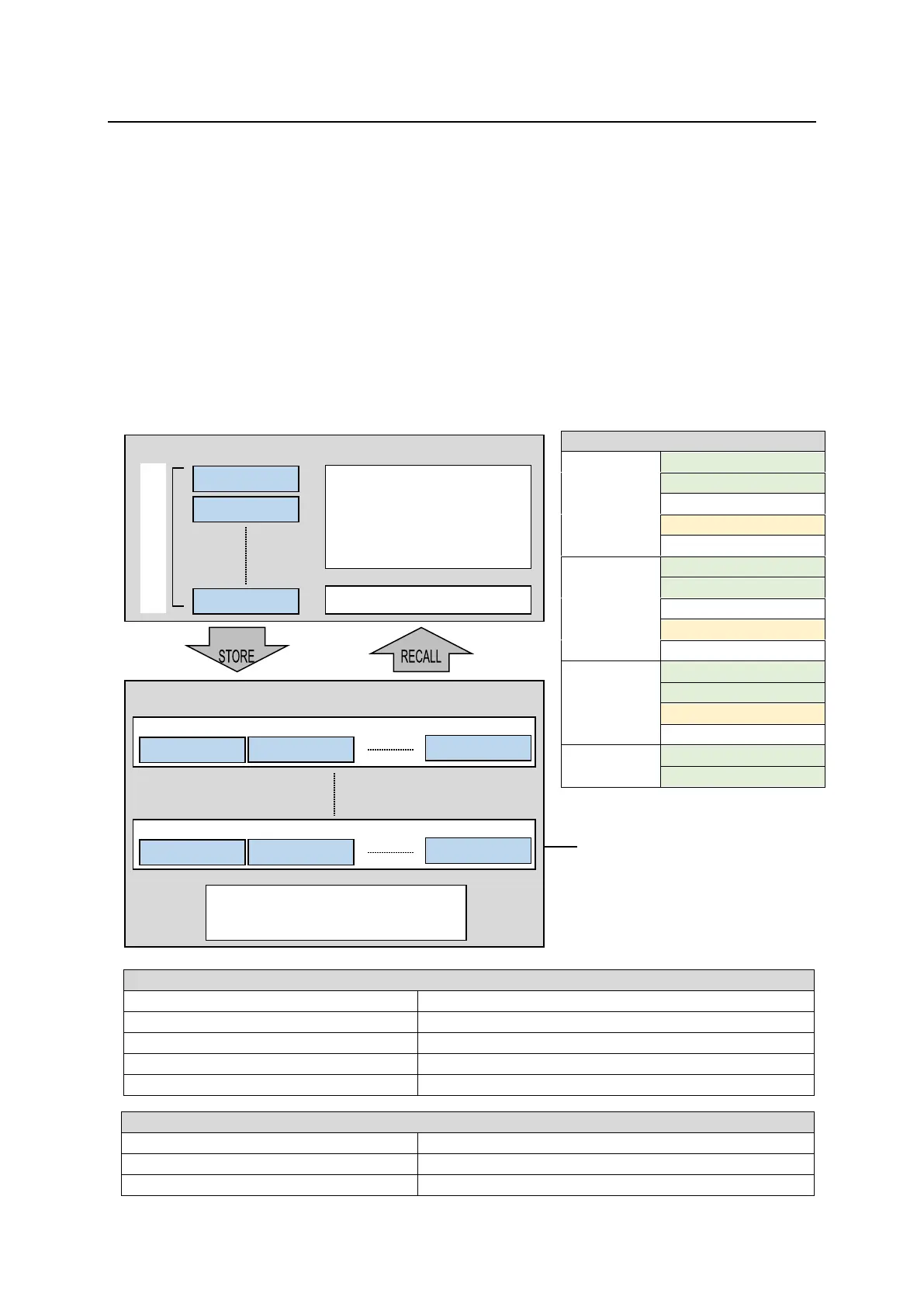
A sequence is a function for joining individual images into a sequential video and recalling it for playback
in a single operation. Each sequence is composed of video frames called steps. To make sequences,
create an initial step and save it to the sequence working memory, then create the next step and to save
to the working memory and so on. Although the sequence data saved in the working memory is cleared
and lost when the switcher is powered off, it can be kept and recalled by storing it to sequence memory.
Up to 30 sequences (20 steps at most for each bus) can be saved to sequence memory. Sequence data
can also be backed up to SD cards and loaded to the switcher from SD cards. (See Sec. 22. “File
Operations.”)
Note that the sequence data is not a sequential video itself but a series of states on the control panel as
of when the images were saved as steps. Therefore, the images that are displayed on the monitor during
sequence playback may be different from those that appeared when the sequence was stored, if the
input videos were different. However, the switch timings and 3D effects such as picture-in-picture
display will remain the same.
The flow diagram below shows the basic series of sequence operations.
Available functions and data
Functions and Information Available for Sequence Control
XPT information for each bus
Bus Matte color information
Transition type settings for each bus
Transition direction settings
PGM output bus information
Pattern number settings of bus assignments
Functions and Information Not Available for Sequence Control
USER TRANS and ADV CTRL settings in the TRANS menu
20 steps at most for each bus
Clearing working memory
Creating sequences
Editing sequences
(Add / delete / overwrite steps)
Playback and playback settings
Sequence memory operations:
Overwrite protection
Memory clear
 Loading...
Loading...