Analog-to-digital converters (ADC) RM0440
664/2126 RM0440 Rev 4
If the TROVS bit is set, the content of the DISCEN bit is ignored and considered as 1.
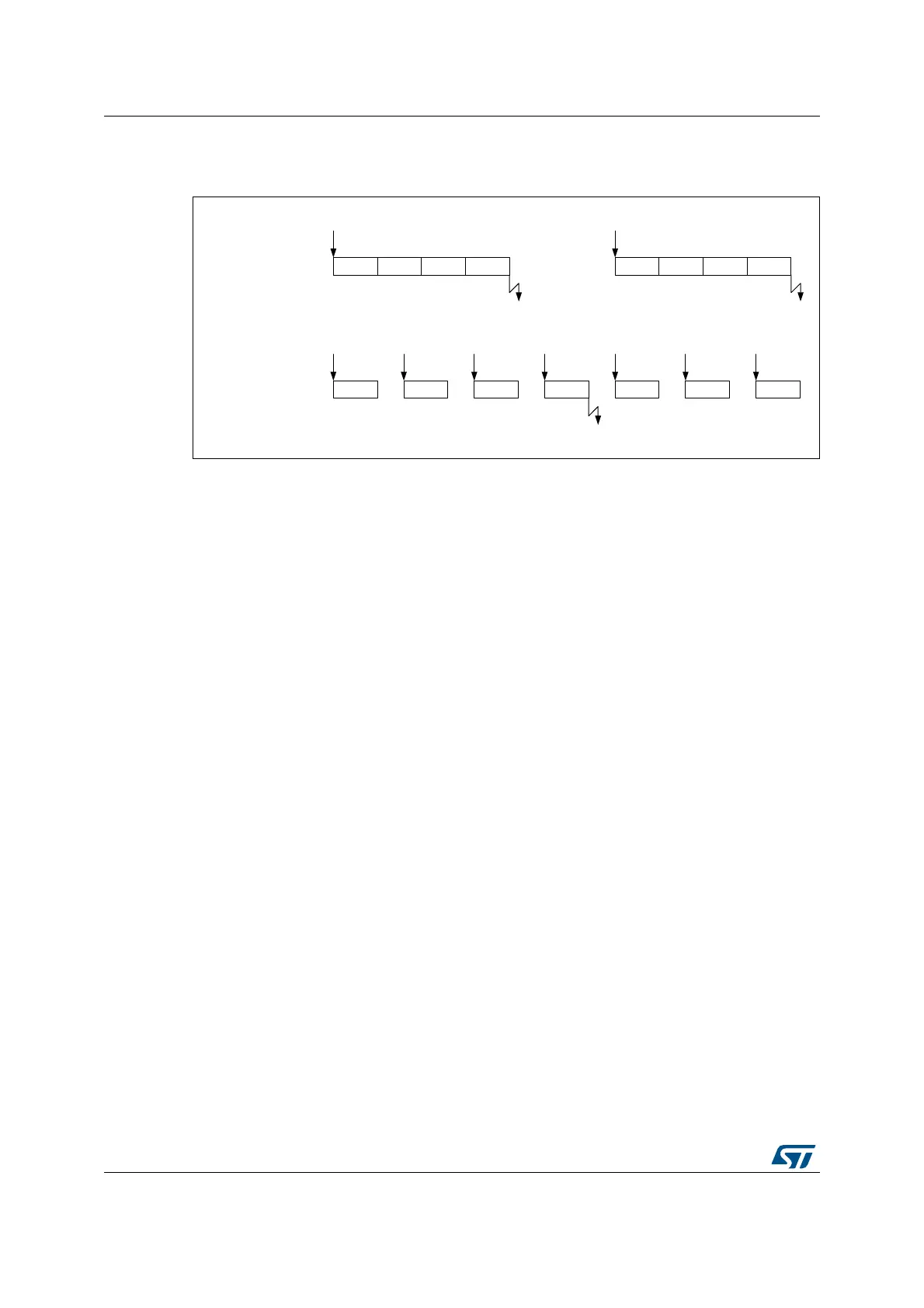
Figure 132. Triggered regular oversampling mode (TROVS bit = 1)
Injected and regular sequencer management when oversampling
In oversampling mode, it is possible to have differentiated behavior for injected and regular
sequencers. The oversampling can be enabled for both sequencers with some limitations if
they have to be used simultaneously (this is related to a unique accumulation unit).
Oversampling regular channels only
The regular oversampling mode bit ROVSM defines how the regular oversampling
sequence is resumed if it is interrupted by injected conversion:
• In continued mode, the accumulation restarts from the last valid data (prior to the
conversion abort request due to the injected trigger). This ensures that oversampling
will be completed whatever the injection frequency (providing at least one regular
conversion can be completed between triggers);
• In resumed mode, the accumulation restarts from 0 (previous conversions results are
ignored). This mode allows to guarantee that all data used for oversampling were
converted back-to-back within a single timeslot. Care must be taken to have a injection
trigger period above the oversampling period length. If this condition is not respected,
the oversampling cannot be completed and the regular sequencer will be blocked.
The Figure 133 gives examples for a 4x oversampling ratio.
MS34455V2
Ch(N)
3
Trigger
CONT=0
DISCEN = 1
TROVS = 0
Ch(N)
2
Ch(N)
1
Ch(N)
0
Ch(N)
3
Trigger
Ch(N)
2
Ch(N)
1
Ch(N)
0
Ch(N)
2
Trigger
Ch(N)
1
Trigger
Ch(N)
0
Trigger
Ch(N)
3
Trigger
Ch(N)
2
Trigger
Ch(N)
1
Trigger
Ch(N)
0
Trigger
CONT=0
DISCEN = 1
TROVS = 1
EOC flag set
EOC flag set

 Loading...
Loading...