6-3
DS35-W00 May. 2007
CLUTCHCLUTCH
CLUTCHCLUTCH
CLUTCH
TRANSMISSIONTRANSMISSION
TRANSMISSIONTRANSMISSION
TRANSMISSION
ENGINEENGINE
ENGINEENGINE
ENGINE
HSTHST
HSTHST
HST
FRONT AXLEFRONT AXLE
FRONT AXLEFRONT AXLE
FRONT AXLE
STEERINGSTEERING
STEERINGSTEERING
STEERING
BARKEBARKE
BARKEBARKE
BARKE
ELECTRICELECTRIC
ELECTRICELECTRIC
ELECTRIC
INDEXINDEX
INDEXINDEX
INDEX
HYDRAULICHYDRAULIC
HYDRAULICHYDRAULIC
HYDRAULIC
GENERALGENERAL
GENERALGENERAL
GENERAL
REAR AXLEREAR AXLE
REAR AXLEREAR AXLE
REAR AXLE
CK22/CK22H
2. OPERATING PRINCIPLE
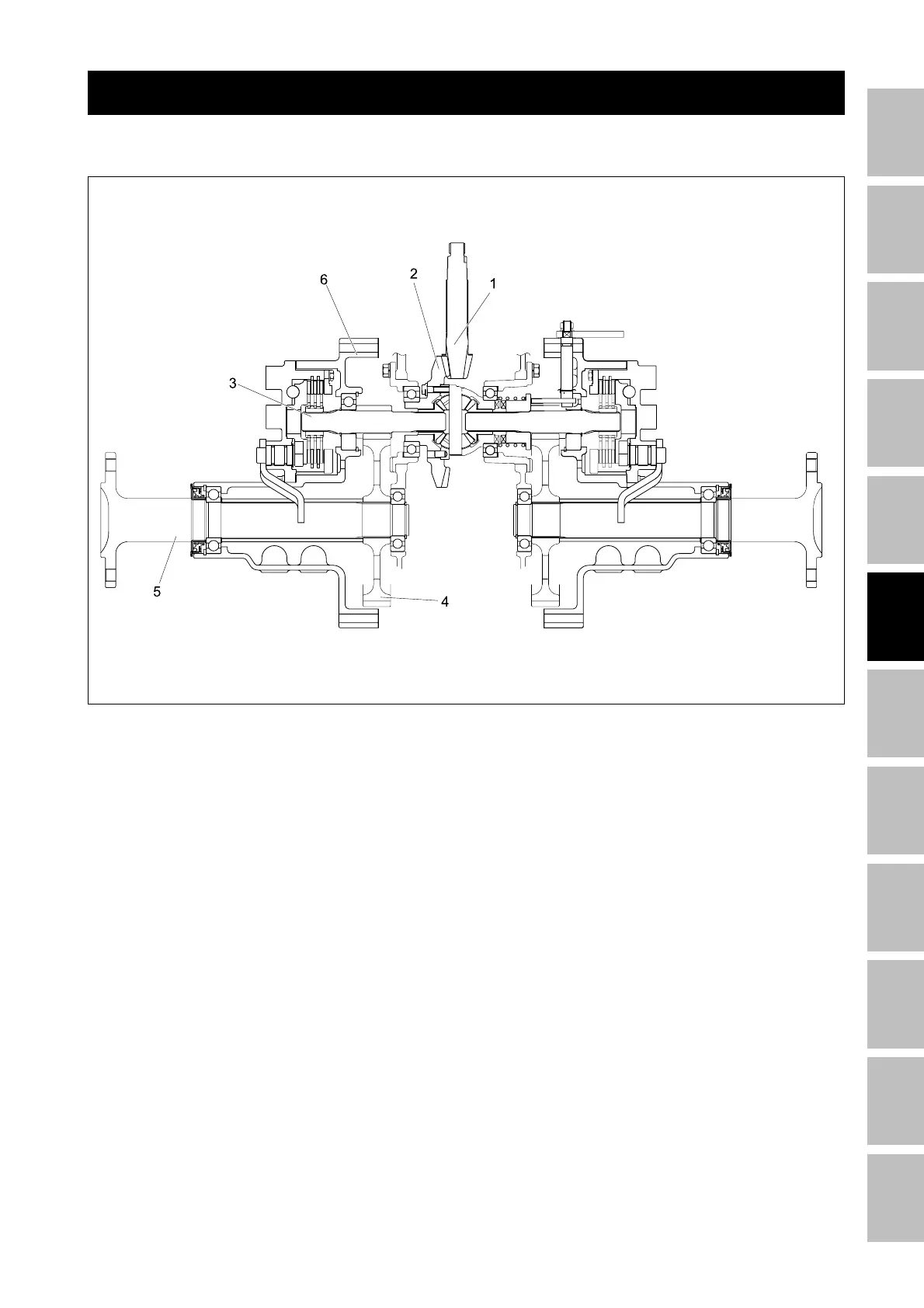
The rear axle is the final mechanism which transmits
power from the transmission to the rear wheels. The
shaft speed, controlled by the transmission, is further
reduced to approx. 1/6.16 (6T/37T) by the spiral bevel
pinion (1) and spiral bevel gear (2), and then reduced
to 1/6.54 (11T/72T) by the 11 gear shaft (3) and 72T
spur gear (4). As a result, its speed is reduced to approx.
1/40.3 before being transmitted to the rear wheels.
The rear axle is semifloating type will ball bearings
between the rear axle (5) and rear axle case (6), which
supports the rear wheel load as well as transmitting
power to the rear wheels.
The differential automatically controls the revolution of
right and left wheel when the rear wheels encounter
unequal road resistance during turning.
(1) Spiral bevel pinion
(2) Spiral bevel gear
(3) 11 gear shaft
(4) 72T spur gear
(5) Rear axle
(6) Rear axle case
196W501A
2.1 POWER TRAIN
REAR AXLE - OPERATING PRINCIPLE
 Loading...
Loading...











