RM0453 Rev 5 641/1450
RM0453 True random number generator (RNG)
646
22.4 RNG interrupts
In the RNG an interrupt can be produced on the following events:
• Data ready flag
• Seed error, see
Section 22.3.7: Error management
• Clock error, see
Section 22.3.7: Error management
Dedicated interrupt enable control bits are available as shown in Table 130.
The user can enable or disable the above interrupt sources individually by changing the
mask bits or the general interrupt control bit IE in the RNG_CR register. The status of the
individual interrupt sources can be read from the RNG_SR register.
Note: Interrupts are generated only when RNG is enabled.
22.5 RNG processing time
In recommended configuration A described in Table 131, the time between two sets of four
32-bit data is either:
• 206 x N AHB cycles if f
AHB
< f
threshold
(conditioning stage is limiting), or
• 128 x N RNG cycles f
AHB
≥ f
threshold
(noise source stage is limiting).
With f
threshold
= 1.6 x f
RNG
, for instance 77 MHz if f
RNG
= 48 MHz.Value N is 2.
Note: When CLKDIV is different from zero, f
RNG
must take into account the internal divider ratio.
If configuration B is selected the performance figures become:
• 206 AHB cycles if f
AHB
< f
threshold
or
• 32 RNG cycles f
AHB
≥ f
threshold
with f
threshold
= 6.5 x f
RNG
.
22.6 RNG entropy source validation
22.6.1 Introduction
In order to assess the amount of entropy available from the RNG, STMicroelectronics has
tested the peripheral using the German BSI AIS-31 statistical tests (T0 to T8), and NIST
SP800-90B test suite. The results can be provided on demand or the customer can
reproduce the tests.
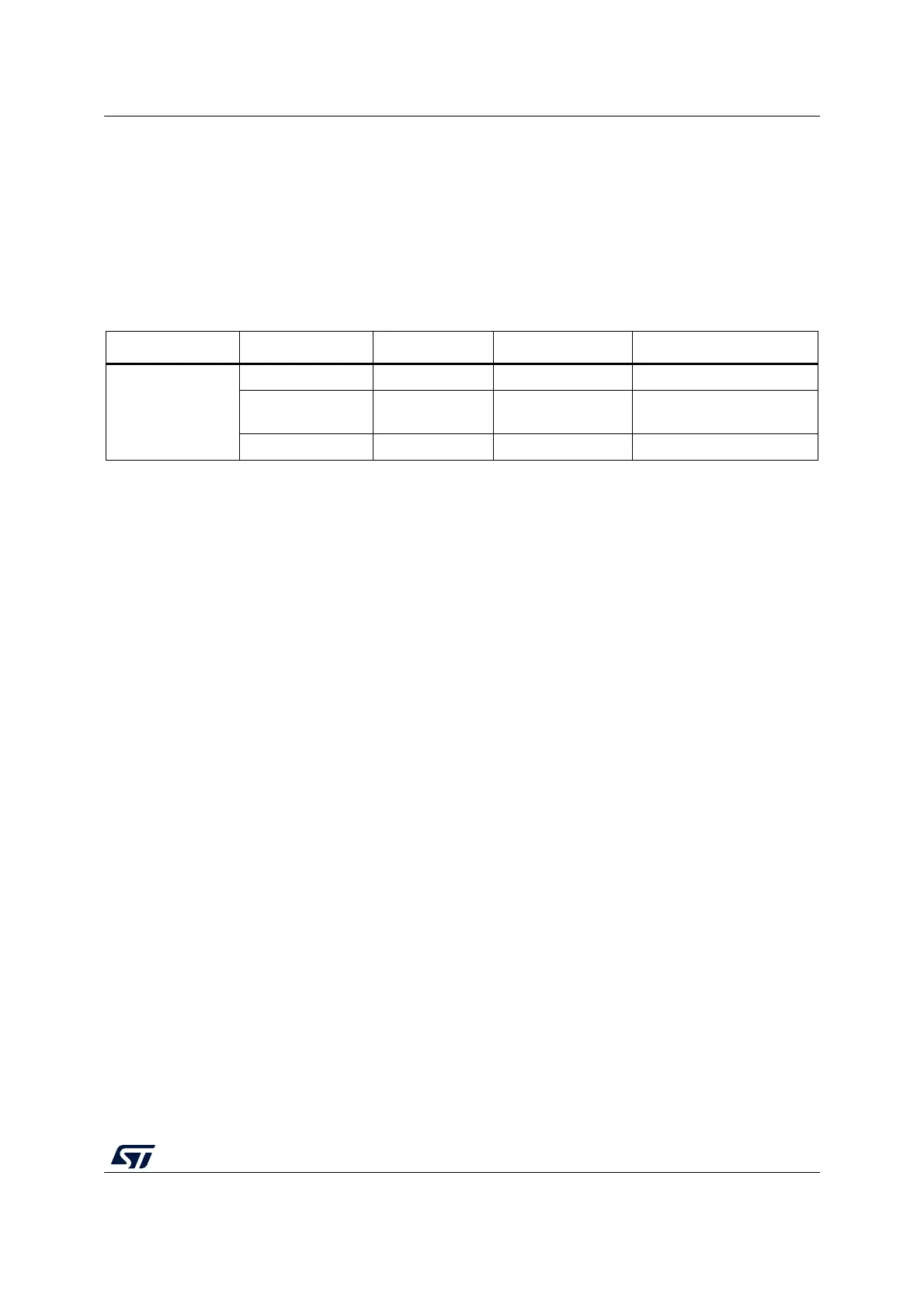
Table 130. RNG interrupt requests
Interrupt acronym Interrupt event Event flag Enable control bit Interrupt clear method
RNG
Data ready flag DRDY IE None (automatic)
Seed error flag SEIS IE
Write 0 to SEIS or write
CONDRST to 1 then to 0
Clock error flag CEIS IE Write 0 to CEIS
 Loading...
Loading...