Model 2601B-PULSE System SourceMeter Instrument Reference Manual Section 4: Sourcing and measuring
2601B-PULSE-901-01A April 2020 4-81
Understanding source settling times
Each 2601B-PULSE can drive up to 50 μF of a capacitance in high-capacitance mode. To accomplish
this, the speed of the 2601B-PULSE SMU is reduced. Source settling times increase when
high-capacitance mode is enabled. The following tables compare the source settling times in normal
and high-capacitance modes.
High capacitance mode
(C
LOAD
= 4.7 μF)
40 V (Add 150 μs when
measuring on the 1 A range
In high-capacitance mode, the frequency compensation capacitance across the measure range
resistors increases. This increase leads to longer settling times on some current measure ranges.
The same range elements that are used to measure current are used to source current. Therefore,
the current limit response times will respond in a similar manner.
Current measure and source settling times
High capacitance mode (typical)
< 80 μs (current < 2.5 A, R
LOAD
> 2 Ω)
When high-capacitance mode is enabled, the amount of time to change the current measure range
increases for each SMU. The current measure range and the current limit range are locked together.
Setting the current limit automatically updates the measure range.
Adjusting the voltage source
When driving large capacitive loads with high-capacitance mode enabled, the response time may be
lengthened by the current limit. For example, see the table titled "Current measure and source settling
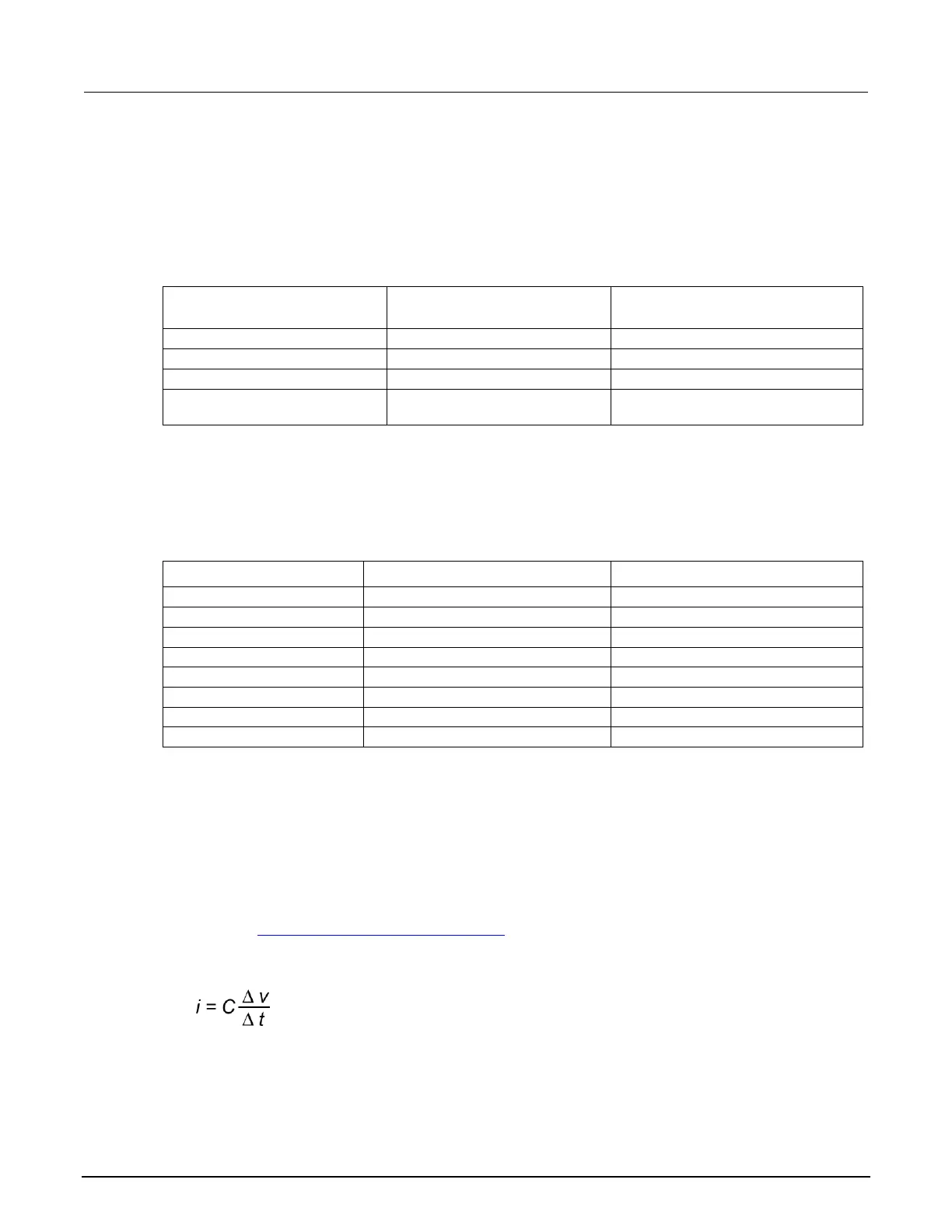
times" in the Understanding source settling times (on page 4-81) topic. If a 1 μF capacitor charges to
10 V in 10 μs with a 1 A limit and the limit is set to 100 nA, the charging time will be 100 seconds (see
the following equation).
The total response times while in high-capacitance mode are a combination of the time spent
charging the capacitor (current limit) or the response time, whichever is greater. There is a direct

 Loading...
Loading...











