Wireless Access Point
Configuring the Wireless AP 203
About Proxy Forwarding
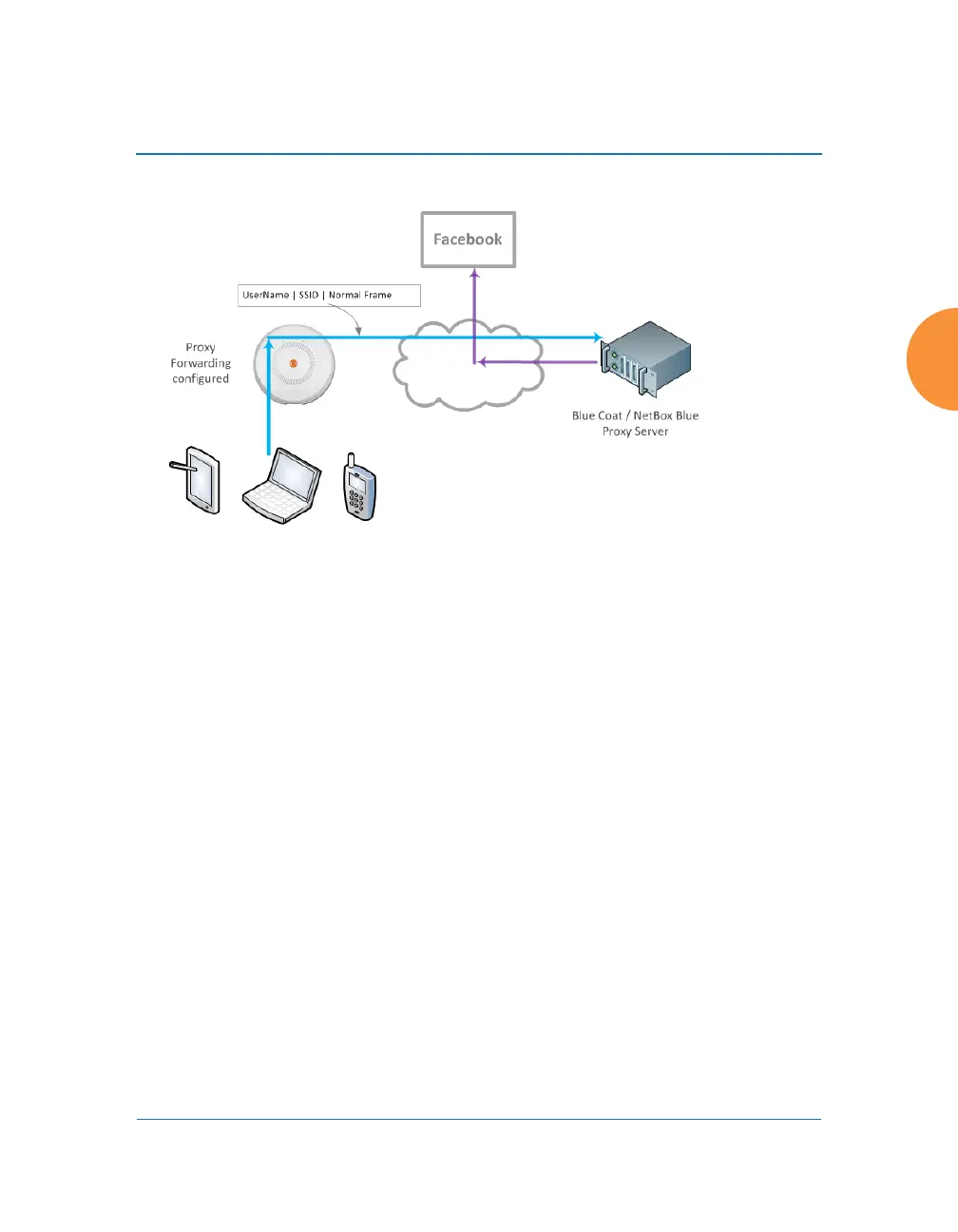
Figure 118. Proxy Forwarding Example
When you configure proxy forwarding settings on the AP, it forwards each HTTP
request to the proxy server (for example, Blue Coat) at the specified URL, which
checks if the policies that you have set up on the server are satisfied. If so, the
proxy server sends the request on to the desired web site. An example is shown in
Figure 118. The user of the laptop tries to open Facebook on a browser. The AP
forwards this request to the proxy server that you have specified, after adding a
prefix with the user’s ID and the SSID (the SSID serves as a user group; for
unauthenticated clients, the MAC address serves as the user name). The proxy
server checks whether its configured policies permit this access for this user and
SSID. If so, the frame is forwarded to the desired web site.
Proxy forwarding on the AP is designed for proxy servers such as Blue Coat and
Netbox Blue whose purpose is restricting Internet access to sites, applications and
content, and the monitoring and reporting of this activity. It is not used for
enhanced performance utilizing content caching.
SSID and client User Name restrictions permit the following characters.
— Blue Coat permits only alphanumerics and + and /.
— Netbox Blue permits only alphanumerics and dot, hyphen, underscore,
and space characters.

 Loading...
Loading...