Controlling Ink Supply During Printing
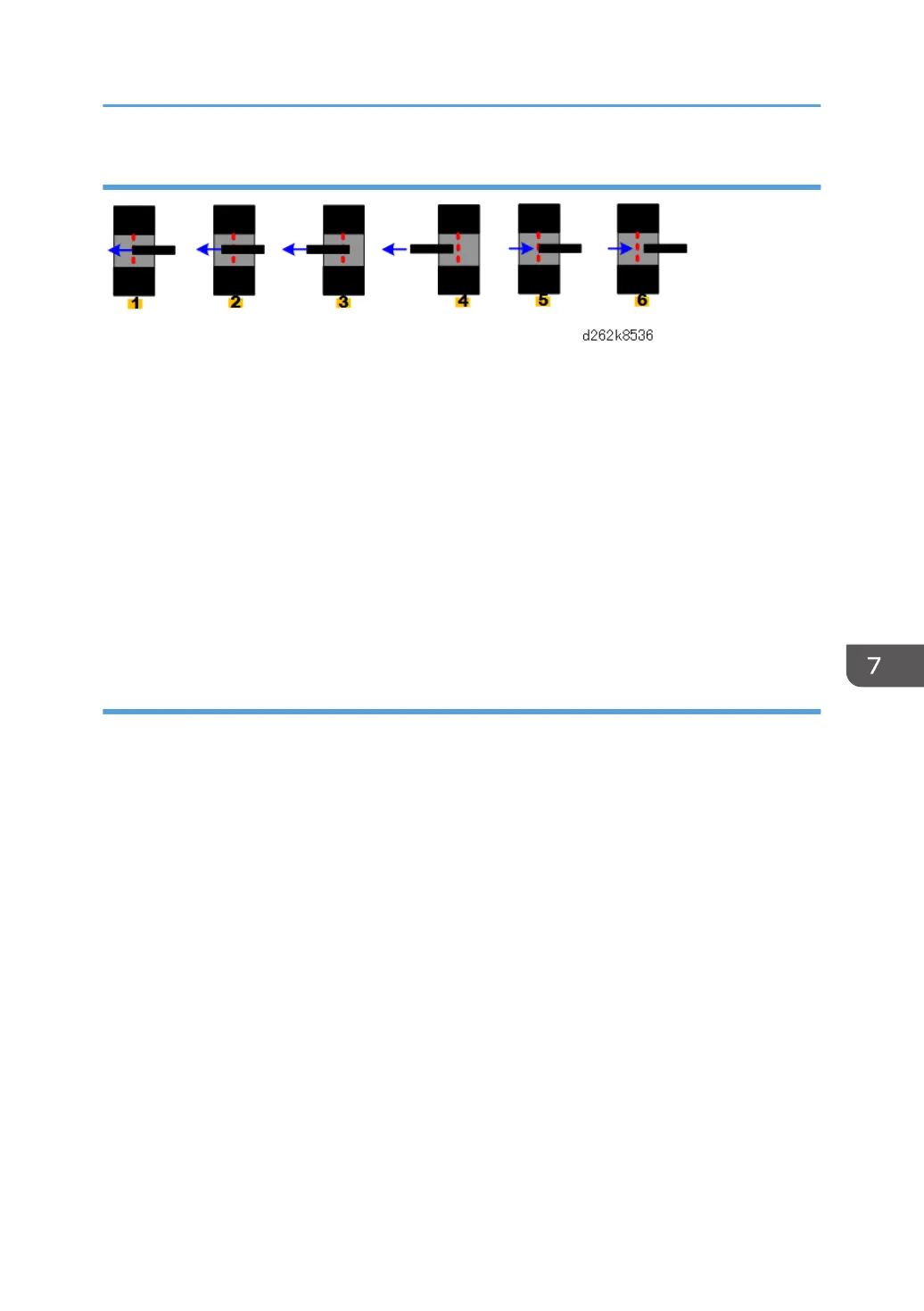
The illustration above shows how the actuator moves through gap of the OCFS (viewed from bottom
front)..
• As ink is consumed, the side of the tank collapses, and the OCFS actuator moves through the OCFS
sensor gap [1] > [2] > [3].
• When the actuator moves out of the gap at [4], the sensor turns off. This signals low ink. When this
occurs, the ink pump motor in the ink supply unit pumps ink to the tank until the sensor returns to [5].
• The motor pumps a prescribed amount of ink (Wcc) determined by the machine’s software to be
enough to turn the sensor back on.
• After that, the machine continues to pump ink a very short time (tsec).
• This is the ink full position [6].
Air Detection and Air Purging
The air sensors on top of each ink sub tank check for the presence of air in the tanks. Air is purged from
the tank after it is detected, and then the sub tank is refilled with ink. The air purge, filling, and full
position ‘learning’ sequence is done when one of the following occurs:
• Air is detected in a tank. (The purging and filling is not done until the end of the job.)
• Before print head flushing
Ink Supply
835

 Loading...
Loading...











