MPC5553/MPC5554 Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 5
25-14 Freescale Semiconductor
25.6 Memory Map/Register Definition
This section provides a detailed description of the NPC registers accessible to the end user. Individual
bit-level descriptions and reset states of the registers are included.
25.6.1 Memory Map
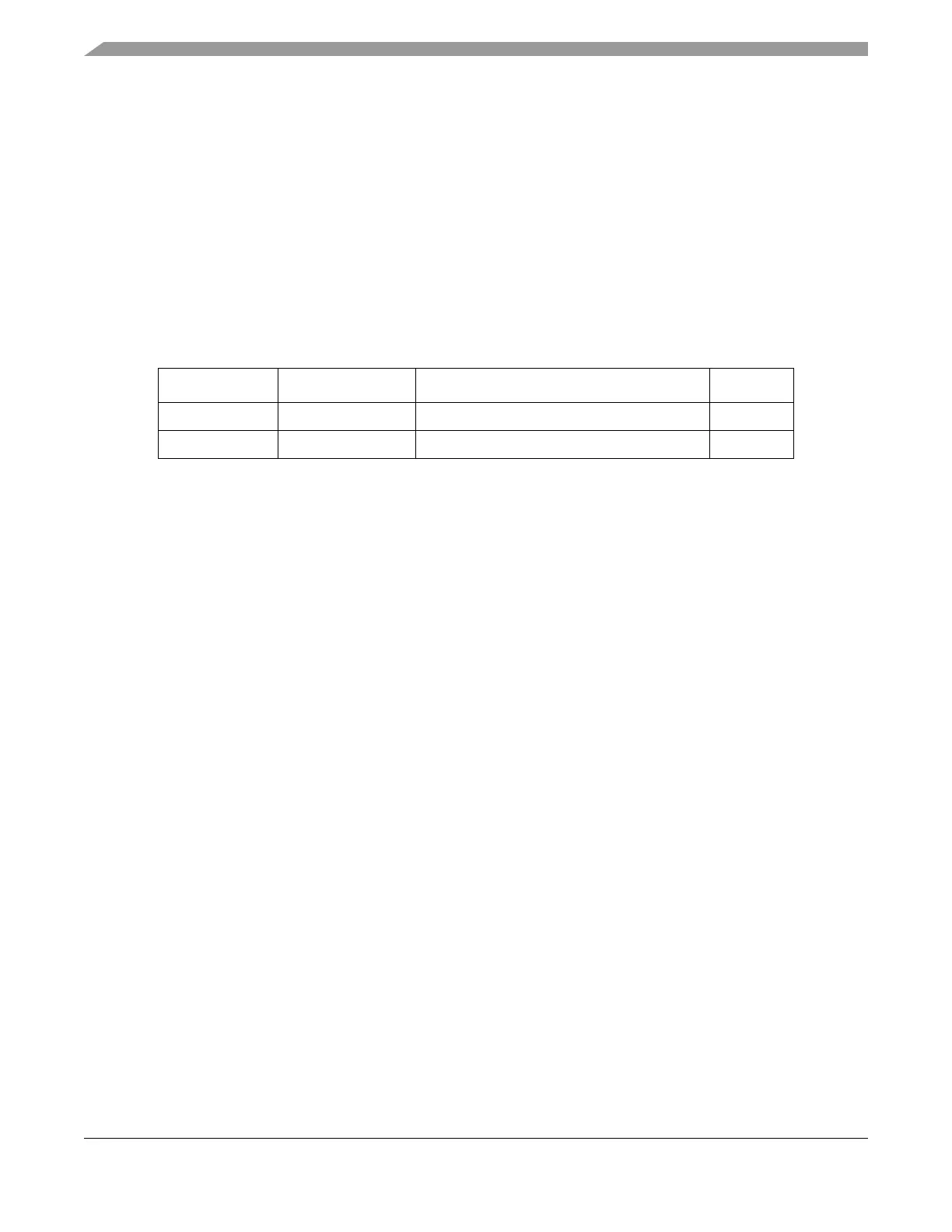
Table 25-9 shows the NPC registers by index values. The registers are not memory-mapped and can only
be accessed via the TAP. The NPC does not implement the client select control register because the value
does not matter when accessing the registers. Note that the bypass register (refer to Section 25.6.2.1) and
instruction register (refer to Section 25.6.2.2) have no index values. These registers are not accessed in the
same manner as Nexus client registers.
25.6.2 Register Descriptions
This section consists of NPC register descriptions. Additional information regarding references to the TAP
controller state may be found in Section 24.4.3, “TAP Controller State Machine.”
25.6.2.1 Bypass Register
The bypass register is a single-bit shift register path selected for serial data transfer between TDI and TDO
when the BYPASS instruction or any unimplemented instructions are active. After entry into the
Capture-DR state, the single-bit shift register is set to a logic 0. Therefore, the first bit shifted out after
selecting the bypass register is always a logic 0.
25.6.2.2 Instruction Register
The NPC uses a 4-bit instruction register as shown in Figure 25-2. The instruction register is accessed via
the SELECT_IR_SCAN path of the tap controller state machine, and allows instructions to be loaded into
the module to enable the NPC for register access (NEXUS_ENABLE) or select the bypass register as the
shift path from TDI to TDO (BYPASS or unimplemented instructions).
Instructions are shifted in through TDI while the TAP controller is in the Shift-IR state, and latched on the
falling edge of TCK in the Update-IR state. The latched instruction value can only be changed in the
Update-IR and test-logic-reset TAP controller states. Synchronous entry into the test-logic-reset state
results in synchronous loading of the BYPASS instruction. Asynchronous entry into the test-logic-reset
state results in asynchronous loading of the BYPASS instruction. During the Capture-IR TAP controller
state, the instruction register is loaded with the value of the previously executed instruction, making this
value the register’s read value when the TAP controller is sequenced into the Shift-IR state.
Table 25-9. NPC Memory Map
Index Register Name Register Description Size (bits)
0 DID Device ID register 32
127 PCR Port configuration register 32
 Loading...
Loading...