MPC5553/MPC5554 Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 5
Freescale Semiconductor 19-109
19.5.2 EQADC/eDMA Controller Interface
This section provides an overview of the EQADC/eDMA interface and general guidelines about how the
eDMA should be configured in order for it to correctly transfer data between the queues in system memory
and the EQADC FIFOs.
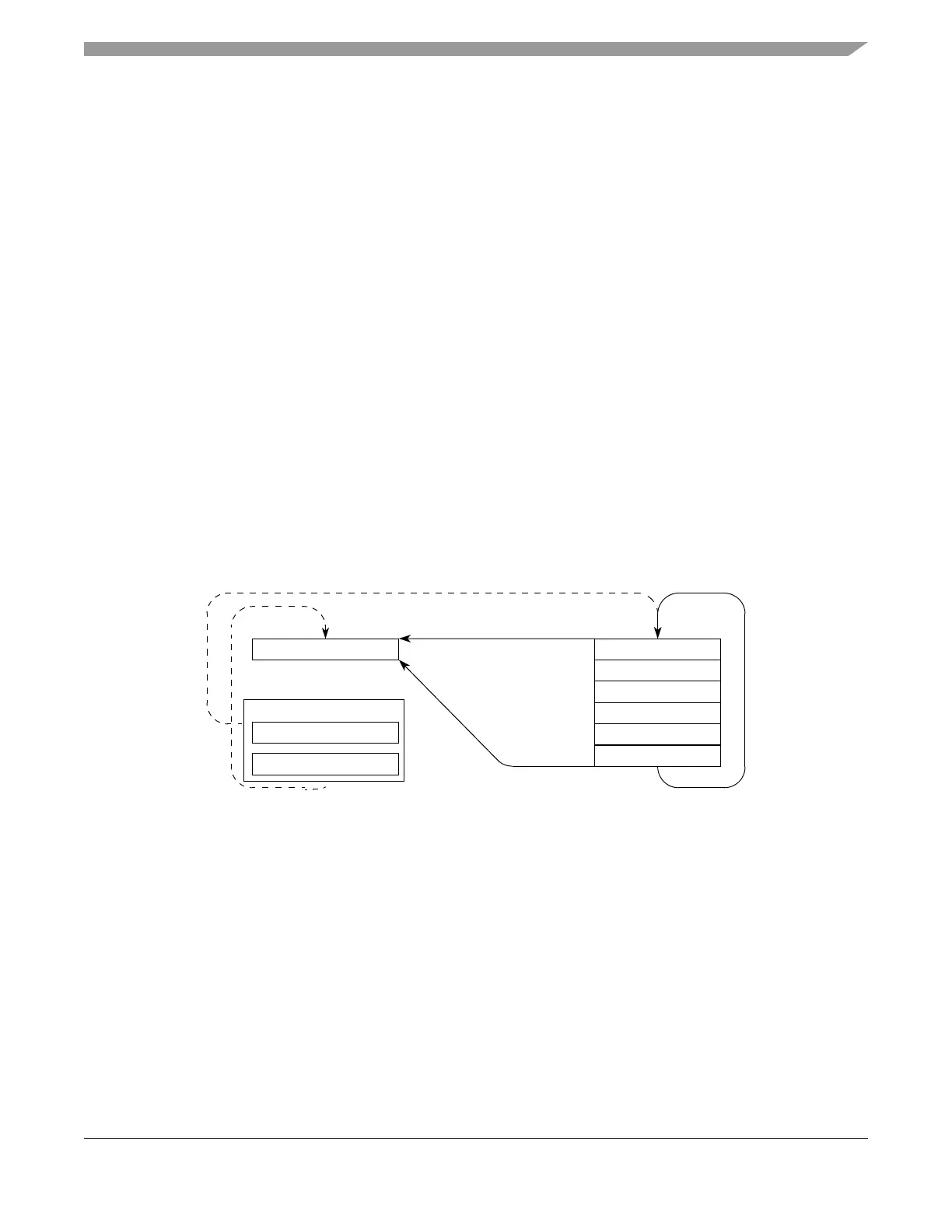
19.5.2.1 Command Queue/CFIFO Transfers
In transfers involving command queues and CFIFOs, the eDMA moves data from a queued source to a
single destination as shown in Figure 19-65. The location of the data to be moved is indicated by the source
address, and the final destination for that data, by the destination address. The eDMA has transfer control
descriptors (TCDs) containing these addresses and other parameters used in the control of data transfers
(See Section 9.3.1.16, “Transfer Control Descriptor (TCD)” for more information). For every eDMA
request issued by the EQADC, the eDMA must be configured to transfer a single command (32-bit data)
from the command queue, pointed to by the source address, to the CFIFO push register, pointed to by the
destination address. After the service of an eDMA request is completed, the source address has to be
updated to point to the next valid command. The destination address remains unchanged. When the last
command of a queue is transferred one of the following actions is recommended. Refer to Chapter 9,
“Enhanced Direct Memory Access (eDMA)” for details about how this functionality is supported.
• The corresponding eDMA channel should be disabled. This might be desirable for CFIFOs in
single scan mode.
• The source address should be updated to pointed to a valid command which can be the first
command in the queue that has just been transferred (cyclic queue), or the first command of any
other command queue. This is desirable for CFIFOs in continuous scan mode, or in some cases,
for CFIFOs in single scan mode.
Figure 19-65. Command Queue/CFIFO Interface
19.5.2.2 Receive Queue/RFIFO Transfers
In transfers involving receive queues and RFIFOs, the eDMA controller moves data from a single source
to a queue destination as shown in Figure 19-66. The location of the data to be moved is indicated by the
source address, and the final destination for that data, by the destination address. For every eDMA request
issued by the EQADC, the eDMA controller has to be configured to transfer a single result (16-bit data),
pointed to by the source address, from the RFIFO pop register to the receive queue, pointed to by the
destination address. After the service of an eDMA request is completed, the destination address has to be
updated to point to the location where the next 16-bit result will be stored. The source address remains
unchanged. When the last expected result is written to the receive queue, one of the following actions is
recommended. Refer to Chapter 9, “Enhanced Direct Memory Access (eDMA)” for details about how this
functionality is supported.
Command 1
Command 2
Command 3
•
Command n-1
Command n
One command transfer
per DMA request
CFPRx
Source Address
Destination Address
CFIFO Push Register
•
•
•
•
•
eDMA_TCDn
 Loading...
Loading...