MPC5553/MPC5554 Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 5
Freescale Semiconductor 20-33
CSI configuration will use. See Section 20.3.2.3, “DSPI Clock and Transfer Attributes Registers 0–7
(DSPIx_CTARn),” for information on DSPIx_CTAR fields.
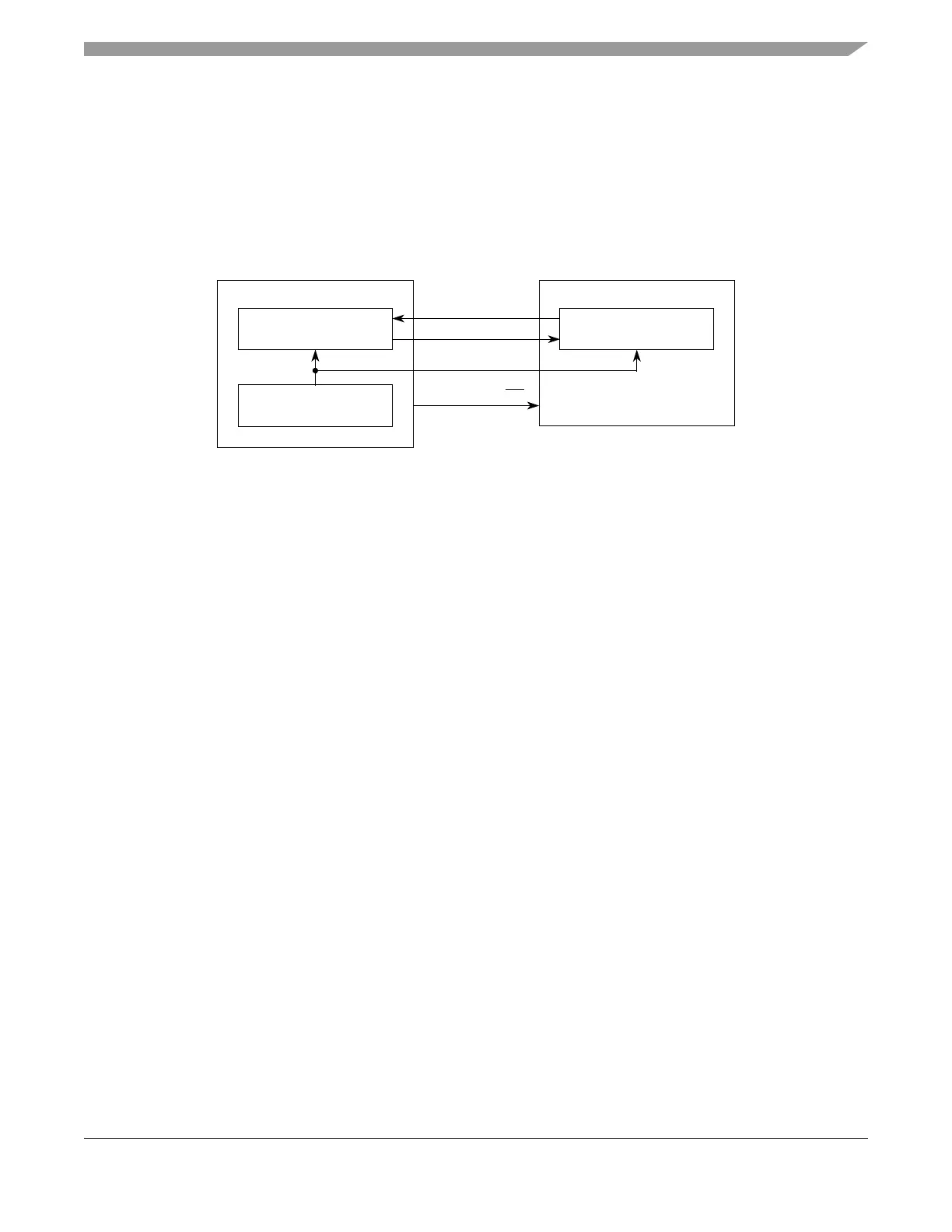
The 16-bit shift register in the master and the 16-bit shift register in the slave are linked by the SOUT and
SIN signals to form a distributed 32-bit register. When a data transfer operation is performed, data is
serially shifted a pre-determined number of bit positions. Because the registers are linked, data is
exchanged between the master and the slave; the data that was in the master’s shift register is now in the
shift register of the slave, and vice versa. At the end of a transfer, the TCF bit in the DSPIx_SR is set to
indicate a completed transfer. Figure 20-17 illustrates how master and slave data is exchanged.
Figure 20-17. SPI and DSI Serial Protocol Overview
The DSPI has six peripheral chip select (PCS) signals that are be used to select which of the slaves to
communicate with.
Transfer protocols and timing properties are shared by the three DSPI configurations; these properties are
described independently of the configuration in Section 20.4.7, “Transfer Formats.” The transfer rate and
delay settings are described in section Section 20.4.6, “DSPI Baud Rate and Clock Delay Generation.”
See Section 20.4.10, “Power Saving Features” for information on the power-saving features of the DSPI.
20.4.1 Modes of Operation
The MPC5553/MPC5554 DSPIs have four available distinct modes:
• Master mode
• Slave mode
• Module disable mode
• Debug mode
Master, slave, and module disable modes are module-specific modes while debug mode is a
MPC5553/MPC5554-specific mode.
The module-specific modes are determined by bits in the DSPIx_MCR. Debug mode is a mode that the
entire MPC5553/MPC5554 can enter in parallel with the DSPI being configured in one of its
module-specific modes.
20.4.1.1 Master Mode
In master mode the DSPI can initiate communications with peripheral devices. The DSPI operates as bus
master when the MSTR bit in the DSPIx_MCR is set. The serial communications clock (SCK) is
controlled by the master DSPI. All three DSPI configurations are valid in master mode.
In SPI configuration, master mode transfer attributes are controlled by the SPI command in the current TX
FIFO entry. The CTAS field in the SPI command selects which of the eight DSPIx_CTARs will be used to
DSPI Master
Shift Register
Baud Rate Generator
DSPI Slave
Shift Register
SOUT
SIN
SOUT SIN
SCK SCK
PCSx SS
 Loading...
Loading...