MPC5553/MPC5554 Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 5
Freescale Semiconductor 19-61
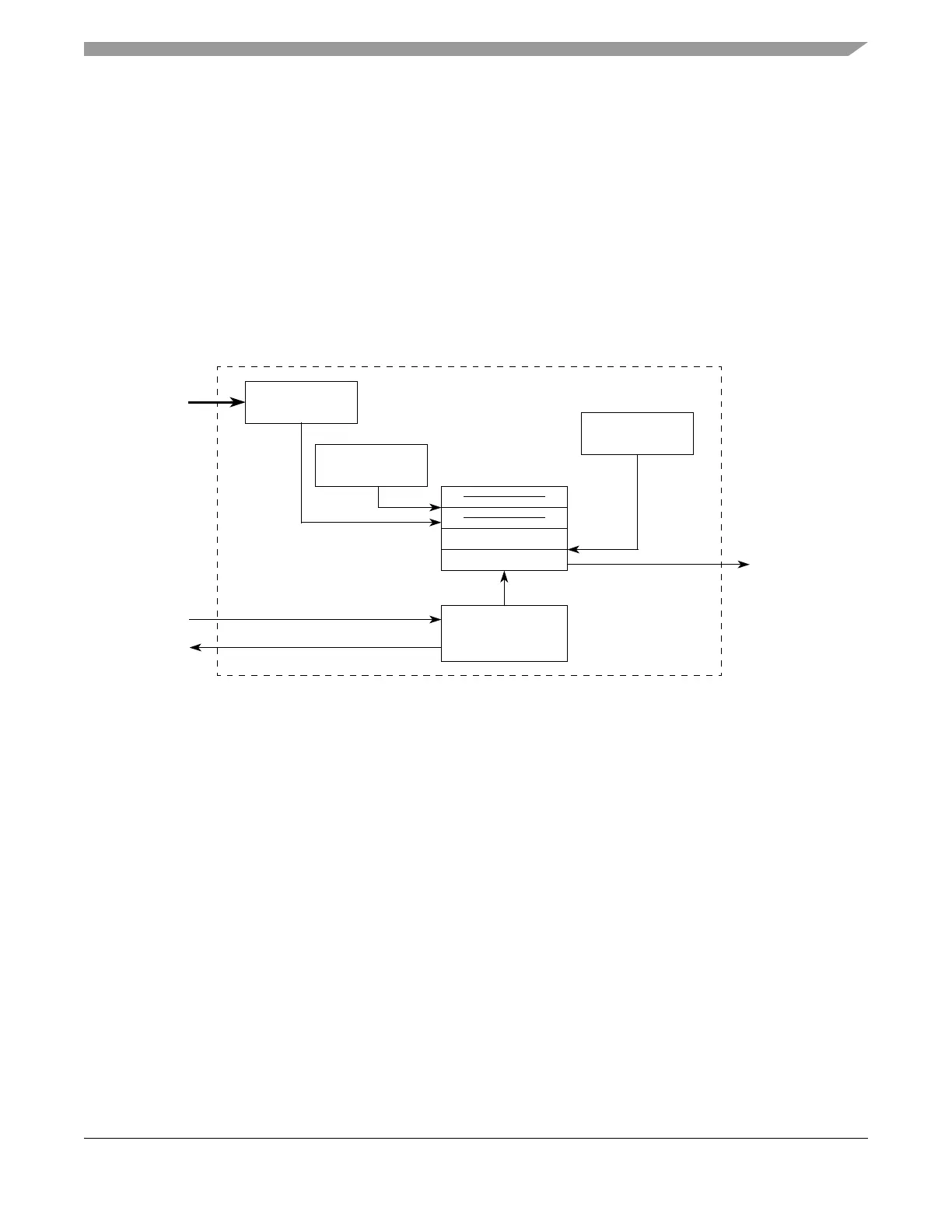
When the eQADC completes the transfer of an entry from CFIFOn: the transferred entry is popped from
CFIFOn, the CFIFO counter CFCTR in the Section 19.3.2.8, “eQADC FIFO and Interrupt Status Registers
0–5 (EQADC_FISRn),” is decremented by 1, and transfer next data pointer n is incremented by 1 (or
wrapped around) to point to the next entry in the CFIFO. The transfer of entries bound for the on-chip
ADCs is considered completed when they are stored in the appropriate ADC command buffer. The transfer
of entries bound for the external device is considered completed when the serial transmission of the entry
is completed.
When the EQADC_CFPRn is written and CFIFOn is not full, the CFIFO counter CFCTRn is incremented
by 1, and the push next data pointer n then is incremented by 1 (or wrapped around) to point to the next
entry in the CFIFO.
When the EQADC_CFPRn is written but CFIFOn is full, the eQADC will not increment the counter value
and will not overwrite any entry in CFIFOn.
Figure 19-35. CFIFO Diagram
The detailed behavior of the push next data pointer and transfer next data pointer is described in the
example shown in Figure 19-36 where a CFIFO with 16 entries is shown for clarity of explanation, the
actual hardware implementation has only four entries. In this example, CFIFOn with 16 entries is shown
in sequence after pushing and transferring entries.
Push Next
32-bit Entry 2
32-bit Entry 1
Control Signals
CFIFO
Transfer Counter
Control Logic
Data Pointer *
Transfer Next
Data Pointer *
CFIFO
Push Register
Data to
External
Device or
to On-Chip
ADCs
Write
to Bus
Interface
by CPU
or DMA
DMA Done
Interrupt/DMA Request
All CFIFO entries are memory mapped and the entries addressed by these pointers
can have their absolute addresses calculated using TNXTPTR and CFCTR.
*
 Loading...
Loading...