MPC5553/MPC5554 Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 5
13-16 Freescale Semiconductor
13.3.2.5 Low/Mid Address Space Block Select Register (FLASH_LMSR)
The FLASH_LMSR provides a means to select blocks to be operated on during erase.
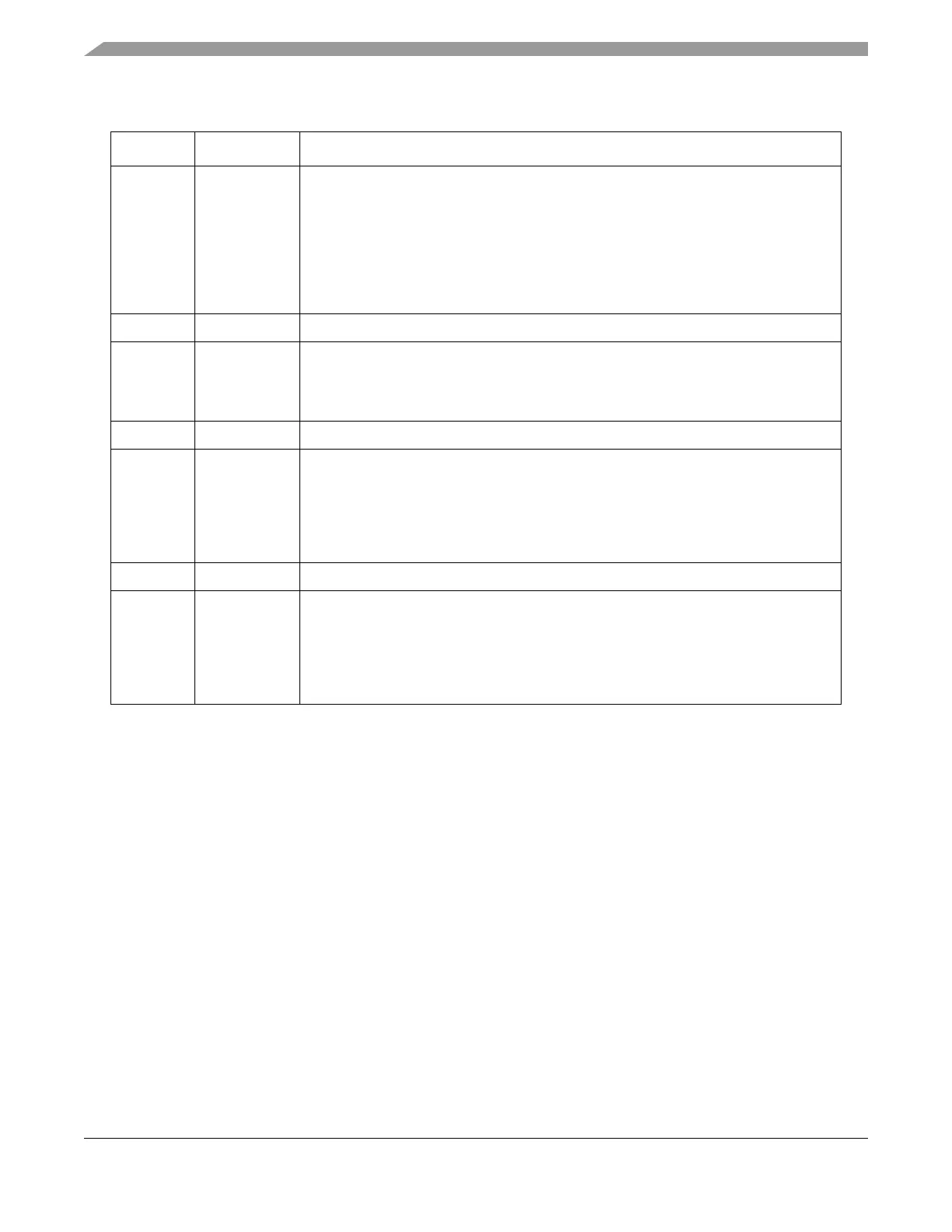
Table 13-10. FLASH_SLMLR Field Descriptions
Bits Name Description
0 SLE Secondary low- and mid-address lock enable. Enables the secondary lock fields
(SSLOCK, SMLOCK, and SLLOCK) to be set or cleared by register writes. This bit is a
status bit only, and may not be written or cleared, and the reset value is 0. The method
to set this bit is to provide a password, and if the password matches, the SLE bit will be
set to reflect the status of enabled, and is enabled until a reset operation occurs. For
SLE, the password 0xC3C3_3333 must be written to the FLASH_SLMLR.
0 Secondary low- and mid-address locks are disabled, and cannot be modified.
1 Secondary low- and mid-address locks are enabled to be written.
1–10 — Reserved.
11 SSLOCK Secondary shadow lock. An alternative method that may be used to lock the shadow
row from programs and erases. SSLOCK has the same description as SLOCK in
Section 13.3.2.2, “Low-/Mid-Address Space Block Locking Register (FLASH_LMLR).”
SSLOCK is not writable unless SLE is high.
12–13 — Reserved.
14–15 SMLOCK
[1:0]
Secondary mid-address block lock. Alternative method that may be used to lock the mid
address space blocks from programs and erases. SMLOCK has the same description
as MLOCK in section Section 13.3.2.2, “Low-/Mid-Address Space Block Locking
Register (FLASH_LMLR).” SMLOCK is not writable unless SLE is set.
In the event that blocks are not present (due to configuration or total memory size), the
SMLOCK bits will default to locked, and will not be writable.
16–25 — Reserved.
26–31 SLLOCK
[5:0]
Secondary low-address block lock. These bits are an alternative method that may be
used to lock the low-address space blocks from programs and erases. SLLOCK has the
same description as LLOCK in Section 13.3.2.2, “Low-/Mid-Address Space Block
Locking Register (FLASH_LMLR). SLLOCK is not writable unless SLE is high.
In the event that blocks are not present (due to configuration or total memory size), the
SLLOCK bits will default to locked, and will not be writable.
 Loading...
Loading...