MPC5553/MPC5554 Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 5
Freescale Semiconductor 18-25
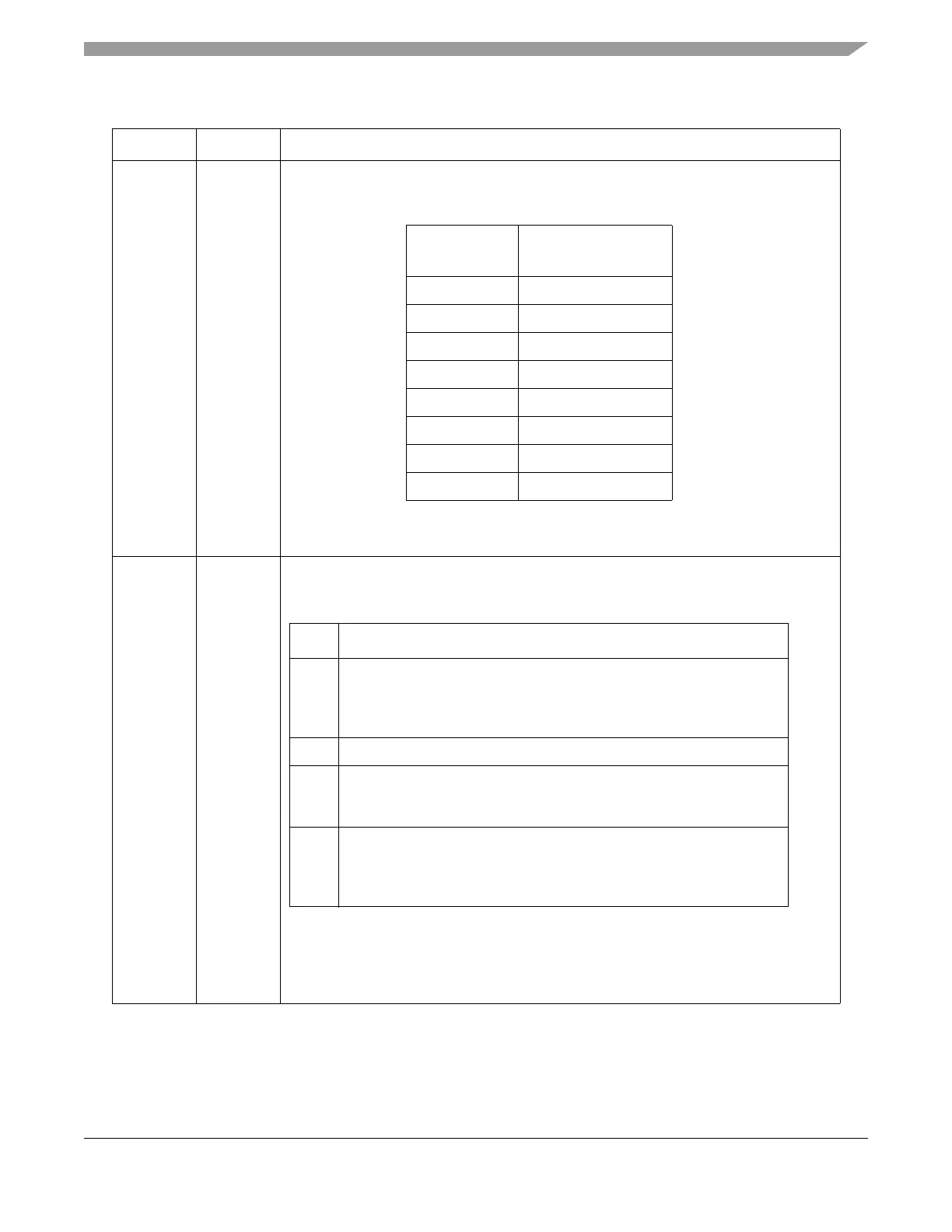
13–15 FPSCK
[0:2]
Filter prescaler clock control. Controls the prescaling of the clocks used in digital filters for
the channel input signals and TCRCLK input. The following table illustrates filter prescaler
clock control.
Filtering can be controlled independently by the engine, but all input digital filters in the
same engine have same clock prescaling. For more details, refer to the eTPU reference
manual.
16–17 CDFC
[0:1]
Channel digital filter control. Select a digital filtering mode for the channels when
configured as inputs for improved noise immunity. Channel digital filter control is illustrated
in the following table.
The eTPU has three digital filtering modes for the channels which provide programmable
trade-off between signal latency and noise immunity. For more information on filtering, refer
to the eTPU reference manual. Changing CDFC during eTPU normal input channel
operation is not recommended because it changes the behavior of the transition detection
logic while executing its operation.
Table 18-11. ETPU_ECR Field Descriptions (Continued)
Bits Name Description
Filter Control
Sample on System
Clock Divided by:
000 2
001 4
010 8
011 16
100 32
101 64
110 128
111 256
CDFC Selected Digital Filter
00 TPU2/3 two sample mode: Using the filter clock which is the system
clock divided by (2, 4, 8,..., 256) as a sampling clock (selected by FPSCK
field in ETPU_ECR), comparing two consecutive samples which agree
with each other sets the input signal state. This is the default reset state.
01 Reserved.
10 eTPU three sample mode: Similar to the TPU2/3 two sample mode, but
comparing three consecutive samples which agree with each other sets
the input signal state.
11 eTPU continuous mode: Signal needs to be stable for the whole filter
clock period. This mode compares all the values at the rate of system
clock divided by two, between two consecutive filter clock pulses. If all
the values agree with each other, input signal state is updated.
 Loading...
Loading...