MPC5553/MPC5554 Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 5
12-48 Freescale Semiconductor
(to take away bus grant from the external master), the EBI does not start an access of its own for 3 cycles
(1 extra cycle in order to detect external BB assertion). If the external master jumps on the bus (by asserting
BB) during the 2-cycle window, the EBI detects the BB assertion and delays starting its access until the
external master access has completed (BB negated for 2 cycles). Figure 12-34 shows this 2-cycle window
of opportunity.
I
Figure 12-34. Internal Arbitration, 2-Cycle Window-of-Opportunity
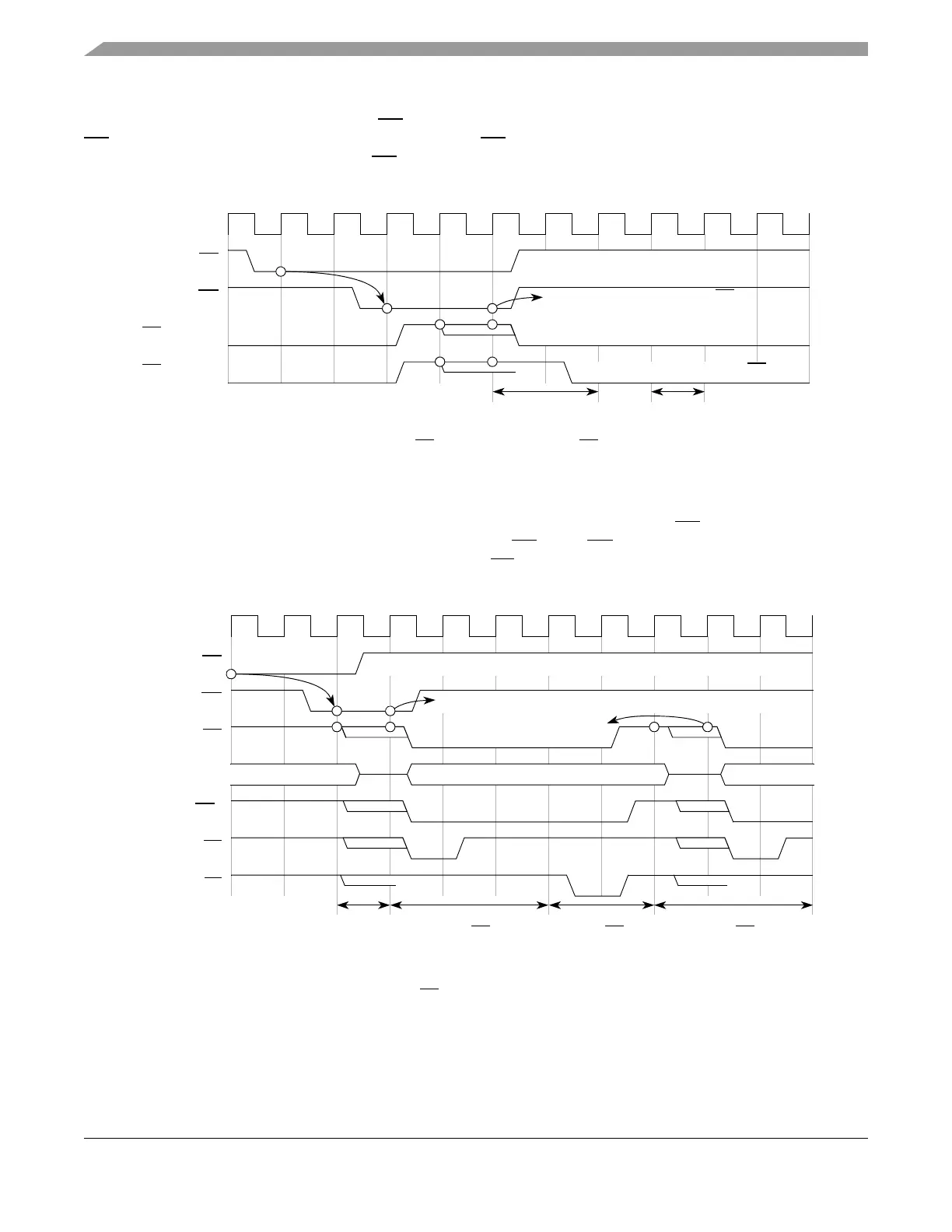
Figure 12-35 shows example timing for the case of one master using internal arbitration (master 0), while
another master is configured for external arbitration (master 1). In this case, the BR signals of each master
are connected together, because only master 1 drives BR. The BG signals of each master are also
connected together, because only master 0 drives BG. See Figure 12-38 for an example of these
connections.
Figure 12-35. Internal/External Arbitration Timing Diagram (EARP = 1)
Table 12-21 shows a description of the states defined for the internal arbiter protocol.
Latest cycle M1 can assert BB
Using internal arbiter for Master 0,
external arbitration for Master 1
M1 receives bus grant and BB
negated for 2nd cycle
Earliest cycle M1 can assert BB
CLKOUT
BR
BG
BB (Case 1)
BB
(Case 2)
Window-of-
opportunity
*
Earliest cycle M0 can assert BB
if M1 has not asseretd BB yet.
*
M0 receives bus busy
negated for 2nd cycle
Fastest req –
>
grant possible
M1 receives bus grant and bus busy negated for 2nd cycle
Using internal arbiter for Master 0, external arbitration for Master 1
CLKOUT
BR
BB
ADDR+ATTR
1
CSx
BG
TA
TS
Both
Masters
off
Master 1
negates BB
and
‘turns off’
(three-states controls)
Master 0
asserts BB and
‘turns on’
(drives controls)
Master 1
asserts BB and
‘turns on’
(drives controls)
1
ATTR refers to control signals such as RD_WR
and TSIZ.
 Loading...
Loading...