MPC5553/MPC5554 Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 5
Freescale Semiconductor 19-87
19.4.5.3 Time Stamp Feature
The on-chip ADCs can provide a time stamp for the conversions they execute. A time stamp is the value
of the time base counter latched when the eQADC detects the end of the analog input voltage sampling. A
time stamp for a conversion command is requested by setting the TSR bit in the corresponding command.
When TSR is negated, that is a time stamp is not requested, the ADC returns a single result message
containing the conversion result. When TSR is asserted, that is a time stamp is requested, the ADC returns
two result messages; one containing the conversion result, and another containing the time stamp for that
conversion. The result messages are sent in this order to the RFIFOs and both messages are sent to the
same RFIFO as specified in the MESSAGE_TAG field of the executed conversion command.
The time base counter is a 16-bit up counter and wraps after reaching 0xFFFF. It is disabled after reset and
it is enabled according to the setting of ADC_TSCR[TBC_CLK_PS] field (see Section 19.3.3.2).
TBC_CLK_PS defines if the counter is enabled or disabled, and, if enabled, at what frequency it is
incremented. The time stamps are returned regardless of whether the time base counter is enabled or
disabled. The time base counter can be reset by writing 0x0000 to the ADC_TBCR (Section 19.3.3.3) with
a write configuration command.
19.4.5.4 ADC Calibration Feature
19.4.5.4.1 Calibration Overview
The eQADC provides a calibration scheme to remove the effects of gain and offset errors from the results
generated by the on-chip ADCs. Only results generated by the on-chip ADCs are calibrated. The results
generated by ADCs on the external device are directly sent to RFIFOs unchanged. The main component
of calibration hardware is a multiply-and-accumulate (MAC) unit, one per on-chip ADC, that is used to
calculate the following transfer function which relates a calibrated result to a raw, uncalibrated one.
CAL_RES = GCC * RAW_RES + OCC + 2;
where:
• CAL_RES is the calibrated result corresponding the input voltage V
i
.
• GCC is the gain calibration constant.
• RAW_RES is the raw, uncalibrated result corresponding to an specific input voltage V
i
.
• OCC is the offset calibration constant.
• The addition of two reduces the maximum quantization error of the ADC. See Section 19.5.6.3,
“Quantization Error Reduction During Calibration.”
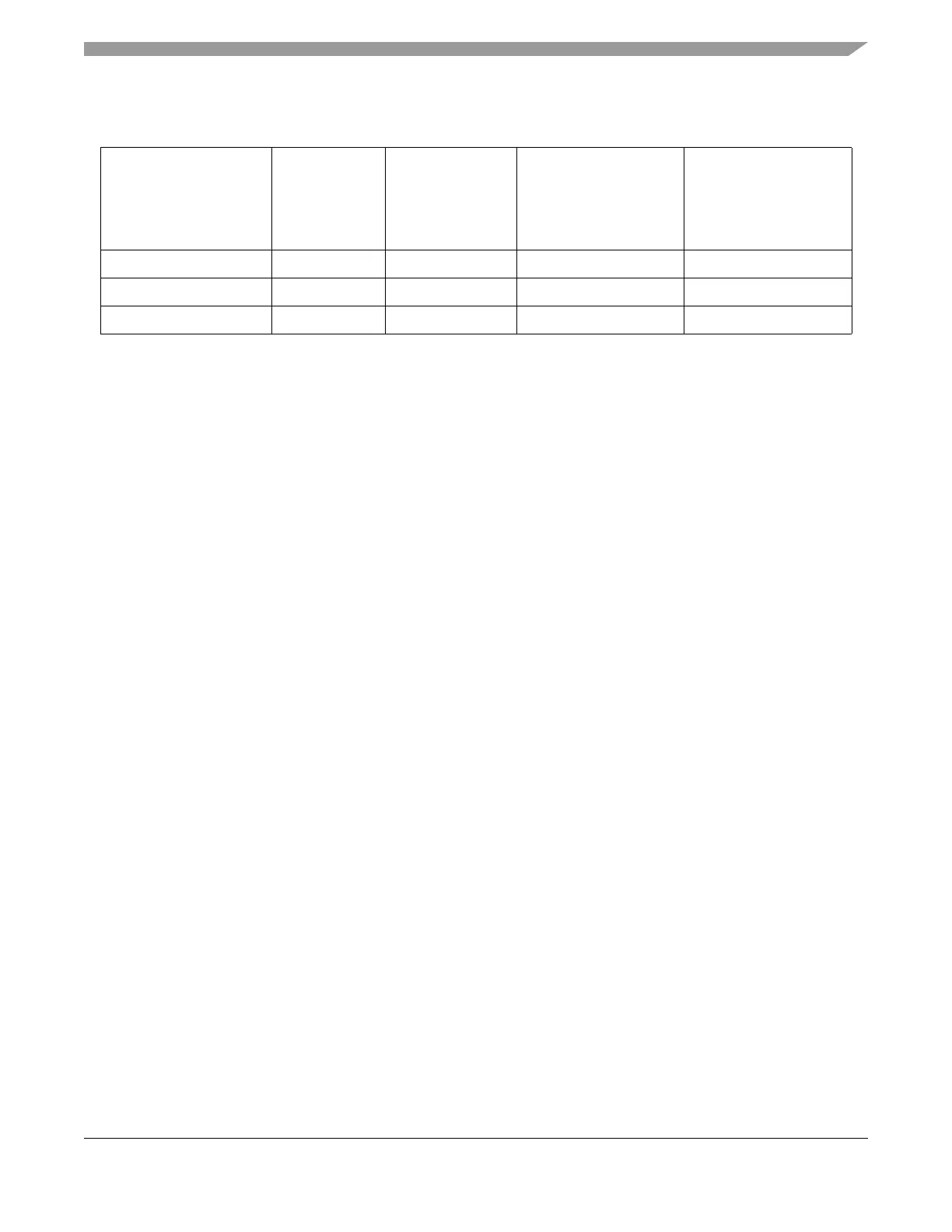
0b11101 60 2.0 133 125
0b11110 62 1.94 129 121
0b11111 64 1.88 125 117
Table 19-47. ADC Clock Configuration Example (Continued)
(System Clock Frequency = 120 MHz)
ADC0/1_CLK_PS[0:4]
System Clock
Divide Factor
ADC Clock in MHz
(System Clock =
120MHz)
Differential Conversion
Speed with Default
Sampling Time
(13 + 2 cycles) in
ksamp/s
Single-Ended
Conversion Speed with
Default Sampling Time
(14 + 2 cycles) in
ksamp/s
 Loading...
Loading...