RM0091 Inter-integrated circuit (I
2
C) interface
Doc ID 018940 Rev 1 503/742
.
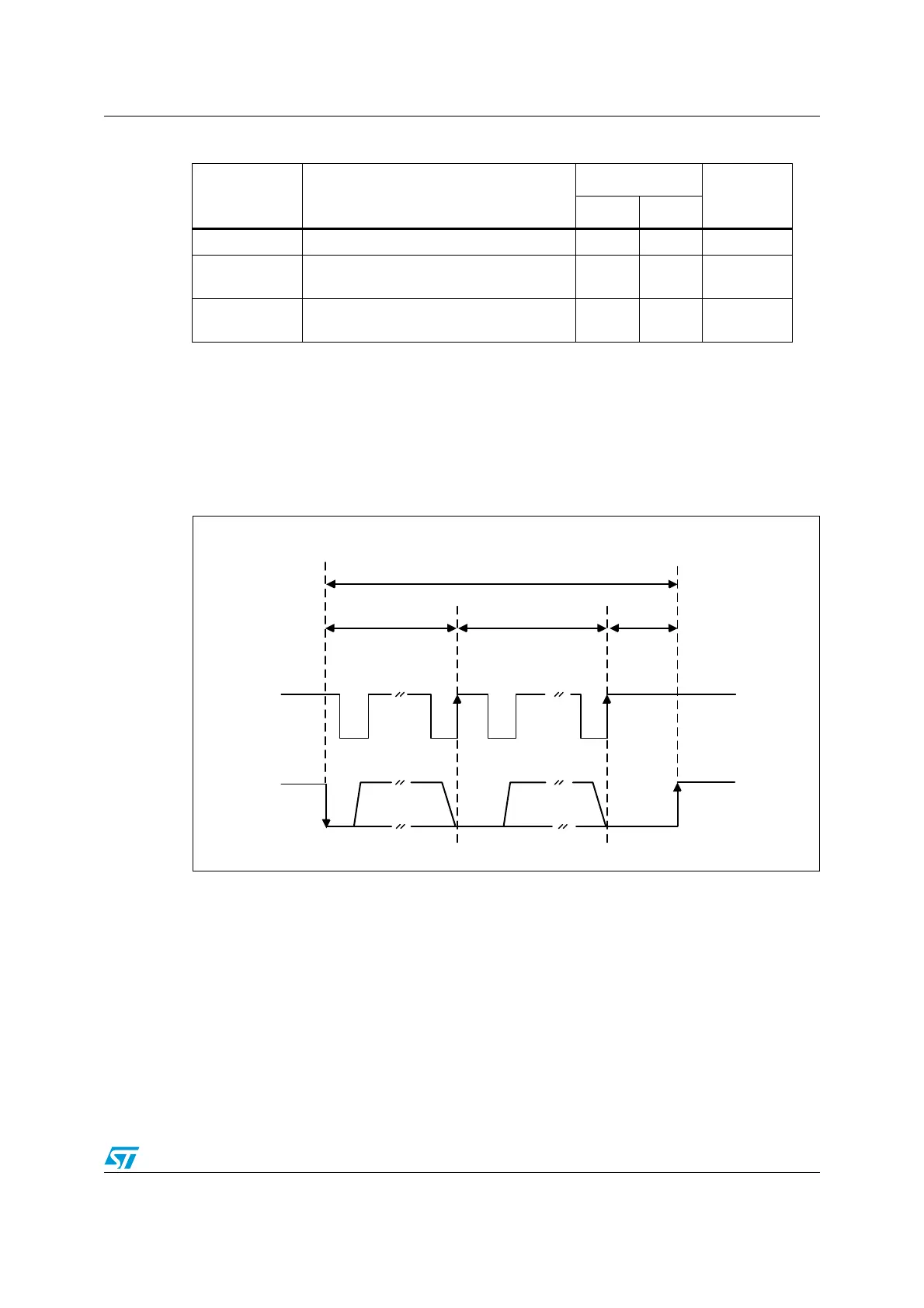
Figure 219. Timeout intervals for t
LOW:SEXT
, t
LOW:MEXT
Bus idle detection
A master can assume that the bus is free if it detects that the clock and data signals have
been high for t
IDLE
greater than t
HIGH
,
MAX
. (refer to Table 66: I2C-SMBUS specification clock
timings)
This timing parameter covers the condition where a master has been dynamically added to
the bus and may not have detected a state transition on the SMBCLK or SMBDAT lines. In
this case, the master must wait long enough to ensure that a transfer is not currently in
progress. The peripheral supports a hardware bus idle detection.
Table 70. SMBus timeout specifications
Symbol Parameter
Limits
Unit
Min Max
t
TIMEOUT
Detect clock low timeout 25 35 ms
t
LOW:SEXT
(1)
1. t
LOW:SEXT
is the cumulative time a given slave device is allowed to extend the clock cycles in one
message from the initial START to the STOP. It is possible that, another slave device or the master
will also extend the clock causing the combined clock low extend time to be greater than t
LOW:SEXT
.
Therefore, this parameter is measured with the slave device as the sole target of a full-speed master.
Cumulative clock low extend time (slave
device)
25 ms
t
LOW:MEXT
(2)
2. t
LOW:MEXT
is the cumulative time a master device is allowed to extend its clock cycles within each byte
of a message as defined from START-to-ACK, ACK-to-ACK, or ACK-to-STOP. It is possible that a
slave device or another master will also extend the clock causing the combined clock low time to be
greater than t
LOW:MEXT
on a given byte. Therefore, this parameter is measured with a full speed slave
device as the sole target of the master.
Cumulative clock low extend time (master
device)
10 ms
MS19866V1
Start Stop
t
LOW:SEXT
t
LOW:MEXT
t
LOW:MEXT
t
LOW:MEXT
Clk
Ack
Clk
Ack
SMBCLK
SMBDAT
 Loading...
Loading...