MPC5553/MPC5554 Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 5
Freescale Semiconductor 12-57
12.4.2.10.2 Bus Transfers Initiated by an External Master
The external master gets ownership of the bus (see Section 12.4.2.8, “Arbitration”) and asserts TS in order
to initiate an external master access. The access is directed to the internal bus only if the input address
matches to the internal address space. The access is terminated with either TA or TEA. If the access was
successfully completed, the MCU asserts TA, and the external master can proceed with another external
master access, or relinquish the bus. If an address or data error was detected internally, the MCU asserts
TEA for one clock.
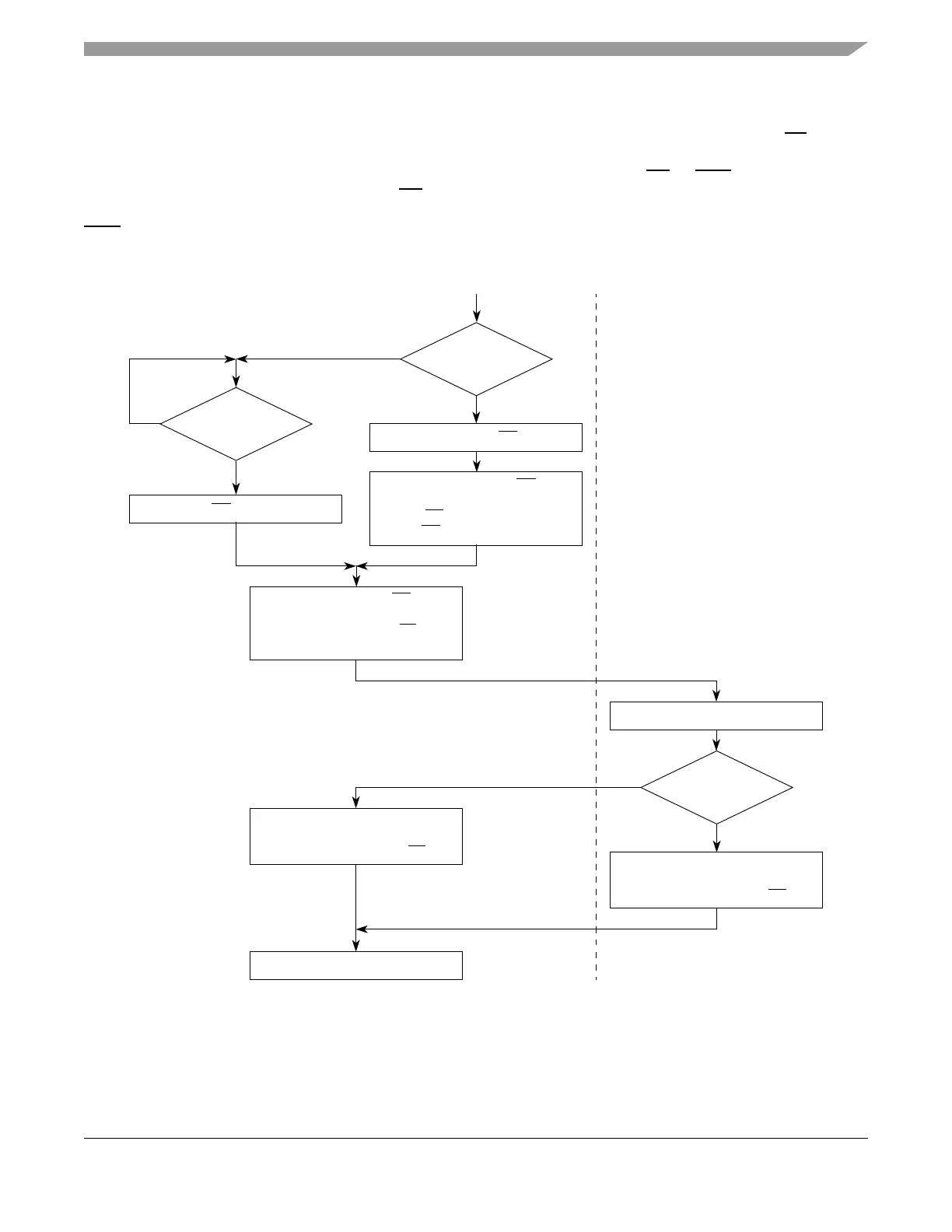
Figure 12-39 and Figure 12-40 illustrate the basic flow of read and write external master accesses.
Figure 12-39. Basic Flow Diagram of an External Master Read Access
External Master EBI (Slave)
No
Yes
External
Arbitration*
?
Request Bus (BR)
Receives Bus Grant (BG)
Asserted from External Arbiter**
Receives BB
Negated for 2 Cycles
Negates BR if No Other Requests
No
Yes
External
Master has
Priority***
Negates BG if Asserted
Asserts Bus Busy (BB)
if No Other Master is Driving
Assert Transfer Start (TS
)
Drives Address and Attributes
?
Receives Address
No
Yes
Address
in Internal Memory
Map
?
Other Shared Device
Drives Data and Asserts
Transfer Acknowledge (TA
)
Receives Data
Drives Data
Asserts
Transfer Acknowledge (TA
)
This refers to whether the external master device is configured for external or internal arbitration.
*
External arbiter is the EBI unless a central arbiter device is used.
**
Determined by the internal arbiter of the external master device.
***
 Loading...
Loading...