22.3.6. PIN mode control of TSI
There are 4 pins in each group and each of these pins is able to be used as a sample pin or
channel pin. Only one pin in a group should be configured as sample pin, and channel pins
can be more than one. The sample pin and channel pin(s) should not be configured as the
same pin in any case.
When a PIN is configured in GPIO (see chapter GPIO) used by TSI, the pin’s mode is
controlled by TSI. Generally, each pin has 3 modes: input, output high and output low.
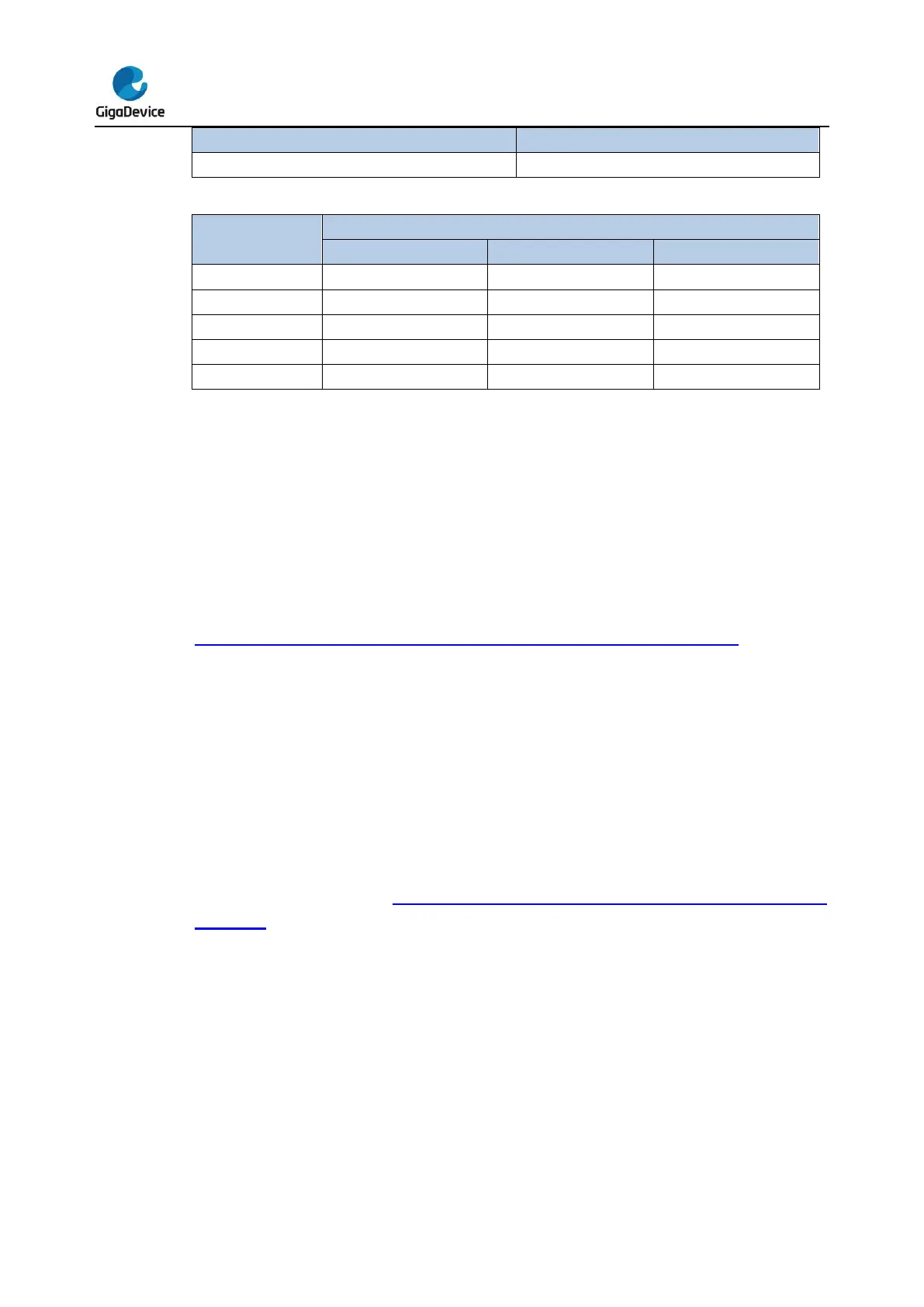
The mode of a channel pin or a sample pin during a charge-transfer sequence is described in
Table 22-1. Pin and analog switch state in a charge-transfer sequence which PIN0
represents a channel pin and PIN1 represents a sample pin, i.e. the charge-transfer FSM
take control of these channels or sample pins’ mode and the states of related analog
switches when the sequence is on-going. When the sequence is in IDLE state, PINMOD bit
in TSI_CTL0 register defines the mode of these pins. Pins that are configured in GPIO used
by TSI but neither sample nor channel in TSI register is called free pins whose mode is
defined by PINMOD bit in TSI_CTL0, too.
22.3.7. Analog switch (ASW) and I/O hysteresis mode
A channel or sample pin’s analog switch is controlled by charge-transfer sequence when
FSM is running, as shown in Table 22-1. Pin and analog switch state in a charge-transfer
sequence. When the FSM is IDLE, these pins’ analog switches are controlled by GxPy bits
in TSI_ASW register. All free pin’s analog switches are controlled by GxPy bits too.
TSI takes control of the analog switches when FSM is IDLE, even if these pins are not
configured to be used by TSI in GPIO. The user is able to perform user-defined
charge-transfer sequence by writing GxPy bits to control these analog switches, while
controlling pin mode directly in GPIO.
TSI controller has the highest priority of GPIO. When TSI is enable, this configuration is
available regardless of the GPIO mode, controlled by GPIO registers or other peripherals
Disable the GPIO’s Schmitt trigger hysteresis of TSI Pins by resetting GxPy bit in TSI_PHM
register could improve the system immunity.
 Loading...
Loading...