Intel
®
EP80579 Integrated Processor Product Line—System Management Bus (SMBus)
Interface
Intel
®
EP80579 Integrated Processor Product Line
Platform Design Guide May 2010
178 Order Number: 320068-005US
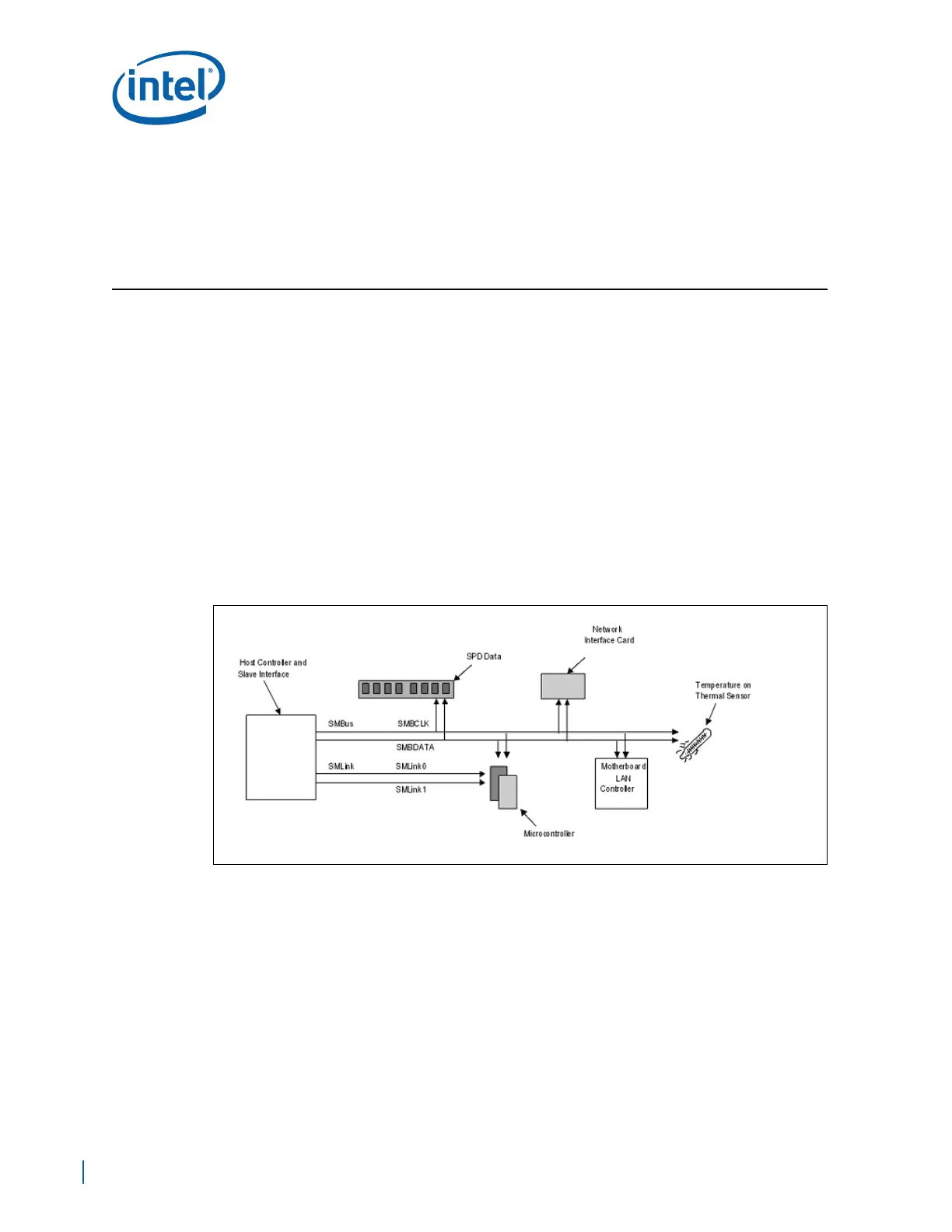
13.0 System Management Bus (SMBus) Interface
13.1 SMBus 2.0/SMLink Interface
The EP80579 integrates two SMBus 2.0 controllers. The SMBus provides an interface to
manage peripherals, such as serial presence detection (SPD) on RAM, thermal sensors,
etc. The slave interface allows an external microcontroller to access system resources.
The EP80579 consists of a host/slave controller and a slave controller, both of which
are I
2
C compliant. These interfaces use signals SMBCLK, SMBDATA, SMBSDA, and
SMBSCL, respectively, to send and receive data from components residing on these
buses.
The host/I
2
C bus has a flexible SMBus/SMLink architecture to optimize for Alert
Specification Format (ASF) and eliminate board requirements. The host interface allows
the processor to communicate via the SMBus. The SMB slave can access internal
configuration registers, allowing a server management card to control system
configuration and read various error and status information.
13.1.1 SMBus Design Considerations
No single SMBus design solution will work for all platforms. Designers must consider
the total bus capacitance and device capabilities when designing SMBus segments.
Routing SMBus to the PCI slots makes the design process more challenging, since they
add extra capacitance to the bus. This extra capacitance has a large effect on the bus
time constant, which in turn affects the bus rise and fall times.
Primary considerations in the design process are as follows:
• Device class (High/Low power—most designs use primarily High Power Devices)
• Devices that must run in S3
Figure 119. SMBus 2.0 / SMLink Interface

 Loading...
Loading...











