C
HAPTER
17
| Multicast Filtering
Multicast VLAN Registration for IPv4
– 643 –
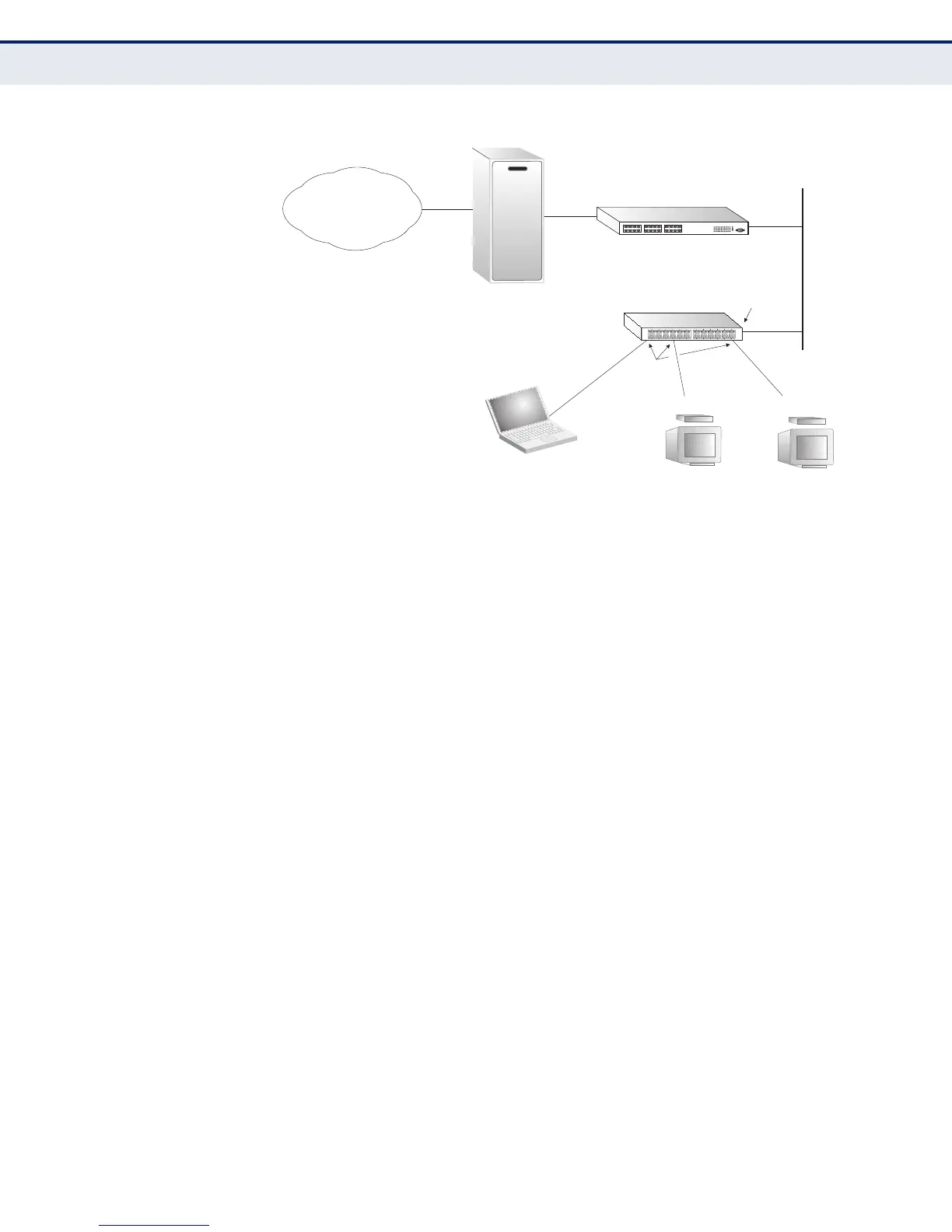
Figure 386: MVR Concept
COMMAND USAGE
◆ General Configuration Guidelines for MVR:
1. Enable MVR for a domain on the switch, and select the MVR VLAN
(see "Configuring MVR Domain Settings" on page 646).
2. Create an MVR profile by specifying the multicast groups that will
stream traffic to attached hosts, and assign the profile to an MVR
domain (see "Configuring MVR Group Address Profiles" on
page 647).
3. Set the interfaces that will join the MVR as source ports or receiver
ports (see "Configuring MVR Interface Status" on page 650).
4. For multicast streams that will run for a long term and be associated
with a stable set of hosts, you can statically bind the multicast
group to the participating interfaces (see "Assigning Static MVR
Multicast Groups to Interfaces" on page 652).
◆ Although MVR operates on the underlying mechanism of IGMP
snooping, the two features operate independently of each other. One
can be enabled or disabled without affecting the behavior of the other.
However, if IGMP snooping and MVR are both enabled, MVR reacts only
to join and leave messages from multicast groups configured under
MVR. Join and leave messages from all other multicast groups are
managed by IGMP snooping. Also, note that only IGMP version 2 or 3
hosts can issue multicast join or leave messages.
CONFIGURING MVR
G
LOBAL SETTINGS
Use the Multicast > MVR (Configure Global) page to configure proxy
switching and the robustness variable.
CLI REFERENCES
◆ "MVR for IPv4" on page 1258
Multicast Router
Layer 2 Switch
Multicast Server
PC
TV
Set-top Box
TV
Set-top Box
Satellite Services
Service
Network
Source
Port
Receiver
Ports
 Loading...
Loading...











