C
HAPTER
5
| Interface Configuration
Saving Power
– 185 –
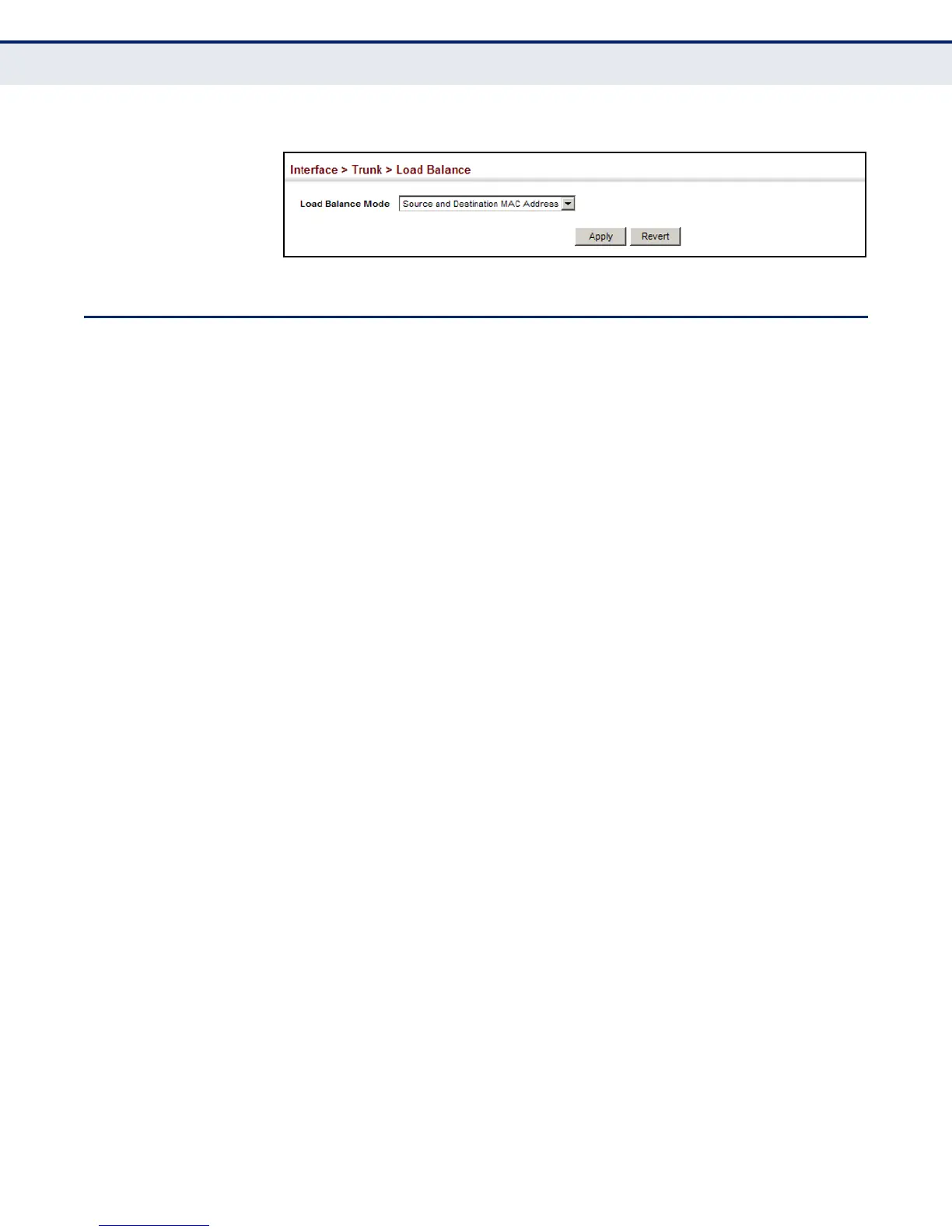
Figure 59: Configuring Load Balancing
SAVING POWER
Use the Interface > Green Ethernet page to enable power savings mode on
the selected port.
CLI REFERENCES
◆ "power-save" on page 1000
◆ "show power-save" on page 1001
COMMAND USAGE
◆ IEEE 802.3 defines the Ethernet standard and subsequent power
requirements based on cable connections operating at 100 meters.
Enabling power saving mode can reduce power used for cable lengths
of 60 meters or less, with more significant reduction for cables of 20
meters or less, and continue to ensure signal integrity.
◆ The power-saving methods provided by this switch include:
■
Power saving when there is no link partner:
Under normal operation, the switch continuously auto-negotiates to
find a link partner, keeping the MAC interface powered up even if no
link connection exists. When using power-savings mode, the switch
checks for energy on the circuit to determine if there is a link
partner. If none is detected, the switch automatically turns off the
transmitter, and most of the receive circuitry (enters Sleep Mode).
In this mode, the low-power energy-detection circuit continuously
checks for energy on the cable. If none is detected, the MAC
interface is also powered down to save additional energy. If energy
is detected, the switch immediately turns on both the transmitter
and receiver functions, and powers up the MAC interface.
■
Power saving when there is a link partner:
Traditional Ethernet connections typically operate with enough
power to support at least 100 meters of cable even though average
network cable length is shorter. When cable length is shorter, power
consumption can be reduced since signal attenuation is proportional
to cable length. When power-savings mode is enabled, the switch
analyzes cable length to determine whether or not it can reduce the
signal amplitude used on a particular link.
 Loading...
Loading...











