PowerPC e500 Core Family Reference Manual, Rev. 1
4-22 Freescale Semiconductor
Execution Timing
The following factors affect the FGA of a branch instruction:
• The location of the branch instruction in the cache block
• A control flow that may allow multiple execution paths to reach the branch from different
fetch group addresses
• The presence of other branch instructions in the fetch group that precede the branch
instruction under consideration
• Interrupts taken as a result of accepting an external interrupt or exceptions in instructions
preceding the branch instruction in the fetch group
• Events inside the core causing a synchronization in the pipeline during the execution of an
instruction preceding the branch instruction in the fetch group
• The presence of instructions such as isync before the branch instruction
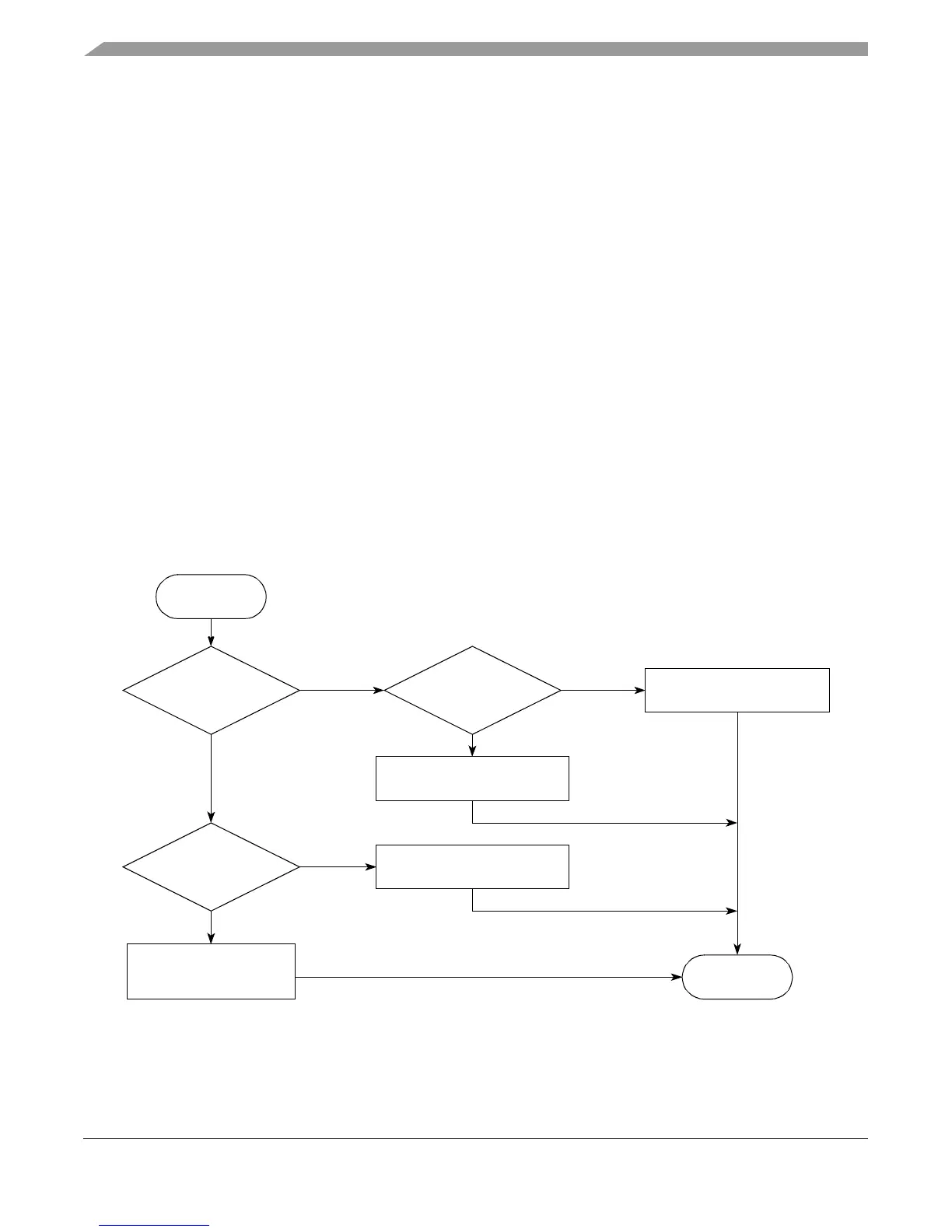
Figure 4-9 shows all possible fetch group addresses (FGAs) that can be associated with a branch
instruction. The location of an instruction is i if it is the i
th
instruction (i=0…7) from the beginning
of a cache line. The address of an instruction a
i
refers to the address of the i
th
instruction in the
cache block. The condition IB occurs where either a synchronizing instruction (such as isync) or
a branch instruction whose prediction is locked in the BTB occurs at some location. The branch
instruction under consideration is identified as b.
Figure 4-9. Fetch Group Addresses
Is b at location i
Ye s
No
No
Ye s
No
Begin
Is an IB at location j
where i=0,1,2?
where j<i?
Possible FGAs are aj+1…ai
Possible FGAs are a0…ai
Is an IB
at location j where
j=i-1,i-2,i-3?
Possible FGAs are aj+1…ai
Possible FGAs are ai-3,
ai-2, ai-1, ai
End
Ye s
 Loading...
Loading...